Class 10 LAKHMIR SINGH AND MANJIT KAUR Solutions Biology Chapter 5 - Our Environment
Our Environment Exercise 226
Solution 1
Solution 2
Artificial ecosystems - Parks and Gardens.
Solution 19
(b) Producers.
(c) Food Chain.
(d) Ecology.
(e) Non - biodegradable; Biodegradable.
Solution 18
Solution 17
Solution 16
Fourth trophic level: Hawk.
Solution 15
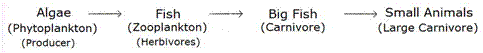
Solution 14
Solution 13
Solution 20
Example - Green plants and certain blue-green algae.
(ii) Those organisms which consume food (eat food) prepared by producers are called consumers.
Example - Lion and Tiger.
Solution 21
Example - Bacteria and Fungi.
(b) The decomposers help in decomposing the dead bodies of plants and animals, and hence act as cleansing agents of environment.
Solution 22
Example - Goat
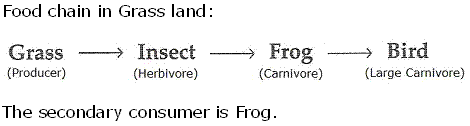
(ii) The small carnivores which feed on herbivores (primary consumers) are called secondary consumers.
Example - Frog
(iii) The Large carnivores (or top carnivores) which feed upon the small carnivores (secondary consumers) are called tertiary consumers.
Example - Lion
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
(b) True.
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
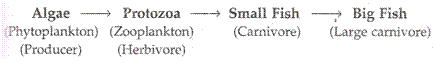
Solution 12
Fourth trophic level: Snakes
Our Environment Exercise 227
Solution 33
(b) Second trophic level
(c) Third trophic level
(d) Second trophic level
(e) Fourth trophic level
Solution 34
(b) Three
Solution 35
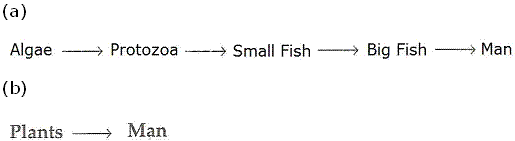
Solution 36
(b)
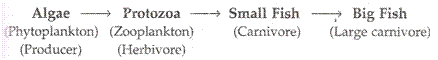
Solution 37
Solution 38
Solution 39
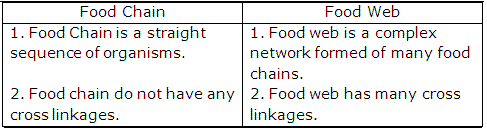
Solution 40
(b) Abiotic components
(c) Consumers
(d) Environment
(e) Ecosystem
Solution 41
Solution 31
Solution 30
Paper - Biodegradable
Ball point pen refill - Non- biodegradable
Hay - biodegradable
DDT - Non- biodegradable
Wheat - Biodegradable
Cake - Biodegradable
Wood - Biodegradable
Polythene Bag - Non-biodegradable
Jute Bag - Biodegradable
Cotton Cloth - Biodegradable
Grass - Biodegradable
Vegetable peels - Biodegradable
Solution 29
| Bioderghradable Wastes | Non-Biodegradable Wastes |
|
1. Those waste materials which can be broken down to non-poisonous substances in nature by the action of microorganisms (like bacteria) are called biodegradable wastes.
Example:- Paper, Wood, etc.
|
1. Those waste materials which cannot be broken down to non-poisonous substances in nature are called non-biodergradable wastes. 3. The harmful chemical leach out of these wastes when they are dumped in soil. This leads to soil pollution. |
Solution 28
Solution 27
Solution 26
Solution 25
Solution 24
(b) If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level, then the transfer of food (and energy) to the next trophic level will stop due to which the organisms of next trophic level will starve and die or migrate to other areas. The killing of all the organisms in one trophic level will also lead to the overpopulation of organisms in the previous trophic level. These effects will cause an imbalance in the ecosystem. For example, if we kill all the herbivorous animals like deer, rabbits, etc., in a forest, then the carnivorous animals like lions, tiger, etc., will not get food. Due to this, the lions and tigers etc., will starve and die or migrate from forest and go towards human settlements and attack people. Moreover, in the absence of herbivores like deer, rabbits, etc., the population of the previous trophic level 'plants' (or vegetation) will increase too much (because there are no deer or rabbits to eat them). All these effects will create an imbalance in the ecosystem.
Solution 23
Solution 42
Example - D.D.T and Plastics.
(b) Animal Bones and Leather Belts.
Solution 32
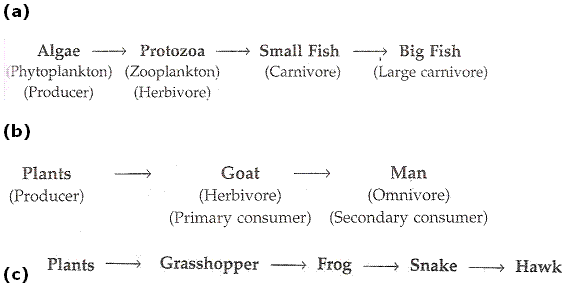
Our Environment Exercise 228
Solution 43
Example - a grassland and a forest.
(b)
(i) Biotic component - The biotic components of the ecosystem is a community of organisms which is made up of many different inter-dependent populations. It includes - producers, consumers and decomposers.
(ii) Abiotic components - The abiotic components of the ecosystem (non living components) include the physical environment like soil, water and air alongwith the in organic substances like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, water and phosphorous.
Solution 44
(b) The interconnected food chains operating in an ecosystem which establish a network of relationships between various species is called a food web.
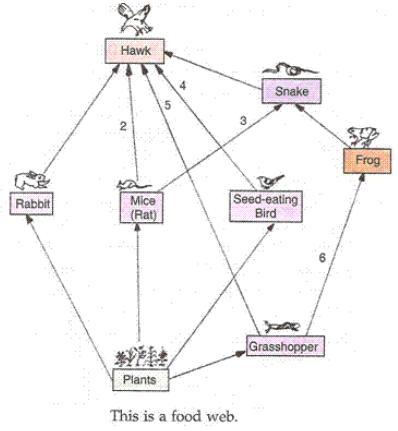
In this food web, we can see a network of numerous pathways along which the food flows within grass land community. This food web starts from the plants which is producer and end in top carnivore hawk.
Solution 45
(b) The non- biodegradable wastes pollutes the environment like plastic and polythene bags.
(c) Human beings are the only organisms which change the natural environment to fulfill their needs. The uncontrolled activities of human beings are damaging the balanced and healthy environment.
(d) Paper bags should be used for shopping because these are biodegradable whereas plastic bags are non- biodegradable.
Our Environment Exercise 240
Solution 15
(b) Producer.
(c) Goat.
(d) Rabbit.
(e) Lion.
Solution 14
Solution 13
Solution 12
Solution 11
Solution 10
Solution 9
Solution 8
Solution 7
Solution 6
Solution 5
Solution 4
Solution 3
Solution 2
Solution 1
Our Environment Exercise 241
Solution 38
(b) (i) Paddy can trap only 1% of the sun's energy falling on them. 1% of 10,000 J is 100 J, so paddy have 100 J of energy available in them as food.
(ii) Paddy is eaten up by mice. Now according to the 10% law, 10% of 100 J is 10 J of energy which is available in mice.
(iii) The mice will transfer 10% of its 10 J energy to the snake. Thus, the food energy available to the snake will be 10% of 10 J, which is 1 J.
(iv) 10% of 1 J will be transferred to hawk which will be 0.1 J.
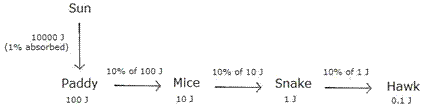
Solution 37
(b)
(i) Small algae can trap only 1% of the sun's energy falling on them. 1% of 10,000 J is 100 J, so the small algae have 100 J of energy available.
(ii) Small algae are eaten up by zooplankton. According to the 10% law, 10% of 100 J is 10 J of energy which is available in zooplankton.
(iii) The zooplankton will transfer 10% of its 10 J energy to the fish. Thus, the food energy available to the fish will be 10% of 10 J, which is 1 J.
(iv) 10% of 1 J will be transferred to big fish which will be 0.1 J.
The above result can be clearly shown as:

Solution 36
(b)
(i) The producer level in the food chain are plants, so 100 J of energy is available in plants as food. Applying the 10% law to the above food chain:
1. According to the 10% law, 10% of energy of plants will be available as food in mice. Thus, the energy available to mice will be 10% of 100 J, which is 10 J.
2. The energy available to snakes will be 10% of 10 J, which is 1 J.
3. The energy available to hawks will be 10% of 1 J, which is 0.1 J.
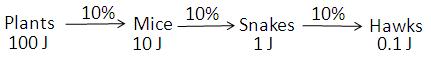
(ii) The producer level in the food chain is plants, so 100 J of energy is available in plants as food. Applying the 10% law to the above food chain:
1. According to the 10% law, 10% of energy of plants will be available as food in mice. Thus, the energy available to mice will be 10% of 100 J, which is 10 J.
2. The energy available to hawks will be 10% of 10 J, which is 1 J.
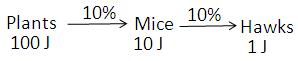
Hawks will get more energy in food chain (ii) because in this food chain there are three trophic levels so the energy available will be more as compared to food chain (i) which has four trophic levels.
Solution 35
The free oxygen atoms thus produced are very reactive. One oxygen atom reacts with an oxygen molecule to form an ozone molecule:
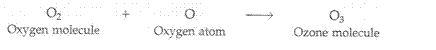
(b) Ozone layer protect us from harmful effects as it absorbs most of the ultraviolet radiations coming from the sun and prevents them from reaching the earth.
(c) UNEP - United Nation Environment Program. In 1987, in an attempt to protect ozone layer, the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) forged an agreement among its member countries to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels.
Solution 34
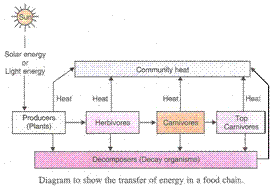
(a) The energy from sun flows through various trophic levels. The food and energy are transferred from producer organisms to herbivores and from herbivores to carnivores, through the food chain.
First Step - The green plants trap solar energy with the help of green pigment called chlorophyll which converts the sunlight energy into chemical energy. This gets stored as carbohydrates in the plants. About 1% of the sun's energy falling on the leaves is used by the plants in the process of photosynthesis and stored as chemical energy of food. The plants utilize the stored energy for their metabolic activities like respiration and growth. Some of the energy is not utilised and it is released as unusable heat into the environment.
Second Step - The plants are eaten up by herbivores and the chemical energy of plants is transferred to them. The herbivores utilize this energy for various metabolic activities and release unused energy as heat energy to the environment.
Third Step - The herbivores are eaten up by carnivores. The chemical energy stored in the flesh of herbivores is transferred to the carnivores and they utilise this energy for their metabolic activities like respiration and growth and some of the energy which remains unutilised, is released into the environment. This process of transfer of energy is repeated with large carnivores and so on.
(b) The flow of energy in the ecosystem is said to be unidirectional because the energy lost as heat from the living organisms of a food chain cannot be reused by plants in photosynthesis.
Solution 16
Ten PerCent Law - According to ten per cent law, only 10 per cent of the energy entering a particular trophic level of organisms is available for transfer to the next higher trophic level.
Example - Suppose 1000 Joules of light energy emitted by the sun falls on the plants.
Consider a food chain:
The plants or first trophic level has 10 joules of energy in it. Now according to 10 percent law, only 10% of 10 joules of energy (which is 1 joule) will be available for transfer to the next trophic level, so that the herbivore will have only 1 joule of energy stored as food at the second trophic level. 10% of the remaining 1 joule will be transferred to third trophic level of carnivore. So, the energy available in the lion as food will be only 0.1 joule.
Solution 17
Chlorofluorocarbons released into the air react with ozone gas present in the ozone layer and destroy it gradually.
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
Solution 21
Solution 22
The increase in concentration of harmful chemical substances like pesticides in the body of living organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification.
The organism which occurs at the highest trophic level (on the extreme right side) in the food chain will have the maximum concentration of harmful concentration of harmful chemicals in its body. In this case grass is eaten by grasshopper; grasshopper is eaten by frog; frog is eaten by snake and finally snake is eaten by peacock. So, the food chain will be:
Since the peacock occurs at the highest trophic level (on the extreme right side) in this food chain, it will have the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in its body.
Solution 23
Solution 24
Solution 25
(i) Recycling
(ii) Preparation of compost
(iii) Incineration
(iv) Landfill
(v) Sewage treatment
Solution 26
Solution 28
Solution 33
Solution 32
(i) It can cause skin cancer.
(ii) It damages the eyes by causing the eye disease called cataract.
(iii) It damages the immune system by lowering the body's resistance to diseases.
Solution 31
Solution 30
(i) Paper cups are biodegradable. So, even if paper cups are thrown away after use, they will decompose (break down) automatically by the action of micro-organisms in due course of time. On the other hand, plastic cups are non-biodegradable. They will remain as such and pollute the environment.
(ii) Paper cups can be disposed off by burning without causing much air pollution. On the other hand, burning of plastic cups produces toxic gases (poisonous gases) which causes too much air pollution.