Class 11-science NCERT Solutions Biology Chapter 16 - Excretory Products And Their Elimination
Excretory Products And Their Elimination Exercise 215
Solution 1
The amount of the filtrate formed by the kidneys per minute is called glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Solution 2
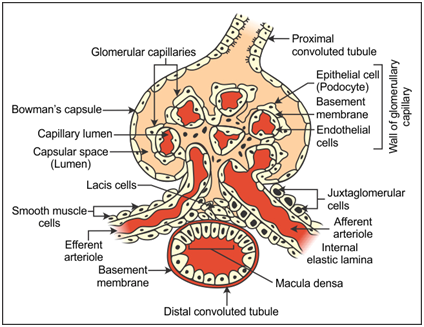
- DCT comes in close contact with the afferent arteriole of the glomerulus of the same nephron.
- In this region of contact, the cells of DCT are modified to form macula densa and the cells of the afferent arteriole are modified to form juxtaglomerular cells.
- Macula densa monitors the level of sodium chloride in urine and influences the juxtaglomerular cells.
- Macula densa and juxtaglomerular cells are collectively called juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA).
- When there is a decrease in the GFR, JGA activates and secretes renin.
- Renin converts angiotensinogen (protein) into angiotensin (peptide).
- Angiotensin constricts efferent arteriole which increases the glomerular blood pressure which in turn brings the GFR back to normal.
Solution 3
(a) Micturition is carried out by a reflex.
True
(b) ADH helps in water elimination, making the urine hypotonic.
False. ADH helps in water reabsorption which makes the urine hypotonic.
(c) Protein-free fluid is filtered from blood plasma into the Bowman's capsule.
True
(d) Henle's loop plays an important role in concentrating the urine.
True
(e) Glucose is actively reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule.
True
Solution 4
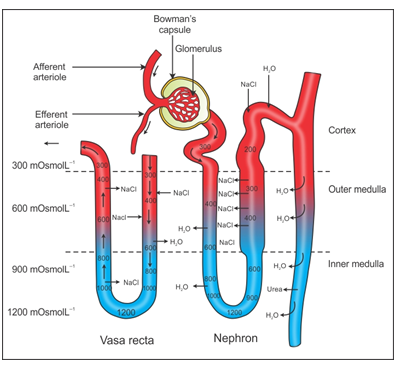
- In the two limbs of the loop of Henle, urine flows in the opposite direction which forms the counter current.
- Similarly, the flow of blood in the two limbs of the vasa recta is also in the opposite direction forming a counter current.
- This system of a liquid flowing in the two limbs in two opposite directions is termed counter current mechanism.
- Counter current mechanism helps in concentrating the urine and maintaining the high solute concentration in the kidney medulla.
- The osmolarity in the medulla is higher than in the cortex.
- The loop of Henle dips from the cortex to the medulla of the kidney. Here, it is surrounded by the medullary interstitial fluid.
- The mechanism takes place in the following way:
- When the filtrate passes from the ascending limb of the loop of Henle, Na+ ions leave the filtrate and enter the surrounding interstitial fluid.
- This increases the osmolarity of the interstitial fluid (makes the fluid hypertonic).
- This draws out more water from the filtrate present in the descending limb of the loop of Henle to the interstitial fluid.
- Water which enters the interstitial fluid is absorbed into the vasa recta.
- This time the descending limb is permeable to Na+ ions. The ions passively diffuse into the descending limb (i.e. into the filtrate).
- This causes balance in the osmolarity between the filtrate in the descending limb and the interstitial fluid.
- The thick segment of the ascending limb during this time continues to pump Na+ ions into the interstitial fluid; hence, the osmolarity of the interstitial fluid is higher than the filtrate present in the ascending limb.
- The Na+ ions keep on accumulating in the interstitial fluid and the water is absorbed by the descending limb of the vasa recta.
- Because of this, the filtrate becomes more concentrated.
- When the above process takes place, a small amount of urine is absorbed by the thin segment of the ascending limb of the loop of Henle.
- Urea is transported back into the interstitial fluid by the collecting tubule.
- The water and the Na+ ions present in the interstitial fluid are absorbed by the limbs of the vasa recta to maintain the osmolarity of the interstitial fluid.
Solution 5
Liver:
- The liver is the main site of elimination of cholesterol, inactivated products of steroid hormones, vitamins and drugs.
- The haemoglobin of dead erythrocytes is also broken down into bile pigments bilirubin and biliverdin which are considered waste.
- The substances are carried by bile to the intestine and are eliminated with the waste.
Lungs:
- Carbon dioxide is expired by the lungs.
- The lungs remove approximately 200 ml CO2 per minute.
- Water is also removed in the form of water vapour.
- Water loss increases in cold conditions and decreases in hot, humid climate.
- Some volatile materials are also expelled during expiration.
Skin:
- Skin is primarily concerned with thermoregulation (cooling of the body).
- It excretes sweat which contains nitrogenous waste.
- Sweat is excreted only when required, i.e. for cooling the body.
- Sweat is produced by the sweat glands and it contains NaCl, urea and lactic acid.
- The sebaceous glands eliminate substances such as sterols, hydrocarbons and waxes through the sebum.
- Sebum provides a protective oily covering for the skin.
Solution 6
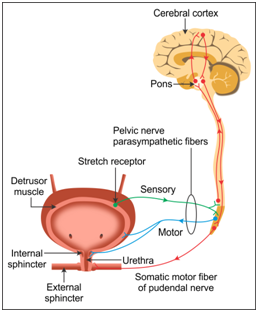
- The process of release of urine is called micturition.
- The neural mechanism causing micturition is called the micturition reflex.
- Urine formed is temporarily stored in the urinary bladder.
- When the bladder is filled with urine, the stretching of the urinary bladder initiates the signal.
- In response to the stretching of the urinary bladder, the receptors present in the walls of the bladder send signals to the central nervous system.
- The central nervous system passes on motor messages which initiate the contraction of the smooth muscles of the urinary bladder and the relaxation of the urethral sphincters, causing the release of urine.
Solution 7
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(a) Ammonotelism |
(iii) Bony fish |
|
(b) Bowman's capsule |
(v) Renal tubule |
|
(c) Micturition |
(iv) Urinary bladder |
|
(d) Uricotelism |
(i) Birds |
|
(e) ADH |
(ii) Water reabsorption |
Excretory Products And Their Elimination Exercise 216
Solution 8
The process of regulating the osmotic concentration inside the body cells by controlling the amount of salts and water is called osmoregulation.
Solution 9
- Ammonia is highly toxic nitrogenous waste. Large amount of water is required to make ammonia less toxic inside the body of an organism.
- Terrestrial animals do not have sufficient amount of water in their bodies for the dilution of ammonia.
- If ammonia is accumulated in the body of terrestrial animals, then it may turn highly poisonous for them.
- In terrestrial animals, ammonia is always converted to less toxic urea and uric acid.
- Hence, terrestrial animals are generally either ureotelic or uricotelic.
Solution 10
- The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) helps in maintaining the glomerular filtration rate.
- It works through the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS).
- When there is a decrease in GFR, JGA activates and secretes renin.
- Renin converts angiotensinogen (protein) into angiotensin (peptide).
- Angiotensin is a hormone which raises the blood flow and GFR in the following three ways:
- It constricts efferent arterioles to increase the glomerular pressure.
- It stimulates the walls of PCT to reabsorb more NaCl and water.
- It stimulates the adrenal gland to produce aldosterone, which promotes reabsorption of NaCl and water in DCT.
- This results in an increase in blood pressure and blood volume and a decrease in urine volume and hypertonic urine.
Solution 11
(a) A chordate animal having flame cells as excretory structures: Amphioxus
(b) Cortical portions projecting between the medullary pyramids in the human kidney: Columns of Bertini
(c) A loop of capillary running parallel to the Henle's loop: Vasa recta
Solution 12
- The ascending limb of Henle's loop is impermeable to water, whereas the descending limb is permeable to it.
- Reabsorption of water from the distal parts of the tubules is facilitated by the hormone vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone).
- Dialysis fluid contains all the constituents as in plasma except nitrogenous waste.
- A healthy adult human excretes (on an average) 25–30 gm of urea/day.