Class 10 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 3 - Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise Ex. 3
Solution 1
- To prevent rusting, a layer of zinc metal is applied on iron sheets.
- The conversion of ferrous sulphate to ferric sulphate is Oxidation reaction.
- When electric current is passed through acidulated water electrolysis of water takes place.
- Addition of an aqueous solution of ZnSO4 to an aqueous solution of BaCl2 form a white precipitate is an example of double displacement reaction.
Solution 2 (a)
- Chemical reaction in which one reactant gets oxidized while the other gets reduced is called a redox reaction.
- Example: CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
- CuO is getting reduced to Cu and H2 is getting oxidised to H2O.
Solution 2 (b)
- The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen takes place slowly at room temperature. However, the same reaction occurs at a faster rate on adding manganese dioxide (MnO2) powder in it. Therefore, the rate of reaction can be increased by adding a catalyst manganese dioxide (MnO2) powder.
Solution 2 (c)
- The substances that are used up in a chemical reaction (starting material) are the reactants and the new substances formed are called the products.
- Reactants are written on the L.H.S. of the arrow. Products are written on the R.H.S. of the arrow.
- For example,
2H2+ O2 → 2H2O - Reactant Product
Solution 2 (d)
There are main three types of chemical reactions with reference to oxygen and hydrogen:
- Combination Reaction
- Decomposition Reaction
- Oxidation and reduction reaction
- Combination Reaction
The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a single product are known as combination reactions.Example: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O - Decomposition Reaction Decomposition reactions are those reactions in which single compound breaks or splits into two or more simpler substances.
For example: 2H2O→2H2+O2 - Oxidation and reduction reaction:
Example:
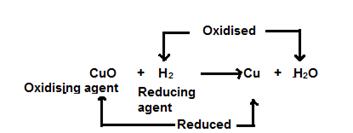
In this reaction, hydrogen acts as a reducing agent and reduces copper oxide to copper. This is a reduction reaction.
Reduction: Cu+2+ 2e-→ Cu
Simultaneously, copper oxide acts as an oxidizing agentand oxidises hydrogen to water. This is an oxidation reaction.
Oxidation: 2H - 2e-→2H+
Solution 2 (e)
Reaction between NaOH and water: NaOH + H2O → Na+ + OH-
Reaction between CaO and water : CaO + H2O→ Ca(OH)2+ heat
Solution 3
- Endothermic reaction:
Endothermic reactions are those which require energy that isthe reactants require energy externally to get converted into products. Example: electrolysis of water to form hydrogen and oxygen is endothermic. - Combination reaction:
The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a single product are known as combination reactions.
Example:
When magnesium ribbon is burnt in air, magnesium oxide is formed. 2Mg + O2 ⟶ 2MgO - Balanced chemical equation:
When the total number of atoms on the reactant side and the product side is equal, the equation is called a balanced equation.
Need for balancing a chemical equation
A chemical equation needs to be balanced because a chemical reaction is just a rearrangement of atoms.
Atoms themselves are neither created nor destroyed during the course of a chemical reaction.
The chemical equation needs to be balanced to follow the law of conservation of mass. - Displacement reaction:
Displacement Reaction: One element takes the place of another element in a compound.
Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Solution 4 (a)
- When CO2 is passed through lime water for a short duration, it turns lime water milky due to the formation of a white precipitate of calcium carbonate.

Solution 4 (b)
As we know, Rate of reaction is depend on the surface area of the reactants. When HCl is added to pieces of Shahabad tile, the CO2 effervescence is formed slowly. However, when HCl is added to Shahabad powder, the CO2 effervescence is formed at a faster rate. Hence, it takes time for pieces of Shahabad tile to disappear in HCl, but its powder disappears rapidly.
Solution 4 (c)
- Dilution of concentrated acid is an exothermic process. If water is added to a concentrated acid, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and cause burns. When the acid is added to water slowly with constant stirring, the mixture will not splash out.
Solution 4 (d)
- When edible oils or fats are left for a long period without use, they react with atmospheric oxygen and get oxidised. As a result, the substances become rancid, i.e. unfit for use. Rancidity can be prevented by storing food in airtight containers retards oxidation.
Solution 5
- Fe is oxidised to Fe2+ in the anode region.
Fe (s) ⟶ Fe2+(aq) + 2 e- - O2 is reduced to form water in the cathode region.
O2 (g) + 4H+(aq) + 4 e- ⟶ 2H2O (l)
When Fe2+ ions migrate from the anode region they react with water and further get oxidised to form Fe3+ ions.
A reddish coloured hydrated oxide is formed from Fe3+ ions. It is called rust. It collects on the surface. - 2Fe3+(aq) + 4H2O (l)⟶ Fe2O3 H2O (s) + 6H+(aq)
Solution 6
- Fe + S → FeS
In the above reaction, Fe is converted to FeS. i.e, iron need to lose electrons to form FeS and as we know loss of electron from a substance is called oxidation, therefore iron undergoes oxidation. - 2Ag2O → 4 Ag + O2 ↑
In the above reaction, silver oxide is converted to silver. Removal of oxygen from substance is called reduction, so silver oxide undergoes reduction as oxygen is removed from silver oxide. - 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
In the above reaction, magnesium is converted to magnesium oxide. Oxygen is being added to magnesium, addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation, so magnesium undergoes oxidation. - NiO + H2 → Ni + H2O In the above reaction, Nickel oxide is converted to Nickel. That is, oxygen is being removed from Nickel oxide. Removal of oxygen from substance is called reduction, so Nickel oxide undergoes reduction. In a reaction, hydrogen is changing to H2O. That is, oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Addition of oxygen to a substance is called oxidation, so hydrogen undergoes oxidation.
Solution 7
- H2S2O7(l) + H2O(l) → 2H2SO4(l)
- SO2(g) + 2H2S(aq) → 3S(s) + 2H2O(l)
- 2Ag(s) + 2HCl(aq) →2AgCl + H2
- 2NaOH (aq) + H2SO4(aq) →Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Solution 8
- HCl + NaOH →NaCl + H2O + heat
it is neutrilisation reaction and neutrilisation reactions are exothermic, - 2KClO3(s) →2KCl(s) + 3O2
Energy is require to break the bonds of KClO3, it is endothermic reaction. - CaO + H2O →Ca(OH)2 + heat
This is an exothermic chemical reaction and gives off heat. - CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2
This is an endothermic reaction. Limestone decomposed to calcium oxide (quicklime) and carbon dioxide required heat.

