Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 18: Ecosystems
Ecosystems Exercise Exercise
Solution 1
a. Air, water, minerals, soil are physical factors of an ecosystem.
b. River, ponds, ocean are aquatic ecosystems.
c. Man is consumer in an ecosystem.
Solution 2
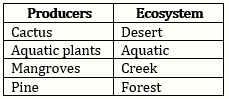
Solution 3.a
Ecosystem
- An ecosystem is a self-contained area composed of different kinds of organisms which interact with each other as well as with the physical conditions such as sunlight, air, water, soil and climatic factors prevailing in the area.
- Ecosystem is the structure formed by the interrelationships between the living organisms and the non-living components in their surrounding habitats.
- Living organisms are also called biotic factors while the non-living components are called abiotic factors. The abiotic and biotic factors have a reciprocal relationship with each other.
- The ecosystem has plants as producers, animals as consumers and microbes as decomposers.
- The decomposers return the materials back to the nature by the process of decomposition in which the organic complex molecules are reduced to their inorganic constituents.
- In this way, the dead remains of plants and animals are recycled back to the nature in a healthy ecosystem.
Solution 3.b
Biome
- In some regions on the Earth, a large areas have same climate and abiotic factors.
- The living organisms in these areas are similar and a specific ecosystem develops in these vast areas. Such large ecosystems are called 'biomes'.
- Biomes are a larger collection of small ecosystems which are similar in their structure.
- These biomes contain many small ecosystems.
- The Earth itself is a vast ecosystem.
- Two types of biomes are found on the Earth:
- Land biomes - Grasslands, evergreen forests, deserts,
- Aquatic biomes - Freshwater ecosystem, marine ecosystem and brackish water ecosystem found in the creeks.
Solution 3.c
Food web
A network of interconnecting food chains in a natural community of different organisms is called a food web.
Consider six food chains which are interconnected to form a food web. The food web begins with plants and ends with the top carnivore, the vulture.
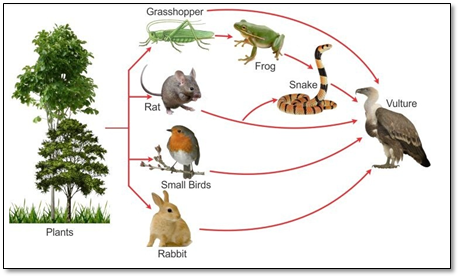
In the first food chain, the plants are eaten by the grasshopper, and the grasshopper, in turn, is eaten by the vulture.
Plants → Grasshopper → Vulture
In the second food chain, the plants are eaten by the rabbit. The rabbit is then consumed by the vulture.
Plants → Rabbit → Vulture
In the third food chain, the plants are eaten by the rat. The rat is then eaten by the vulture.
Plants → Rat → Vulture
In the fourth food chain, the plants are eaten by the rat, the rat is eaten by the snake, and the snake, in turn, is eaten by the vulture.
Plants → Rat → Snake → Vulture
In the fifth food chain, the plants are eaten by the grasshopper, and the grasshopper, in turn, is eaten by the frog. The frog is eaten by the snake, and the snake is consumed by the vulture.
Plants → Grasshopper → Frog → Snake → Vulture
Finally, in the sixth food chain, the plants are eaten by small birds which in turn are eaten by the vulture.
Plants → Small birds → Vulture
Solution 4.a
- Plants prepare their own food by the process of photosynthesis.
- All other living organisms are dependent on plants for their food requirements.
- As plants provide food for all living organisms, they are called producers of an ecosystem.
Solution 4.b
- Dams cover vast lands. So, when a large dam is constructed, the original landscape is changed.
- The forests or grassland in that area get converted into aquatic ecosystems.
- Dams also lessen the water current in lower areas. Therefore, the previous ecosystems in that running water get destroyed.
- Trees are cut down resulting in deforestation. The wild animals lose their habitat. Several species become extinct.
- There is a great loss of flora and fauna due to construction of large dams.
- There is undue pressure on the land surface caused due to stored water column. This may cause earthquakes.
- The human settlements are removed as their houses and farms are immersed under water.
Solution 4.c
- Long ago in the last century, Dudhwa forest was the natural habitat of the one-horned Rhino.
- But, Rhinos became extinct in the 20th century due to relenting hunting and poaching in the Dudhwa forest.
- However, they were again restored by several measures taken by the government.
- Rhinos were bred in captive and then released in their natural habitat under observation.
- Saving the precious wildlife is important and hence these efforts were done.
Solution 5.a
Effect of increased population on ecosystems:
- The growth rate of human population is very large as compared to other animals.
- Moreover, humans are apex consumers in an ecosystem. Like other organisms, ecosystems cater to all basic needs of humans as well.
- However, human demands are much more due to ever-increasing population. The natural resources are utilized on a large scale only by man.
- Changing lifestyles, consumerism, degradation of nature and pollution occur only because of human beings.
- All these factors cause increased stress on the ecosystems.
- Large-scale human population also produces large-scale solid wastes.
Solution 5.b
- When people do not get sufficient food and other amenities, they migrate to the cities.
- The cities provide employment for many people due to industries, factories and other facilities.
- Large part of the rural population migrates to cities which results in urbanisation.
- There is more demand for housing due to increased population in cities. This results in loss of agricultural lands, marshlands, wetlands, forests and grasslands.
- The natural ecosystems are lost in an attempt to support developmental work.
- Human interference causes changes in the ecosystems.
- When land usage is changed, several naturally occurring species of plants and animals are exterminated.
- Animal-human conflicts are very common in newly established urban areas which are near natural forests.
Solution 5.c
Reasons of war:
- Differences of opinion and competition over land, water and mineral resources
- Economic factors
- Political reasons
- Religion and ethnicity
- International conflicts
Solution 5.d
Interactions among the factors of an ecosystem:
- An ecosystem consists of two main components: biotic components and abiotic components.
- The biotic components are the living components of an ecosystem. They constitute the food-obtaining steps or trophic levels of the ecosystem. These include plants and animals.
- The abiotic components are the non-living components of an ecosystem. Abiotic factors include light, temperature, water, soil, air, inorganic nutrients, etc.
- Both abiotic and biotic factors together affect the ecosystem.
- They interact with each other to maintain balance in an ecosystem.
- The type of abiotic factors in an ecosystem determines the survival of biotic factors. The population of these biotic factors is also dependent on the quality of abiotic factors.
- The proportion of abiotic factors is not constant and always keeps on changing as they are used or excreted by biotic factors.
Solution 5.e
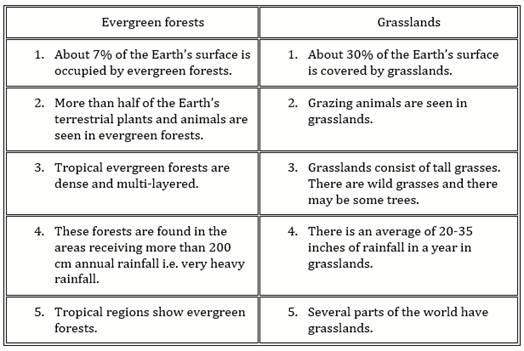
Differences between evergreen forests and grasslands:
Solution 6
The first picture represents a desert ecosystem. Here, the producers are green Cactus plants and a palm tree. Since in desert there are scanty rains, the vegetation is very less. The soil is sandy. The consumers of the desert are also limited. Camel is is a primary consumer in the desert ecosystem which is very well adapted for desert life. Since there is scarcity of water in the desert, cactus shows xerophytic adaptations.
The second picture represents a forest ecosystem because we can see an elephant and a tiger in the picture. Also, giant hornbill is sitting on the tree. This forest must be tropical evergreen forest. The rainfall is heavy in such areas and hence different types of wetlands can be seen in forests. Wetlands support variety of life. The birds utilize the fish as their prey. The wild animals come to wetlands to quench their thirst. In this picture, the plants, i.e. the grasses are producers while the small fishes in the lake are primary consumers. They will be eaten by larger fishes which are secondary consumers in the aquatic ecosystem. The elephant is a herbivorous animal and hence, it is a primary consumer. Snake is a secondary consumer while the eagle and tiger are tertiary consumers.
