Class 10 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 7 - Lenses
Lenses Exercise Ex. 7
Solution 1
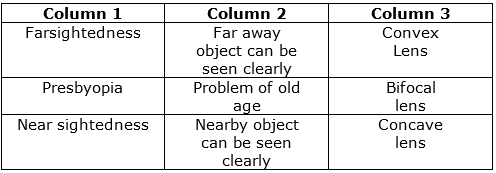
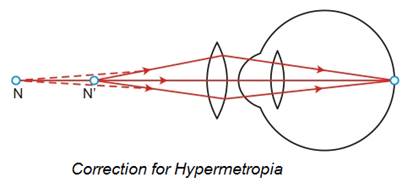
Farsightedness is also known as Hypermetropia.
It is defect where person is unable to see nearby objects but can see far away objects. It is corrected by using convex lens.
• It occurs in old age when the ciliary muscles holding the eye lens weaken and the eye lens loses some of its flexibility.
• To correct presbyopia, an old person has to wear spectacles with a convex lens of suitable focal length (as in hypermetropia).
Sometimes, a person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia. Such a person requires bi-focal lenses. The upper part of a bi-focal lens consists of a concave lens facilitating distant vision, and the lower part consists of a convex lens facilitating nearby vision.
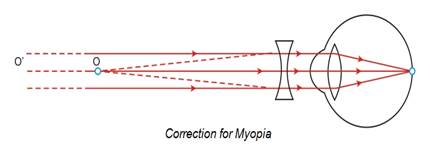
Near sightedness is also known as myopia. It is a defect where in the person cannot see far away objects clearly but can see nearby objects clearly. It is corrected by using concave lens.
Solution 2
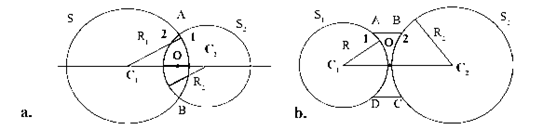
Centre of curvature (C): The centres of spheres whose parts form surfaces of the lenses are called centres of curvatures of the lenses. A lens with both surfaces spherical, has two centres of curvature C1 and C2.
Radius of curvature (R): The radii (R1 and R2) of the spheres whose parts form surfaces of the lenses are called the radii of curvature of the lens.
Principal axis: The imaginary line passing through both centres of curvature is called the principal axis of the lens.
Optical centre (O): The point inside a lens on the principal axis, through which light rays pass without changing their path is called the optical centre of a lens.
Principal focus (F): When light rays parallel to the principal axis are incident on a convex lens, they converge to a point on the principal axis. This point is called the principal focus of the lens.
Focal length (f): The distance between the optical centre and principal focus of a lens is called its focal length.
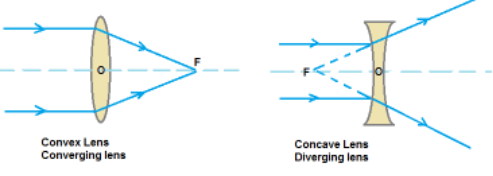
Solution 3
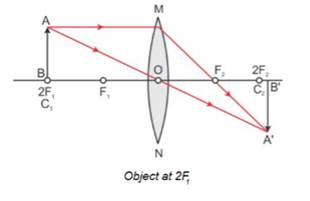
The object should be placed at 2F1 so as to get an image of same size as that of object which will be formed at 2F2.
Solution 4
a.
i. A magnification of simple microscope is about 20 times.
ii. When object is placed within the focus of convex lens, the magnified and erect image is formed.
iii. Dues this, the watch repairer can observe minute watch parts more clearly with simple microscope than he will see with a naked eye.
b.
i. The numerous light-sensitive cells contained in the retina of the eye are of two types:
ii. Rod-shaped cells which respond to the brightness or intensity of light.
iii. Cone-shaped cells which respond to the colour of light.
iv. Thus, one can sense colours only in bright light.
c.
i. The ciliary muscles help in adjustments of focal length of lens.
ii. The minimum distance of an object from a normal eye for which the eye lens can decrease its focal length is 25 cm. 25 cm is a least distance of distinct vision. It is least distance required to see any object clearly for normal human eye.
iii. Thus, we cannot clearly see an object kept at a distance less than 25 cm from the eye.
Solution 5
The telescopes used to observe astronomical sources like the stars and the planets are called astronomical telescopes. Telescopes are of two types.
1. Refracting telescope - This uses lenses
2. Reflecting telescope - This uses mirrors and also lenses.
In both of these, the image formed by the objective acts as object for the eye piece which forms the final image. Objective lens has large diameter and larger focal length because of which maximum amount of light coming from the distant object can be collected.
On the other hand, the size of the eyepiece is smaller and its focal length is also less. Both the lenses are fitted inside a metallic tube in such a way that the distance between them can be changed.
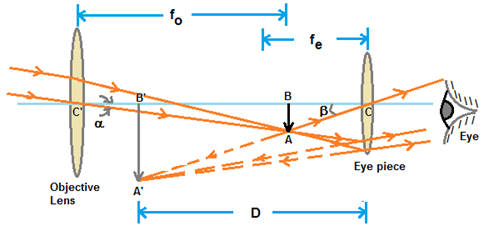
Solution 6
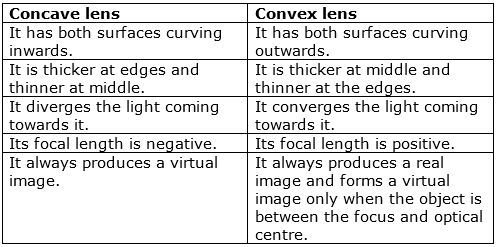
Farsightedness and Nearsightedness
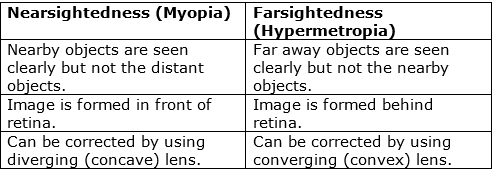
Concave lens and convex lens
Solution 7
Function of iris is to control the size of the pupil, which in turn controls the amount of light entering the eye.
Function of ciliary muscles is to held eye lens in position. The focal length of the eye lens is adjusted by expansion and contraction of ciliary muscles.
Solution 8i
P = +1.5 D
f = 1/P = 1/ (+1.5) = +0.67 m
Since the focal is positive, the lens prescribed for correction is convex lens. The defect of vision is hypermetropia.
Solution 8ii
ho = 5 cm, u = -25 cm
Since the lens is converging it is a convex lens
f = 10 cm
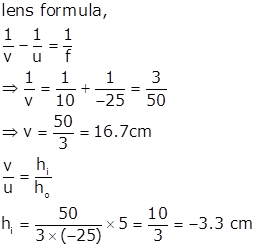
The size of image is 3.3 cm. Negative sign indicates that the image formed real and inverted.
Solution 8iii
P1 =2D, P2 = 2.5 D, P3 = 1.7D
P = 2 + 2.5 + 1.7 = 6.2 D
Solution 8iv
u = - 60 cm, v = - 20 cm
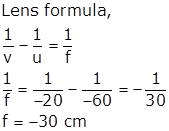
The focal length is negative, the lens is concave lens.

