Class 10 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Social Studies Chapter 3 - Physiography and Drainage
Physiography and Drainage Exercise 23
Solution 1 (a)
i. Highlands
Solution 1 (b)
ii. Ancient plateau
Solution 1 (c)
iii. covered by dense forests
Solution 1 (d)
iv. fishing is done
Solution 1 (e)
ii. Coral islands
Solution 1 (f)
i. lies in the Mewad plateau
Solution 2(a)
Differences between the physiography of Brazil and India:
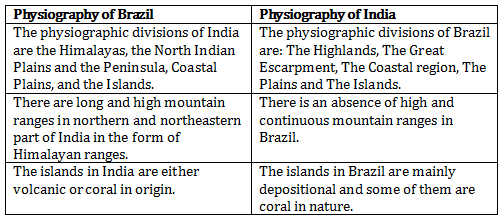
Solution 2 (b)
The following measures are being taken to control pollution in the rivers of India:
- creating awareness among people about the hazards of polluting river water
- Treating wastes before discharging them into water bodies
- Setting up of Pollution Control Boards at the state and national level to prevent pollution of rivers
- Carrying out the cleaning and purification of the river water under the National River Conservation Plan (NRCP)
Solution 2 (c)
The characteristics of the Northern Indian Plains:
- The Northern Indian Plains have been formed due to the depositional activities of the Himalayan Rivers.
- Since it is extremely fertile, it is one of the most densely populated regions in the world.
- Favourable climate and adequate water supply has made it agriculturally an extremely productive part of India. On the basis of regional characteristics, the Northern Plains are divided into:
➢ The Punjab Plains: The western part of the Northern Plains is referred to as the Punjab Plains
➢ The Ganga Plains: The Ganga Plains are called so as they are mainly drained by River Ganga and its tributaries
➢ The Brahmaputra Plains: The Brahmaputra Plains are drained by the river Brahmaputra and its tributaries. This plain mostly lies in the state of Assam.
Solution 2 (d)
Pantanal is one of the largest wetlands in the world. It lies towards the southwest part of the highland areas. It is a gently sloped basin which is submerged throughout the year due to the filling of the sediments and water in the depression area of the Pantanal.
Solution 2(e)
Water divide is an elevated land feature like mountain, upland or hill that separate two drainage basins. The major water divide of India are:
- Western Ghats are a water divide which separates east flowing rivers from the west flowing rivers.
- Vindhya ranges: It divides the drainage basin of the River Ganga and the River Narmada.
- Aravali ranges: The Aravali ranges separate the west flowing river Luni from the east flowing river Banas.
- Satpuda ranges: The Satpudas separate the Narmada drainage basin and the Tapi drainage basin.
Solution 3 (a)
- Amazon collects its headwaters from the eastern slopes of Andes Mountains in Peru. It receives a huge discharge.
- Consequently, sediments are not deposited even at the mouth. A dense network of distributaries is absent in the mouth region of Amazon.
- The mouth the width of Amazon channel is 150 km. Most of the course of the Amazon river is suitable for navigation.
Solution 3 (b)
- The Himalayas are the largest young fold mountains extending from Pamir Knot in Tajikistan to the east. It is a major mountain system of the Asian continent. In India, it extends from Jammu and Kashmir to Arunachal Pradesh.
- The Himalayas is not a single mountain range. There are many parallel ranges in the system. The southernmost is known as Siwaliks. Next to Siwaliks are Lesser Himalayas, Greater Himalayas (Himadri) and Trans Himalayan.
- These mountain ranges are also divided into Western Himalayas, Central Himalayas and Eastern Himalayas.
Solution 3 (c)
- Brazil has a coastline of about 7400 km. It can be namely northern and eastern coast.
- The northern coast is characterized by mouths of many rivers including the Amazon. Therefore, this region is a low-lying region.
- The eastern coast has large number of smaller rivers. The only major river which meets the Atlantic Ocean here is Sao Francisco.
- The Brazilian coast is characterized by many beaches and sand dune complexes. The Brazilian coast is protected in some areas by coral reefs and atoll islands.
Solution 3 (d)
- The Indian peninsula lies to the south of the Northern Indian Plains. They taper or narrow down towards the Indian Ocean.
- It mainly consists of many plateaus and hill ranges.
- The Indian Peninsula includes a series of plateaus bordering the Plains, Vindhyas and Satpuda ranges in the central part and the hilly regions of Western and Eastern Ghats.
Solution 3 (e)
- It is one of the physiographic features in Brazil.
- The eastern side of the Highlands is demarcated because of the escarpment. It is very steep particularly from Sao Paulo to Porto Alegre.
- The escarpment act as a barrier to the Southeast Trade winds giving rise to the rain- -shadow area in the northeastern part of the highlands. The region to the north of this area is called 'Drought Quadrilateral'.
Solution 4 (a)
Several Brazilian rivers originate from the Brazilian Highlands and flow northwards to meet the Atlantic Ocean which lies on the eastern border of Brazil. The altitude of the Brazilian Highlands decreases gradually from South to North and from west to East. Thus, there are no west flowing rivers in Brazil.
Solution 4 (b)
The western coast borders the Arabian Sea. It is by and large a rocky coast. On the other hand, the eastern coast borders the Bay of Bengal. It has formed as a result of depositional work of rivers. Rivers originating from Western Ghats are short and swift and hence they form estuaries and not deltas. However, on the eastern coast, because of the gentle slope of the land, rivers flow at lower velocities and deposit the sediments brought with them at the coast. As a result, deltas are found along this coast.
Solution 4 (c)
The Eastern coast has formed as a result of depositional work of rivers. Eastern rivers form delta. Sediments deposited by rivers make the coast shallow. Therefore, it becomes difficult for ships to reach the east coast covered with sediments.
Solution 4(d)
River Amazon, for a very large part of her course flows through the dense forest and inhabited area whereas river Ganga flows through the most densely populated areas, resulting in more pollution. Also, in India several people are dependent on river Ganga and hence are affected by pollution.
Solution 5 (a)
ii. Guyana Highlands- Amazon river basin - Brazilan Highlands
Solution 5(b)
i. Juruika- Xingu- Aragua
Solution 5 (c)
i. Karnataka - Maharashtra - Bundelkhand

