Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 10: Cell and Cell Organelles
Exercise
Cell and Cell Organelles Exercise Exercise
Solution 1
a. Mitochondria
b. Vacuole
c. Endoplasmic reticulum
d. Mitochondria
e. Chloroplast (Chlorophyll)
Solution 2.a
- RBCs are found in blood. Their function is to carry oxygen to different cells and tissues of the body.
- They do not contain mitochondria for two reasons:
- It saves space in RBCs and so more oxygen can bind to it.
- 2. It prevents the use of oxygen which is bounded to RBCs
- If mitochondria were present in RBCs, the oxygen which is carried by them will be used up by mitochondria for the oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins and fats to produce energy.
- Thus, there will be less or no oxygen left which can be transported to the cells and tissues.
Solution 2.b
- Mitochondria are found in plants and animals while plastids are found only in plants.
- Mitochondria carry out oxidation of carbohydrates, proteins and fats to produce energy for the cells to carry out various life processes.
- Plastids help in the synthesis of carbohydrates in the presence of solar energy and chlorophyll.
- If there would have been no difference between mitochondria and plastids, then the specific functions of each of these cell organelles would not have taken place.
Solution 2.c
- Genes are functional segments on the chromosomes which contain genetic information which is passed on from parents to offspring.
- They are required for the transmission of hereditary information from one generation to another.
- They are responsible for the characteristics of all living organisms.
- If genes are absent in chromosomes, then the offspring will lack the characteristics of its parents
Solution 2.d
- Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane of the cell which regulates the entry and exit of substances in the cell.
- It maintains homeostasis, i.e., constant internal composition of the cell.
- If plasma was not selectively permeable, the constant internal composition of the cell will be lost and the cell will not be able to perform its basic functions and the intracellular contents will leak out.
- There would be no control over the entry and exit of substances and the process of osmosis would also be erroneous in such case.
Solution 2.e
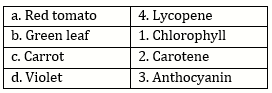
- Anthocyanin is a pigment which is present in plants.
- It imparts a characteristics purple colour to the plant parts. This attracts the insects for pollination and seed dispersal.
- In absence of anthocyanin pigment, no part of the plant would display purple or blue colour and would appear colourless.
- The processes of pollination and seed dispersal would not occur.
Solution 3
a. Plastids. They are organelles which are found only in plant cells and others are found in both plants and animals.
b. Chlorophyll. It is found only in plants while DNA and ribosomes are found in both plants and animals.
Solution 4.a
Functions of plasma membrane:
- Separates cellular contents from the surroundings
- Acts as an effective barrier and regulates the entry of certain solutes and ions through diffusion and osmosis
- Maintains the shape of the cell (in animal cells)
- Aids in ingestion of materials
- Keeps homeostasis in the cell
Solution 4.b
Functions of cytoplasm:
- Different organelles contained in it perform different functions
- Medium for several cellular chemical reactions
- Centre of all metabolic activities
- Seat of occurrence of glycolysis (production of pyruvic acid)
- Storage of vital chemicals such as glucose and amino acids
- Cytosol helps in the cellular movements
Solution 4.c
Functions of lysosome:
- Helps in the destruction of attacking viruses and bacteria and thereby assists in immune response
- Act as demolition squads and destroy worn-out cellular organelles and organic debris. This process is called autolysis which means self-destruction.
- Act as suicide bags where lysosomes in a worn out, damaged or old cell automatically burst. The lytic enzymes present in the lysosome digest their own cells.
- Digest stored proteins and fats during starvation
Solution 4.d
Functions of vacuole:
- Storage of water and other substances, food, pigments and waste products
- Provides turgidity and rigidity to the cells
- Helps to maintain osmotic pressure in the cells
Solution 4.e
Functions of nucleus
- Regulates cell functions
- Controls all metabolic activities of the cell
- Cells die in the absence of nucleus
- Contains chromosomes, made of genes, which control hereditary characteristics
- Regulates cell cycle and cell division
Solution 5