Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 9: Disaster Management
Disaster Management Exercise Exercise
Solution 1.a
- Several changes occur in the surrounding hilly ground before the actual landslide.
- The hard rocks develop cracks and crevices.
- These are natural changes but due to man-made activities, the cracks are widened due to erosion.
- These cracks cause the big rocks to break into smaller rocks.
- The cracks widen further due to excessive rainfall.
- The smaller rocks further get eroded and they fall down along with soil from the slopes.
- The entire process is speeded up due to rainwater.
Solution 1.b
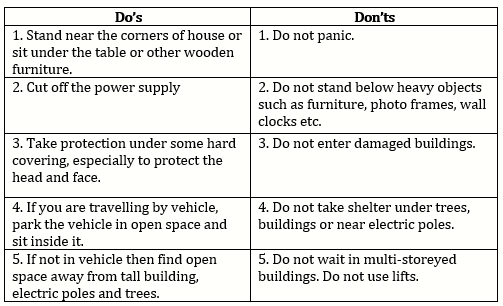
'Do's' and 'Don'ts' at the time of earthquake:
Solution 1.c
Specifications of an earthquake-proof building:
- Constructions which do not get damaged due to earth movements up to a certain limit, are called earthquake-resistant buildings.
- To construct tall buildings, 'Indian Standard Institute' has made some code of conduct.
- Buildings are constructed as per I.S. 456 and earthquake resistant constructions are performed as per IS 1893 (Criteria for earthquake resistant design of structure) and IS 13920 (Ductile detailing of reinforced concrete structures subjected to seismic forces).
- Advanced technology is used for earthquake resistant construction.
- The foundation of earthquake-proof building is separated from lower land.
- The walls are of less weight or they are wooden.
- The houses constructed with special light materials are preferred in earthquake-prone regions.
Solution 1.d
Effects of landslide:
- The rivers get flooded and change their paths.
- The waterfalls are displaced from their original positions.
- New and artificial water reservoirs are formed.
- There is large-scale loss of finances, property and life as trees, buildings, rocks on sloppy area collapse on low-lying land.
- Transportation is affected as the roads and railway tracks are blocked due to debris.
- Landslide destroys plant life which was present on it.
Solution 1.e
Relation between dam and earthquake:
- Construction of dams creates a huge water reservoir in which large portion of the land gets submerged.
- Dams exert tremendous water pressure in the micro-cracks and create fissures in the ground.
- This generates excessive pressure and the water seeps into the ground and lubricates rocks.
- When water pressure is high, water reaches the fault planes and lubricates them.
- This lubrication reduces friction between tectonic plates and causes their slipping, resulting in earthquakes.
Solution 2.a
- When an earthquake takes place, vibrations in the Earth's surface, may cause the roof and walls of the house to fall. This may result in injuries due to falling of heavy objects from height.
- Taking shelter below hard-supporting structures such as a table or a bed will protect us from these things falling on our head directly and thus, there are reduced chances of getting hurt.
- Hence, it is safer to find shelter under things like a bed or a table at the time of earthquake.
Solution 2.b
- During monsoons, there are high chances of heavy rainfall.
- Excessive rainfall can cause landslides.
- The soil and rocks from the hillside can be pushed down along with the flow of rainwater.
- This debris slides to the lower heights from the hills.
- Taking shelter near the base of the hillside can be disastrous as one can get buried in the debris due to sudden landslide.
- Hence, it is not advisable to take shelter near hillside during monsoon.
Solution 2.c
- Lifts or elevators run on electricity. During earthquakes, the power supply is cut off and thus, there are chances of you being stuck into the lift for a long period of time which may lead to suffocation.
- Also, if the earthquake is severe then there are chances that lift may fall to the bottom and cause damage to you.
- The building may also collapse due to earthquake.
- Hence, it is advisable to not use the lift or elevator during earthquakes.
- It is always better to use stairs at the time of such calamities, so that one can safely come out of the building.
Solution 2.d
- The surface of the Earth trembles at the time of earthquake.
- These tremors cause seismic waves which are responsible for the movements of the Earth's surface.
- A seismic wave absorber layer is laid between the ground and the foundation of earthquake-resistant building.
- This layer absorbs pressure exerted by the earthquake tremors on sidewalls of the building.
- As a result, the building will not shake with the same intensity as that of the Earth during an earthquake.
- Thus, foundation of earthquake-proof building is separated from other land to withstand high intensity of seismic waves.
Solution 3
If a crowd gather at the place of earthquake, there will be:
- Delay in clearing debris
- Hindrance for the path of ambulance which will be carrying victims
- Possibilities of stampede and theft
- Shortage of essential resources
- Panicky state and difficulty in managing the situation
Solution 4
International government organisations working for disaster management:
a. The United Nations and its organisations:
- The Food and Agricultural Organisation of the UN (FAO): It gives early warning of impending food crises, and keeps a track of global food supply problems.
- The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP): It helps disaster-prone countries with disaster mitigation, prevention and preparedness measures.
- The World Food Programme (WFP): It is the main supplier of relief food aid.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO): It gives global public health leadership by setting standards, monitoring health trends, and providing direction on emergency health issues. Its role is to reduce avoidable loss of life and the burden of disease and disability.
b. The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC):
- It gives physical rehabilitation to people injured by explosive weapons or other types of accidents.
c. The International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC):
- It coordinates and gives international help to victims of natural and technological disasters, to refugees and in health emergencies.
International non-governmental agencies working for disaster management:
a. International Rescue Committee (IRC):
- It provides lifesaving care and life-changing help to refugees forced to flee from war or disaster.
b. IMA World Health:
- It builds sustainable health care systems in collaboration with USAID, the World Bank and many other organisations.
c. CARE:
- It is an organisation fighting global poverty. It provides emergency aid to survivors of war and natural disasters, and helps people rebuild their lives.
Indian organisations and institutes working for disaster management:
a. National Disaster Response Force (NDRF):
- The multi-disciplinary, multi-skilled, force of the NDMA are capable of dealing with all types of natural and man-made disasters.
b. National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA):
- It lays down the policies, plans and guidelines for disaster management to ensure timely and effective response to disasters.
c. National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM):
- It is responsible for human resource development, capacity building, training, research and documentation in disaster management.
Solution 5
This an activity based question. You can take help of your teacher and write answer to this question based on your school specifications. Include the following points in your survey:
Primary information of the school
a. Name and address of the school
b. Name and residential address of the Head Master with contact number
c. Names and contact numbers of school management members
d. Total number of staff
School Disaster Management Committee
a. Fire extinguisher
b. Awareness
c. Instructions
d. Traffic Management
e. Safety
f. Communication committee (2-3 members/ subcommittee)
Detailed information about school building
a. Total number of rooms
b. Number of classrooms
c. Classes
d. Type of roof (wooden/cement/sheets)
e. Age of the building, building year.
Information about school ground
a. Types of playground
b. Distance of the ground from main road.
Daily routine of the school
a. Time to start, school breaks and time to leave the school.
b. Daily activities taking place in the school.
Possible hazards in the school
a. Name and type (normal/ medium/ acute) of the danger.
b. Destruction in the past and current planning.
Disaster management map of the school
The map must contain information about all buildings of the school, their structure, grounds, entrances, place of probable dangers in the school, safe places at the time of disaster and nearest road.
This map must be put up at the entrance of the school and all students must be given detailed knowledge about it.
Mock drill in the school
Every month a mock drill must be conducted in the school.
It should include possible hazards and the measures taken against them. The date, time, number of students and shortfalls must be noted down.
Solution 6
Landslides are very common in the hilly regions. The regions where more landslides occur have many constructions and large scale deforestation. There are no landslide prone places in my area as there are no hills and mountains in the vicinity.
Solution 7
The nature of risk is unknown from the given picture. We can support the person in the following ways:
- Tell him not to panic and enquire with him about the type of risk.
- Ask his location.
- If he is facing manmade disaster, then call the police station.
- Provide necessary details of the victim to the police.
- If he has faced some accident, then call the ambulance and police.
- In case of fire, call fire brigade, ambulance and police. Also provide all the required details of the victim to them.
