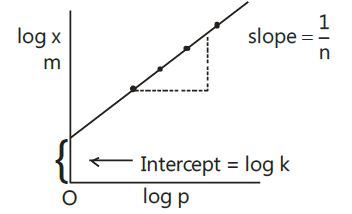
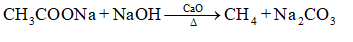(1) How is Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm used to correlate the experimental facts regarding the adsorption of gas at low, high and intermediate pressure ?





- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
You have rated this answer 2/10
Browse free questions and answers by Chapters
- 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- 2 Structure of Atom
- 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- 5 States of Matter
- 6 Thermodynamics
- 7 Equilibrium
- 8 Redox Reactions
- 9 Hydrogen
- 10 The s-Block Elements
- 11 The p-Block Elements
- 12 Organic Chemistry
- 13 Hydrocarbons
- 14 Environmental Chemistry