Class 10 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 1 - Heredity and Evolution
Heredity and Evolution Exercise Exercise
Solution 1
Solution 2.a
- Approximately around 7 crore years back, the ice age began on the Earth. In such conditions, dinosaurs became extinct. The evolution and diversity of mammals began. Due to a change in climate, the forest cover also declined rapidly.
- Ancestors of monkey-like animals called Lemurs evolved during this time period. The tails of these creatures started vanishing gradually around 4 crore years ago. The body and brain both increased in volume forming first ape-like animals.
- The monkey-like ancestors gave rise to two evolutionary links - the apes and human-like animals.
- Later, human evolution took place accompanied by changes in the brain volume, the ability to walk upright and excessive use of hand for manipulation.
- This journey of human evolution began 7 crore years ago. However, the true wise and intelligent man arose around 50,000 years ago.
Solution 2.b
- Speciation may be defined as an evolutionary process, which involves the formation of one or more species from an existing species.
- Every species survives under specific geographical conditions. The requirements of food and habitat, is specific for each species. The reproductive ability and time period of reproduction is also different for different species.
- As a result, individuals of one species cannot breed or reproduce with individuals from other species.
- When these species are separated by distance or a geographical barrier, they are said to be isolated geographically.
- When they cannot reproduce with each other, they are said to be isolated reproductively.
- The ancestral species of both these sub-species may be the same but there exists a genetic variation between them due to isolation over a very long time duration. Thus, geographical and reproductive isolation gradually leads to speciation.
Solution 2.c
- Fossils represent the ancestors of plants and animals, which are alive even today.
- They offer palaeontological evidences of evolution by revealing the characteristics of the past organisms, and the changes that have occurred in these organisms to give rise to a present organism.
- Study of fossils informs us about the types of organisms that existed in the past.
- They inform us about the extent to which living organisms have changed over time.
- Carbon dating method also helps in finding out exact age of the fossil. According to the structure of earth's crust the fossils are obtained at specific depths. The oldest ones are obtained at the depth while the relatively recent ones occupy the upper surface. Thus, they inform us about the time when a particular life form existed.
- In this way, study of fossils unfold the evolutionary secrets.
Solution 2.d
- Fetal science or embryology is used as an evidence of evolution.
- Comparative study of embryos in vertebrates/chordates shows that very young embryos of fishes, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals show quite similar structure in the early stages.
- As the further growth takes place, they acquire different patterns and this similarity decreases gradually.
- The initial similarity in the development of embryos represents common origin of organisms.
Solution 3
- The causality behind the sudden changes was understood due to mutation principle of Hugo de Vries.
- The proof for the fact that protein synthesis occurs through genes was given by George Beadle and Edward Tatum.
- Transfer of information from molecule of DNA to mRNA is called transcription process.
- Evolution means gradual development.
- Vestigial organ appendix present in human body is proof of evolution.
Solution 4.a
Lamarckism
- Lamarckism is the theory of evolution proposed by Jean Baptiste Lamarck.
- This theory is based on two principles:
- Use and disuse of organs
- Inheritance of acquired characters
- According to this theory, the characters such as organs develop due to specific activities performed by an organism.
- If an organ is not used, it gets degenerated. Thus, morphological changes take place due to activities or inactivity of a particular organism.
- To emphasise this theory, Lamarck quoted several examples.
- The giraffe's neck became long due to constant extension of the neck to eat foliage from the top of the trees.
- The blacksmith has strong arms due to constant work.
- Flightless ostrich and emu did not fly and hence their wings became useless.
- Aquatic birds like swan and duck made their feet suitable for swimming by living in water.
- Such acquired characters are passed from the parental generation to the offspring. This is called inheritance of acquired characters.
- However, the theory of inheritance of acquired characters is not accepted as transmission of acquired characters does not take place as stated by Lamarck. It is only the genetic character which is transmitted and not the physical character.
Solution 4.b
Darwin's theory of natural selection
- Darwin is known for his theory of evolution called 'The Theory of Natural Selection' which he published in the book titled 'Origin of Species'.
- This theory is based on the concept of survival of the fittest. He stated that all organisms reproduce prolifically. Hence, there is a continuous competition between organisms for survival and the organisms which constantly adapt, survive in the long run.
- The chances of survival are higher for the organisms which show modifications which help them to survive.
- Darwin also stated that the nature plays an important role in the selection of the fittest organisms. Nature selects only those organisms which are capable of adapting to the changing situations while the rest which are incapable to do so perish away.
- The organisms which are selected by the nature then reproduce and give rise to a new species over a period of time, which then have their own characteristics.
Solution 4.c
Embryology
- Embryology is the study of the formation and development of embryo and foetus.
- Comparative study of embryos in vertebrates shows that these embryos in their initial stages are very similar to each other. The similarities decrease later in the developmental process.
- This similarity in initial stages of embryo development indicates that the different classes of vertebrates have originated from a common ancestor.
- In evolutionary science, comparative study of embryos of different classes of vertebrates provides evidence for evolution.
Solution 4.d
Evolution
- The sequential and gradual changes in living organisms over a long period of time is called evolution.
- Evolution is also described as the formation of new species due to natural selection.
- The process of evolution takes millions of years for development and speciation of different organisms.
- Changes in stars and planets in space and the changes in biosphere occurring on the Earth are all included under study of evolution.
- Life originated on the Earth about 3.5 billion years ago. It is believed that there might have been the presence of simple elements on Earth which may have given rise to simple organic and inorganic molecules.
- From these simple molecules, complex molecules like proteins and DNA may have been formed.
- Other evolutionary changes may have resulted in the formation of simple cells and because of continuous evolution on Earth, several species of plants and animals began to exist on the Earth.
- Due to evolution organisms become fit, biodiversity is increased, and new species are created. Today, the diversity on the Earth varies from unicellular Amoeba to a human being and from a unicellular algae like Chlorella to a huge banyan tree.
- Different scientists have put forth different theories to explain the process of evolution. Among these, Charles Darwin's theory of natural selection and speciation is accepted worldwide.
Solution 4.e
Connecting link
Some living organisms possess certain characters which are distinctive features of different groups or phyla. Such individuals are known as connecting links as they connect these two different groups by sharing the characters of both the groups. Connecting links indicate the direction and hierarchy of evolution.
Several examples of connecting links are stated below:
- Peripatus: It is the connecting link between annelids and arthropods. It shows a segmented body, thin cuticle and parapodia-like organs similar to annelids. It also shows tracheal respiration and open circulatory system similar to arthropods.
- Duck-billed platypus: It is the connecting link between reptiles and mammals. It lays eggs like reptiles but possesses mammary glands like mammals.
- Lung fish: It is a connecting link between fishes and amphibians. Although a fish, it shows lungs for respiration as in amphibians.
Solution 5
- Heredity is the process by which biological characters from the parental generation are transmitted to the next generation through genes.
- Gregor Johann Mendel proposed that heredity is controlled by factors, which are now believed to be segments of chromosomes called genes. The characters or traits are passed on in the form of genetic information from the parents to offspring. This genetic information is stored in molecules called DNA.
- During the process of reproduction, a child receives genetic information from both the parents in the form of DNA. 50% of genetic information is passed on from the paternal DNA whereas the rest 50% of information is passed on by the maternal DNA.
Mechanism of hereditary changes:
- Mutation: Sudden changes in the parental DNA can cause mutations. This results in changes in the hereditary characters.
- Meiosis: At the time of meiosis, crossing over takes place which creates recombination of the genetic information resulting in change in hereditary characters.
Solution 6
Vestigial organs are degenerated or underdeveloped organs of organisms which do not perform any function in those organisms.
Vestigial organs in human body:
- Appendix
- Tail-bone or coccyx
- Wisdom teeth
- Body hair
The vestigial organs in one animal may perform an important function in some other animal.
Below are some examples:
- Appendix is vestigial for humans, but in ruminant animals it is associated with digestion.
- Ear muscles are vestigial for humans, but they are functional in monkeys and cattle.
Solution 7.a
- Hereditary characters are transmitted from the parental generation to the offspring. These characters are maintained through inheritance.
- However, the genes which are beneficial for the organisms and enable them to adapt to the changing environment are transmitted to the next generation in a greater proportion. This happens due to natural selection.
- The process of evolution happens at a very slow pace. The favourable genes are preserved in the species as they bring about better survival of the individuals. Such individuals reproduce more efficiently and evolve.
- The individuals with unfavourable genes are not selected by nature and are thus eliminated from the population.
- The process of evolution is thus truly supported by the hereditary changes which occur in organisms.
Solution 7.b
Formation of complex proteins occurs in three steps, viz. transcription, translation and translocation. Protein synthesis takes place with the help of RNA molecules according to the sequence of nucleotides present on the DNA molecule. This is known as the central dogma of protein synthesis.
Steps in protein synthesis:
- Transcription: In this process, mRNA is produced according to the nucleotide sequence on the DNA. For this, the two strands of DNA are separated and only one strand participates in the formation of mRNA. The sequence of nucleotides which is complementary to that present on the DNA is copied on the mRNA. Instead of thymine present in DNA, uracil is added on the mRNA. Transcription takes place in the nucleus but the mRNA leaves nucleus, carries the genetic code and enters the cytoplasm. This genetic code is always in triplet form and hence is known as a triplet codon. The code for each amino acid always consists of three nucleotides.
- Translation: Each mRNA may carry thousands of codons. However, each codon is specific for only one amino acid. The tRNA molecule brings the required amino acid as per the code present on the mRNA. There is anticodon on each tRNA which is complementary to the codon on mRNA. This process is known as translation.
- Translocation: In this process, the ribosome keeps on moving from one end of the mRNA molecule to other end by a distance of one triplet codon. While this process takes place, rRNA helps in joining the amino acids together by peptide bonds. The peptide chains later come together to form complex protein molecules.
Solution 7.c
Theory of evolution:
- According to the theory of evolution, first living material existed in the form of protoplasm which was formed in the ocean.
- Gradually, it gave rise to unicellular organisms. Changes took place in these unicellular organisms which later evolved into larger and more complex organisms.
- All evolutionary changes occurred very slowly and gradually and took about 300 crore years.
- Different types of organisms were developed as the changes and development that occurred in living organisms were all round and multi-dimensional. Hence, this overall process of evolution is called organisational and progressive.
- During the process of evolution, a variety of plants and animals developed from the ancestors having different structural and functional organisation.
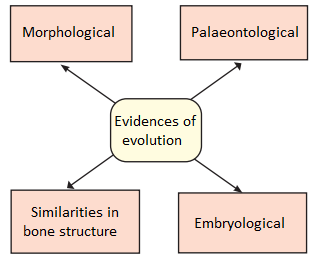
Proof for the theory of evolution:
The proof of evolution implies the evidences of evolution. These evidences were in the form of:
- Morphological evidences
- Anatomical evidences
- Vestigial organs
- Palaentological evidences
- Connecting links
- Embryological evidences
Solution 7.d
Importance of anatomical evidences in evolution
- There are similarities in the structure and anatomy of different animal groups. This acts an anatomical evidence in the process of evolution.
- For example, human hand, forelimb of bull, patagium of bat and flipper of whale are all similar in their internal anatomy. There is a similarity in the bones and joints of all these organisms.
- The external morphology of these organisms does not show any similarity. The use of each of these organ is also different in different animals.
- However, the similarities in the anatomy is an evidence that these organisms may have evolved from a common ancestor.
- In this way, the anatomical evidence throws light on the process of evolution.
Solution 7.e
Fossils are preserved remains of living organisms from remote past. Due to some natural calamities, the organisms get buried. The impressions and remnants of such organisms remain preserved underground. The hot lava also traps some organisms or their impressions. All such formations form fossils.
Importance of fossils as proof of evolution:
- Fossils offer palaeontological evidence for the evolutionary process, revealing the characteristics of the past organisms, and the changes that have occurred in these organisms to give rise to a present organism.
- Study of fossils informs us about the types of organisms that existed in the past.
- They inform us about the extent to which living organisms have changed over time.
- Carbon dating method also helps in finding out exact age of the fossil. According to the structure of earth's crust the fossils are obtained at specific depths. The oldest ones are obtained at the depth while the relatively recent ones occupy the upper surface. Thus, they inform us about the time when a particular life form existed.
- Accordingly, the fossils of invertebrates were seen in very old Palaeozoic era. Later, the fossils of Pisces, Amphibia and Reptilia were seen. The Mesozoic era was dominated by reptiles while Coenozoic era showed the presence of mammals.
In this way, study of fossils unfold the evolutionary secrets.
Solution 7.f
Evolutionary history of modern man:
- Ancestors of humans developed from animals which resembled lemur-like animals.
- Around 7 crore years ago, monkey-like animals evolved from some of these lemur-like animals.
- Around 4 crore years ago, in Africa the tails of these monkey-like creatures gradually disappeared. Simultaneously, there was an enlargement in their body and brain volume. The hands also improved and were provided with opposable thumb. In this way, ape-like animals were evolved.
- These ape-like animals independently gave rise to two lines of evolution -
- Ape-like gibbon and orangutan in the South and North-East Asia and gorilla and chimpanzee which stayed in Africa around 2.5 crores years ago.
- Human-like animals around 2 crore years ago.
- The climate became dry and this resulted in reduction of forest cover. This made arboreal apes to descend on land and begin terrestrial mode.
- As a result, there were changes in the pelvic girdle and vertebral column. The hands were also freed from locomotion and thus they became more manipulative.
- Later, the journey of hominoid species started from around 2 crores years ago. The first record of human-like animal is Ramapithecus ape from East Africa.
- The important steps in human evolution are:
Ramapithecus → Australopithecus → Neanderthal man → Cro-Magnon.
- Neanderthal man was said to be the first wise man. The increasing growth of brain made man more and more intelligent and a thinking animal.
- Later, more than biological evolution, it was the cultural evolution, when man started agriculture and animal rearing. There was a development in civilization, arts and science.
- About 200 years ago, there were industrial inventions and thus man now rules the Earth.

