Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 4: Current Electricity and Magnetism
Current Electricity and Magnetism Exercise Exercise
Solution 1
a. Water in the waterfall flows from a higher level to the lower level because of potential difference.
b. In an electric circuit, electrons flow from a point of higher potential to the lower point of potential.
c. The difference between the electrostatic potential of the positive end the negative end of an electric cell is the potential of the cell.
d. Three electric cells of potential difference 1.5 V each have been connected as a battery. The potential difference of the battery will be 4.5 V.
e. An electric current flowing in a wire creates magnetic field around the wire.
Solution 2
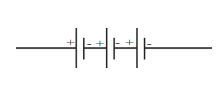
Solution 3
- Check whether the positive terminal of one battery is connected to negative terminal of other.
- Check whether the connecting wires are in proper condition or are broken.
- Check whether the wires as connected to the bulb as shown below:
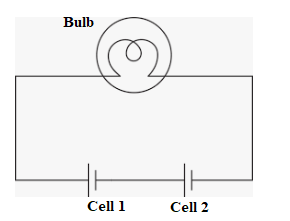
Solution 4
- Total potential difference = 2 + 2 + 2 = 6 V
- Total potential difference = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8 V
Solution 5
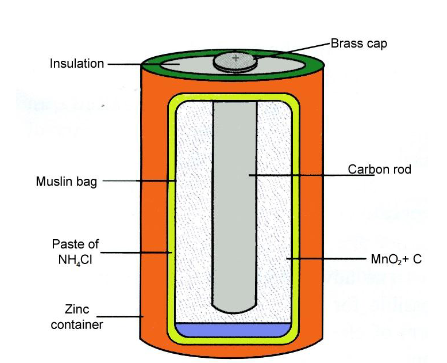
An electric cell is used to operate things such as torches, toys, clocks, calculators and phones.
- It is a small source of energy. It is also known as a pencil cell or dry cell.
- It converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
- It consists of a zinc container with a small brass cap on one side of the cell, which is labeled as positive (+), and a metal base at the other side of the cell, which is labeled as negative (-).
- The positive and negative sides of the cells are called as positive and negative terminals of the cell, respectively.
- A carbon rod is placed at the centre of the cell surrounded by a mixture of manganese dioxide (MnO2) and charcoal (C) in a muslin bag.
- The electrolyte is a moist paste of ammonium chloride (NH4CI), Plaster of Paris, flour, etc. and the outer body (except for the base) of a zinc container is insulated with a thick cardboard or plastic material.
Solution 6
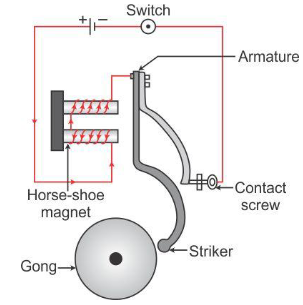
An electric doorbell is a bell that works on the principle of an electromagnet.
- It consists of a horseshoe magnet, striker, contact screw, armature and a gong.
- When a circuit is closed by a switch, the current flows through the horseshoe magnet and the core turns into an electromagnet, which attracts the armature made of iron.
- The striker strikes the gong bell as the armature moves towards the electromagnet, and the contact of the screw breaks the circuit because of which the current stops flowing through the coil. Thus, the electromagnetism is lost and the armature returns back to its original position.
- The circuit is completed and the action is repeated.
- The making and breaking of the circuit of the electromagnet continues as long as the switch is pressed.
- Electric bells are used at railroad crossings, in telephones, fire and burglar alarms, school bells, doorbells, etc.
