JEE Plances Class Answered
Ques13

Asked by rbhatt16 | 19 Jul, 2018, 09:28: AM
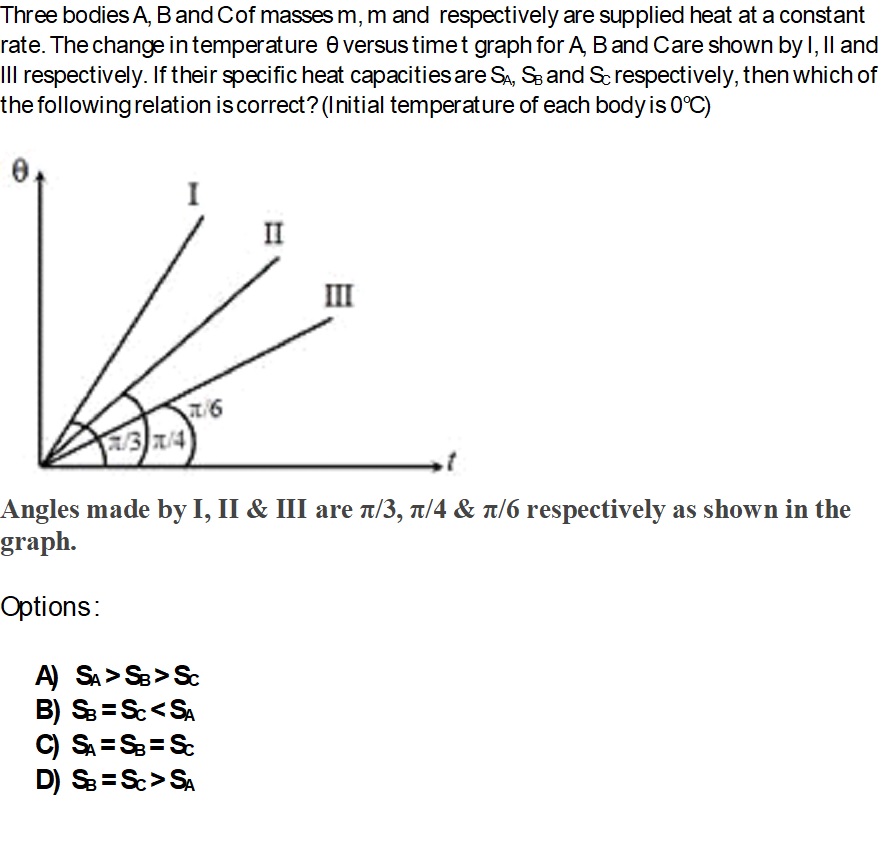
If a magnetic dipole having moment M be rotated through angle θ from equilibrium position in a uniform magnetic field B,
workdone on it is W = MB(1-cosθ)
This work is stored in the system in the form of Energy.
When system is released, dipole starts to rotate to occupy equilibrium position and the energy converts into kinetic energy.
Kinetic energy of the system is maximum when stored energy is completely released.
Magnetic Induction, at centre due to current in larger coil is 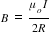
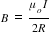
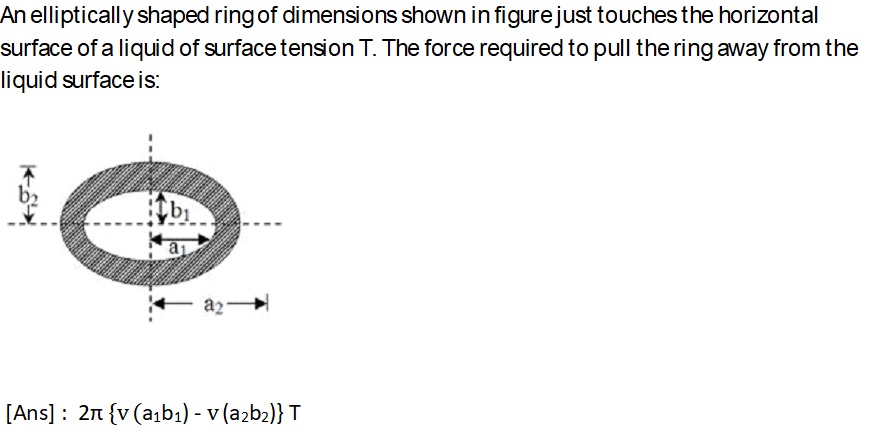
magnetic dipole moment of smaller coil is i×π×r2
Initially, planes of two coils are perpendicular, therfore θ is 90º.
Energy of the system is U = ( i×π×r2 )×B×(1-cos 90) = 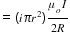
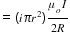
When coils are released, both the coils start to rotate about their common diameter and
their kinetic energies are maximum when they become coplanar.
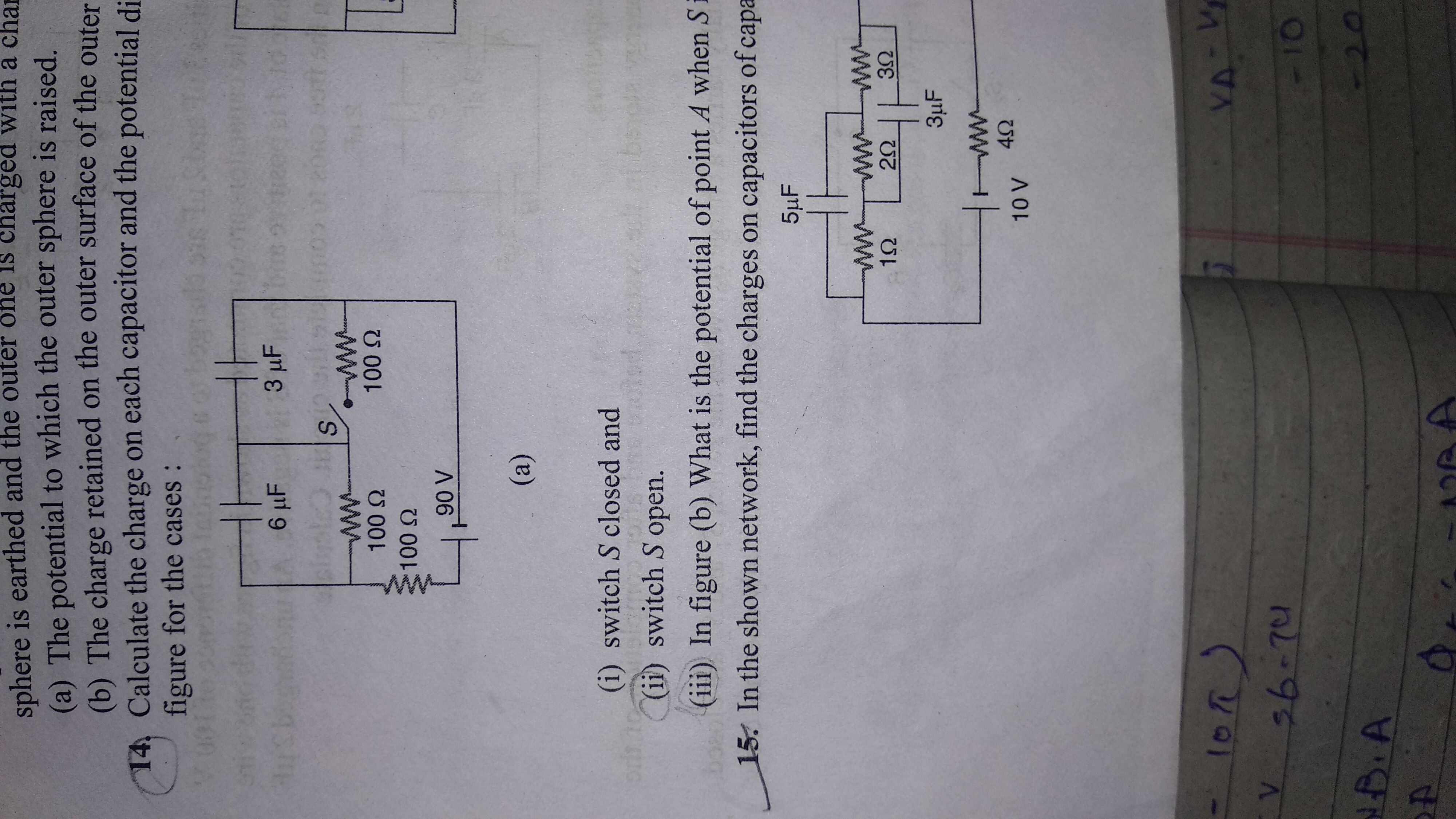
Moment of inertia of larger coil about axis of rotation is I1 = (1/2)MR2 and smaller coil is I2 = (1/2)mr2 .
Since two coils rotate due to their mutual interaction only, therfore if one coil rotates clockwise then other rotates in anticlockwise
Let angular velocities of larger and smaller coil be numerically equal to ω1 and ω2 respectively when they become coplanar.
According to law of conservation of angular momentum, I1 ω1 = I2 ω2 ................... (1)
and according to law of conservation of energy, 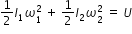 ...................(2)
...................(2)
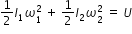 ...................(2)
...................(2)from (1) and (2), we have 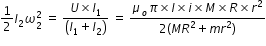
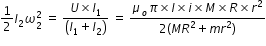
Answered by Thiyagarajan K | 03 Aug, 2018, 12:30: PM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 14 Dec, 2018, 09:49: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 13 Dec, 2018, 10:11: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 13 Dec, 2018, 10:10: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 13 Dec, 2018, 10:08: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 12 Dec, 2018, 09:41: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 12 Dec, 2018, 09:41: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 12 Dec, 2018, 09:40: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 12 Dec, 2018, 09:39: AM
JEE Plances - Physics
Asked by rsudipto | 12 Dec, 2018, 09:38: AM