Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 13: Chemical Change and Chemical Bond
Chemical Change and Chemical Bond Exercise Exercise 13
Solution 1
a. Arrow
b. Slow
c. Smell
d. Milky
e. Chemical
f. Reactant
g. Ionic, covalent
h. Duplet
i. sharing
Solution 2
a. Respiration is a biological process, in this process air is inhaled, oxygen present in the inhaled air reacts with glucose present in the cells of body forming carbon dioxide and water. Moreover, we can not obtain glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water. Hence, respiration is a chemical change.

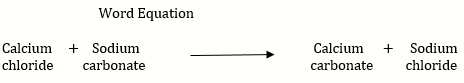
b. Hard water does not form lather with soap and is brackish to taste. This is because contains the chloride and sulphate salts of calcium and magnesium in dissolved state. When a solution of washing soda is added to hard water, it forms a precipitate of calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate, which is removed by filtration , thus water is softened.
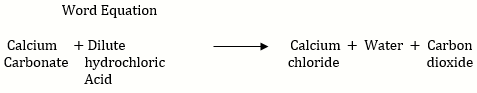
c. In the reaction dil. HCl and lime stone powder (CaC) liberates slowly.
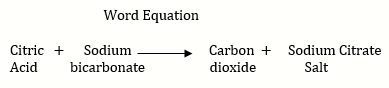
d. When baking soda is added to lemon juice , a chemical change takes place in citric acid present in the lemon juice and carbon dioxide gas is formed.
Solution 3
Solution 4
a. Sodium chloride
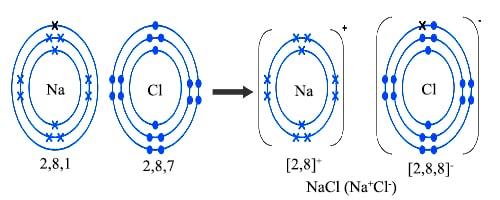
- Sodium has atomic number 11 and electronic configuration 2,8,1
- Sodium atom has 1 electron in its outer most shell
- It looses its one electron from its outer most shell i.e. M shell
Then its L shell becomes the outer most shell with a stable octet.
The nucleus of sodium atom has 11 protons but the number of electrons in the atom has become 10. So there is a net unit positive charge giving a sodium cation (Na+). - On the outer hand, chlorine has electronic configuration 2, 8, 7. Chlorine atom as 7 electrons in its outer most shell and requires one electron to complete its octet.
- Thus, the electron lost by sodium is taken up by chlorine.
- When chlorine atom gains one electron, octet of chlorine is completed and its K,L,M shells have together 18 electrons and the nucleus has 17 protons. This leads to the formation of ion(Cl-)
- Thus a chlorine atom accepts 1 electron from a sodium atom and consequently a chloride ion with 1 unit negative charge and a sodium ion with 1 unit positive charge are formed.
- Sodium and chloride ions, being oppositely charged, attract eachother due to electrostatic force of attraction. An ionic bond is formed and this results in the formation of sodium chloride ( NaCl) molecule.
b. Potassium Fluoride.
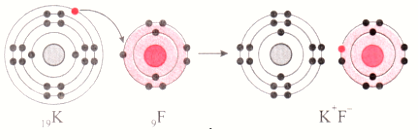
- Potassium has atomic number 19 and electronic configuration 2,8,8,1.
- Potassium electron has 1 electron in its outer most shell.
- It looses 1 electron from its outer most shell i.e. N shell. Then its M shell becomes the outer most shell with stable octet. The nucleus of potassium atom has 19 protons but the number of electrons in the atom has become 18. So there is a net unit positive charge giving a potassium caption (K+).
- On the other hand, fluorine has electronic configuration 2, 7. Fluorine has 7 electrons in the outer most shell and requires 1 electron to complete its octet.
- Thus, the electron lost by potassium is taken up by chlorine.
- When fluorine atom gains 1 electron, octet of fluorine is completed, its K and L shells have together 10 electrons and nucleus has 9 protons. This leads to the formation of an ion(F-).
- Thus, a fluorine atom accepts 1 electron from a potassium atom and consequently a fluoride ion with 1 unit negative charge and a potassium ion with 1 unit positive charge are formed.
- Potassium and fluoride ions being oppositively charged, attract each other due to electrostatic force of attraction. An ionic bond is formed and this results in the formation of potassium fluoride (KF) molecule.
c. Water
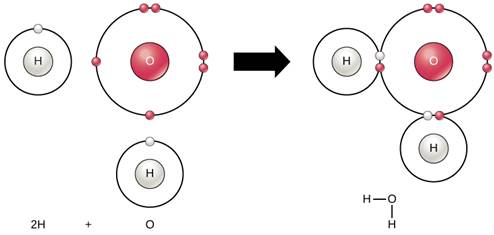
- Hydrogen has atomic number 1 and electronic configuration one.
- Hydrogen has one electron in its K shell.
- Oxygen has atomic number 8 and electronic configuration 2, 6. There are 6 electrons in valence shell of oxygen atom. It means that the electron octet in oxygen is short of two electrons and the valency of oxygen is 2.
- In the H2O molecule, the oxygen atom complete its octet by sharing two electrons one each with two hydrogen atoms, thus, forming two covalent bonds. While this happens, the duplets of two hydrogen atoms are completed.
d. Hydrogen Chloride
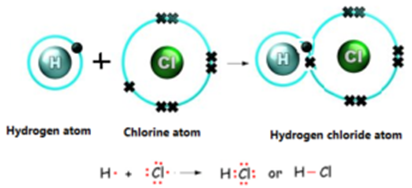
- Hydrogen has atomic number 1 and electronic configuration 1, that means it has 1 electron in its K shell and its duplet is short of 1 electron, therefore the valency of hydrogen is 1.
- On the other hand chlorine has electronic configuration 2,8,7
Chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outer most shell and requires one electron to complete its octet. - The two atoms, hydrogen and chlorine share one electron with each other. As a result, the electron duplet of hydrogen and octet of chlorine is complete and a covalent bond is formed between them.
