Three blocks are placed on smooth horizontal surface and lie on same horizontal straight line.Block 1 and block 3 have mass m each and block 2 has mass M(M greater than m) .Block2 and block3 are initially stationary ,while block1 is initially moving towards block2 with speed v as shown.Assume that all collisions are head on and perfectly elastic .What value of M/m ensures that block1 and block 3 have the same final speed?
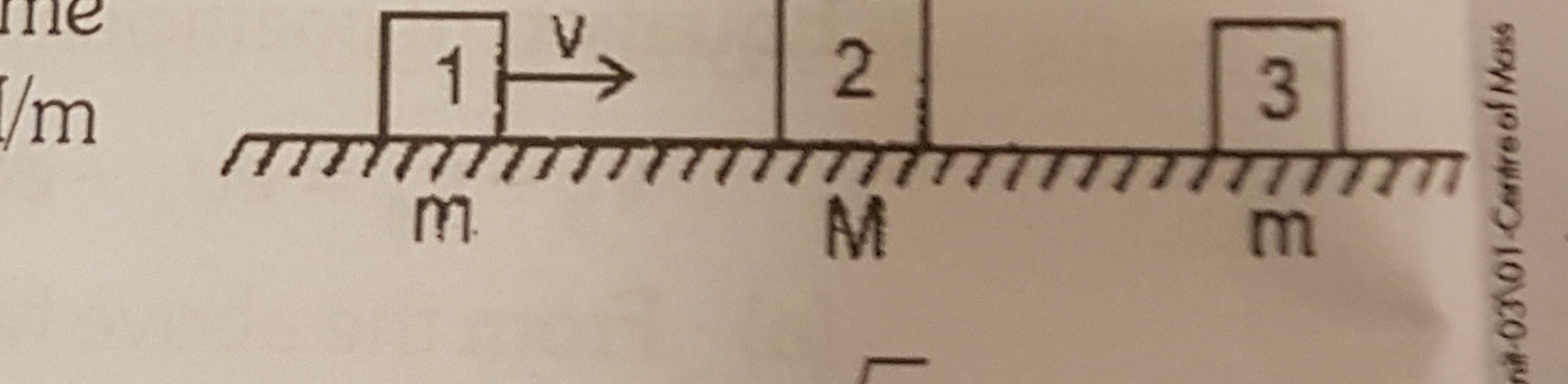
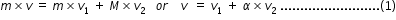
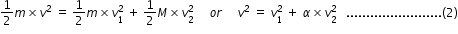


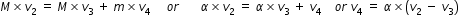 ....................(5)
....................(5)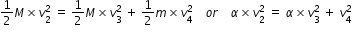 ...........................(6)
...........................(6)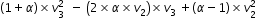 ...................(7)
...................(7)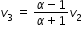
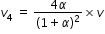
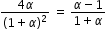 ............................(8)
............................(8)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
You have rated this answer /10
Browse free questions and answers by Chapters
- 1 Thermodynamics
- 2 Gravitation
- 3 Electromagnetic Waves
- 4 Communication Systems
- 5 Laws of Motion
- 6 Current Electricity
- 7 Work, Energy and Power
- 8 Kinematics
- 9 Physics and Measurement
- 10 Rotational Motion
- 11 Properties of Solids and Liquids
- 12 Kinetic Theory of Gases
- 13 Oscillations and Waves
- 14 Electrostatics
- 15 Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- 16 Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- 17 Optics
- 18 Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
- 19 Atoms and Nuclei
- 20 Electronic Devices
