Class 10 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 4 - Effects of electric current
Effects of electric current Exercise Ex. 4
Solution 1
a. Generator
Others restrict the flow of current which generator generates current.
b. Thermometer
Others are used to measure the parameters of electricity while thermometer is used to measure temperature.
c. Magnet
Others are electronic devices while magnet is not an electronic device.
Solution 2
a. Electric motor
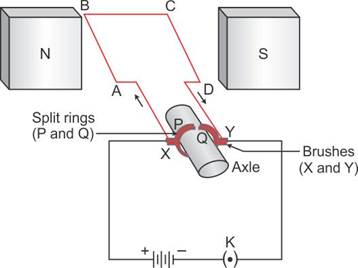
- An electric motor is a device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy, and it works on the principle of force experienced by a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
- An electric motor consists of a rectangular coil of insulated copper wire. The coil is placed between the two poles of a magnet.
- The current in the coil enters from the source battery through the conducting brush X and flows back to the battery through brush Y. Current in the arms AB and CD is in opposite directions.
- On applying Fleming's left-hand rule, we find that the force acting on the arm AB pushes it downwards while the force acting on the arm CD pushes it upwards. Thus, the coil and the axle O rotate in the anti-clockwise direction.
- After half rotation, the current in the coil gets reversed with the help of a commutator. This reverses the direction of the force acting on the two arms AB and CD. However, these arms have reversed positions after that half rotation.
- Thus, the coil and the axle rotate in the same direction, i.e., anti-clockwise.
b. Electric Generator (AC)
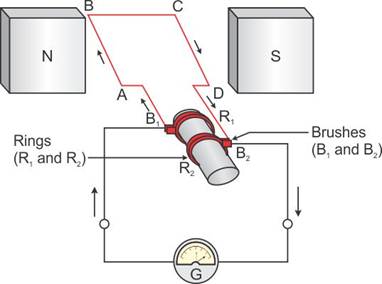
- Electric generators are based on the principle of electromagnetic induction and they convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- An electric generator consists of a rotating rectangular coil placed between the two poles of a permanent magnet.
- The two rings R1 and R2 are internally attached to an axle. The axle may be mechanically rotated from outside to rotate the coil inside the magnetic field.
- Outer ends of the two brushes B1 and B2 are connected to the galvanometer to show the flow of current in the given external circuit.
- When the axle is rotated, arm AB moves up (and the arm CD moves down) in the magnetic field produced by the permanent magnet. Let us say that the coil ABCD is rotated clockwise.
- By applying Fleming's right-hand rule, the induced currents are set up in these arms along the directions AB and CD. Thus, an induced current flow in the direction ABCD. If there are more turns in the coil, the current generated in each turn adds up to give a large current through the coil.
- After half rotation, CD and AB reverse direction, and thus, CD starts moving up and AB starts moving down. As a result, the directions of the induced currents in both the arms change.
- Such a current which changes direction after equal intervals of time is called an alternating current. Thus, this device is also called an AC generator.
Solution 3
Electromagnetic induction means generation of a current in a coil due to relative motion between the coil and the magnet.
Solution 4
Solution 5
Device used to produce electricity is electric generator (DC)
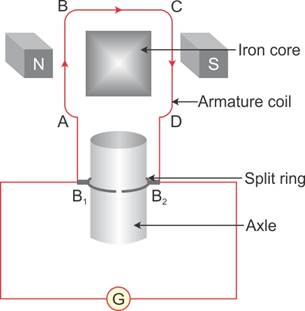
Electric generators are based on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
When a conducting loop is moved in a magnetic field, electric current is induced in the loop.
- Armature ABCD is rotated in anti-clockwise direction inside the magnetic field.
- Applying Fleming's right-hand rule to arm AB (moving downwards), (fig a) the direction of the induced current is found to be upwards (along AB).
- Applying Fleming right hand rule to the arm CD (moving upwards) the direction of the induced current is found to be downwards (along CD)
- For the half rotation of the armature hence the direction of the induced current in the armature is clockwise.
- Similarly for the next half rotation of the armature (fig b) applying Fleming's RH rule gives the direction of induced current to be again clockwise.
- Thus during the entire rotation, the current through load resistor R remains the same. The nature of the current produced is hence dc (direct current).
Solution 6
- Short circuit occurs when uninsulated neutral wire and live wire of circuit come in contact with each other.
- Large amount of heat is produced due to flow of this large current.
Solution 7
a.
- Electric bulb works on principle of heating effect of electric current.
- Solenoid type of coil of bulb has high resistivity and high melting point.
- When current is passed through bulb, solenoid type of bulb gets heated and starts glowing.
b.
A nichrome wire is used as the heating element in appliances such as heater, toaster, oven etc. because the resistivity of nichrome is very high and increase in its value with increase in temperature is also high.
c.
The resistivity of copper and aluminium are very low, so electric current flows easily through them. Hence copper and aluminium wires are usually used for electricity transmission.
d.
Electrical energy = Electric power x time
Practically, devices consume high electrical power and are used over a period of time. Thus, high amount of electrical energy is utilised. To measure such high value, Joule is small unit.
Thus, unit kWh is used practically instead of joule.
1kWh is power of 1 kW used for 1 hour and equals 3.6 x 106 J.
Solution 8
The correct statement is:
The magnetic lines of force are in concentric circles with the wire as the centre, in a plane perpendicular to the conductor.
Solution 9
A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a solenoid.
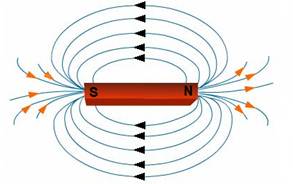
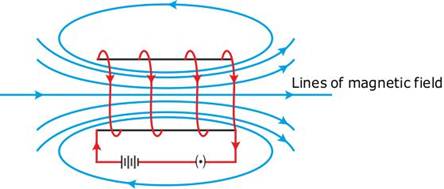
The pattern of the magnetic field lines around a current-carrying solenoid is similar to that produced by a bar magnet as shown in the figure above.
The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of parallel straight lines. Thus, the magnetic field is the same at all the points inside the solenoid. That is, the field is uniform inside the solenoid.
Solution 10
a. Fleming's right-hand rule
Fleming's right-hand rule is used to find the direction of induced current.
According to this rule, "Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the right hand such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points indicate the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb indicates the direction of motion of the conductor, then the middle finger will indicate the direction of induced current in the conductor".
b. Fleming's left-hand rule
Fleming's left-hand rule gives the direction of magnetic force acting on a conductor.
According to this rule, "Stretch the thumb, forefinger and middle finger of the left hand such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field and the middle finger indicates the direction of the current, then the thumb will indicate the direction of motion or the force on the conductor".
Solution 11
- It is fuse. An electric fuse is an electrical safety component which is used to protect the electrical appliances from getting damaged if excess of current flows through it. If the high current flows through the fuse, then the fuse wire will melt and thus breaks the circuit.
- It is miniature circuit breaker (MCB). MCB is used for protection against excessive current in the circuit, which may damage the circuit. Unlike a fuse, which operates once and then has to be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either manually or automatically) to resume normal operation.
- It is DC generator. It is a device that generates electricity by rotating its rotor in a magnetic field. It converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Solution 12.a
P = 100 W
I = 3 A
R =?
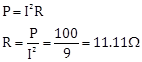
Solution 12.b
P1 = 100 W, P2 = 60 W
Potential difference across both bulbs remains same as they are connected in parallel.
For first bulb,
Current, I1 = 100/220 (Since, P = VI)
Thus, I1 = 0.45 A
For second bulb,
I2 = 60/220 = 0.27 A
Thus, total current flowing = I1+I2 = 0.45 + 0.27 = 0.72 A
Solution 12.c
Power of TV set, PTV = 500 W
Time of TV set, tTV = 30 min x 60 s
Thus, energy consumed by TV set, ETV = Power x time
= 500 x 30 x 60 = 9 x 105 J…(1)
Power of heater, PH = 600 W
Time of heater, theater = 20 min x 60 s
Thus, energy consumed by heater, Eheater = Power x time
= 600 x 20 x 60 = 7.2 x 105 J … (2)
From (1) and (2),
Energy consumed by TV set is more than that consumed by heater.
Solution 12.d
P = 1100 W
Time for which electric iron is operated daily = 2 h = 2 x 60 x 60 = 7200 s
Electric energy consumed by iron in 7200 s
E = 1100 x 7200 = 7920000 J
Total energy consumed in month of April (30 days),
= 7290000 x 30 = 2.376 x 108 J
1 unit = 3.6 x 106 J
1 J = 1/ (3.6 x 106) unit
2.376 x 108 J = 2.376 x 108 J/ (3.6 x 1000000) = 66 units
Cost of 1 unit of energy = Rs. 5
Thus, total expenses for month of April for operation the electric iron = 66 x 5 = Rs. 330

