Class 10 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 8 - Metallurgy
Ex. 8
Metallurgy Exercise Ex. 8
Solution 1
- Sodium almagam
- Al2H2O4 -bauxite
- Amophoteric oxides:aluminum oxide ,lead oxide
- Grinding mill
- Graphite
- Aqua-regia
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
- Metallurgy
The scientific principles and the physical and chemical processes that are applied to obtain pure metals from their ores are known as metallurgy.
In other words, the process used for the extraction of metals in their pure form from their ores is referred to as metallurgy. - Ores
The minerals from which metals are extracted commercially at a comparatively low cost and with minimum effort are called ores. - Minerals
The naturally occuring compounds of metals which are generally mixed with other matter such as soil, sand, limestone and rocks are known as minerals. - Gangue
The earthly impurities including silica, mud etc. associated with the ore are called gangue.
Solution 5 (a)
- Lemon juice contains citric acid and tamarind contains tartaric acid. These acids react with basic layer of copper carbonate on the surface to form soluble salts which are easily removed and surface shines.
Solution 5 (b)
- Ionic compounds have high melting points because there is a strong electrostatic force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions and hence a large amount of energy is required to break the strong bonding force between ions.
Solution 5 (c)
- Sodium (Na) is highly reactive with air, moisture, etc. If it comes in contact, it will react with the moisture present in air and form sodium hydroxide hence to avoid its contact it is stored in kerosene.
Solution 5 (d)
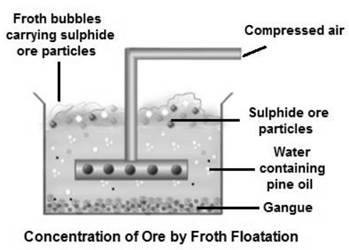
- It is used as a frothier in the process. Frothier are surface-active chemicals that concentrate at the air-water interface. They prevent air bubbles from coalescing or bursting by lowering the surface tension of the slurry.
Solution 5 (e)
- During electrolysis of alumina, the oxygen liberated at the carbon anode reacts with graphite rods (carbon anode) and forms carbon dioxide.
- The carbon anodes slowly disappear because each molecule of carbon dioxide which is given off takes a little piece of carbon away with it.
- The carbon anodes need to be replaced when they become too small.
Solution 6
- Copper is more reactive than silver. Therefore, when copper coin is kept immersed in a solution of silver nitrate, it will displace silver from silver nitrate solution and a solution of copper nitrate will be formed. Thus, copper coin will dissolve in the solution.
Cu + AgNO3 → CuNO3 + Ag
Solution 7
- Metal A with electronic configuration of (2, 8, 1) is sodium (Na).
- Metal B with electronic configuration of (2, 8, 2) is magnesium (Mg).
- If the number of electrons in the outermost orbit is less, then the metal is more reactive. Metal A contains one electron in the outermost shell, while metal B contains two electrons. Hence, metal A is more reactive than metal B.
- Na+HCl→NaCl+H2
- Mg+HCl→MgCl2+H2
Solution 8
a. Magnetic separation method.
Haematite and Magnetite ores can be concentrated by magnetic separation method.
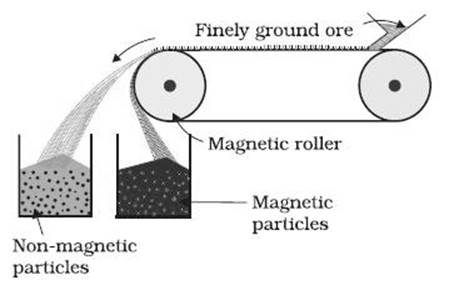
b. Froth floatation method.
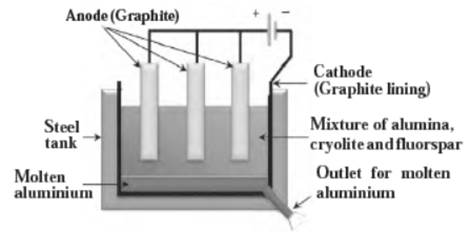
c. Electrolytic reduction of alumina.
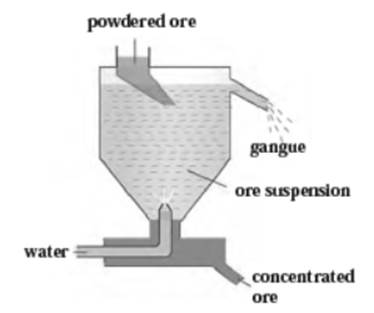
d. Hydraulic separation method.
Solution 9
- 4Al(s) + 3O2(l) → 2Al2O3(s)
The surface of the aluminum metal is covered with a thin layer of oxide that helps protect the metal from attack by air. If the oxide layer is damaged, the aluminum metal is exposed to attack by air. - Iron is more electropositive than copper. It can displace Copper (Cu) from its salt Copper sulfate (CuSO4) and thus its colour changes from blue to green.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu - The reaction of Ferric oxide and aluminum produces aluminum oxide and iron. The chemical equation is:
3Fe3O2 + 4Al → 2Al2O3 + 6Fe - The electrode reactions are:
Anode reaction: 2O2- → O2 + 4e- (Oxidation)
Cathode reaction: Al3+→ Al (l)(Reduction) - ZnO(aq)+2HCl(aq)→ZnCl2(aq)+H2O(l)
Zinc chloride and water are produced in the reaction.
Solution 10
- Silica, Ferric Oxide, and Titanium Oxide are the impurities or gangue in Bauxite
- By Hall's and Bayer's method, where finally the concentrated alumina can be obtained by the calcination process
- Halls Process:
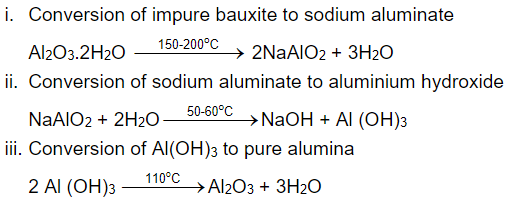
- Since aluminum oxide is amphoteric in nature, it reacts with NaOH to form water-soluble Sodium aluminate
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 + H2O (Acidic nature) Aluminium Sodium Sodium Water oxide Hydroxide aluminate
Solution 11
- Reactive metals: Ca, Mg, Na, Li
- Moderately reactive metals: Zn, Fe
- Less reactive metal: Cu

