Class 11-science NCERT Solutions Biology Chapter 10 - Cell Cycle and Cell Division
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Exercise 129
Solution 1
The average cell cycle span of a mammalian cell is 24 hours.
Solution 2
The division of cytoplasm along with cell organelles into daughter cells is called cytokinesis, while the segregation of duplicated chromosomes into daughter nuclei is called karyokinesis.
Solution 3
The interphase is divided into three further phases:
i. G1 phase (Gap 1): The G1 phase corresponds to the interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication. During the G1 phase, the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA. The cells which divide frequently have a shorter G1 phase, whereas the cells which divide infrequently have a longer G1 phase.
ii. S phase (Synthesis): The S or synthesis phase marks the period during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place. During this time, the amount of DNA per cell doubles. If the initial amount of DNA is denoted as 2C, then it increases to 4C. However, there is no increase in the chromosome number. If the cell had diploid or 2n number of chromosomes at G1, even after the S phase, the number of chromosomes remains the same, i.e. 2n. The S phase in most eukaryotic cells lasts for 6 to 8 hours. When the S phase begins, the cell must undergo mitosis.
iii. G2 phase (Gap 2): In animal cells, during the S phase, DNA replication begins in the nucleus, and the centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm. During the G2 phase, proteins are synthesised in preparation for mitosis while cell growth continues. The G2 phase in most cells lasts for 2 to 5 hours. Some proteins formed in G2 phase cause condensation of chromosomes to initiate mitosis.
Solution 4
The quiescent phase is the stage when the cell becomes inactive, stops dividing and becomes specialised by differentiation.
Cell Cycle and Cell Division Exercise 130
Solution 5
Because the number of chromosomes remains the same in parent and daughter cells, mitosis is also called as equational division.
Solution 6
i. Metaphase
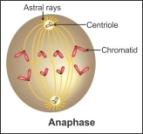
ii. Anaphase
iii. Zygotene stage of prophase I during meiosis.
iv. Pachytene stage of prophase I of meiosis.
Solution 7
a) Synapsis: During the zygotene of prophase I of meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair together. This pairing is called synapsis.
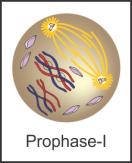
b) Bivalent: The complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes during zygotene of prophase I of meiosis is called a bivalent.
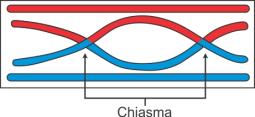
c) Chiasmata: During diplotene, the paired chromosomes make an X-shaped structure. This is called chiasmata. These are the sites where crossing over between two non-sister chromatids occurs.
Solution 8
Differences between plant cytokinesis and animal cytokinesis
|
Plant Cytokinesis |
Animal Cytokinesis |
|
i. It occurs by cell plate formation. ii. The cell plate appears at the centre and extends outwards. iii. Fusion of vesicles begins cell plate formation. iv. A midbody is not formed. |
i. It occurs by cleavage. ii. Cleavage begins at the periphery and proceeds inwards. iii. Cleavage is started by contraction of a peripheral ring of microfilaments. iv. A midbody of dense material is formed at the middle of the cell. |
Solution 9
During microsporogenesis in flowering plants, the four daughter cells formed are equal in size. On the other hand, during megasporogenesis, the four daughter cells formed are unequal in size. This can be seen in many other organisms also during the formation of male and female gametes. Meiosis usually leads to formation of equal-sized male gametes and unequal-sized daughter cells while forming female gametes.
Solution 10
|
Anaphase of Mitosis |
Anaphase I of Meiosis |
|
During anaphase of mitosis, the centromere splits and the chromatids separate.
|
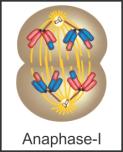
During anaphase I of meiosis, the centromere does not split and the sister chromatids remain associated at their centromeres.
|
Solution 11
Differences between mitosis and meiosis
|
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
|
i. Takes place in somatic cells. |
i. Takes place in gametic cells. |
|
ii. Two daughter cells are formed in the end. |
ii. Four daughter cells are formed in the end. |
|
iii. The number of chromosomes remains the same in daughter cells as compared to those in parent cells. |
iii. The number of chromosomes is halved in daughter cells as compared to those in parent cells. |
|
iv. Chromosomes replicate before each mitotic division. |
iv. Chromosomes do not replicate before the second meiotic division. |
Solution 12
Significance of meiosis:
i. Formation of gametes: Meiosis produces gametes for sexual reproduction.
ii. Crossing over: It introduces a new combination of traits or variations.
iii. Maintenance of chromosome number: Meiosis reduces the number of chromosomes to half in the gametes so that fertilisation may restore the original diploid number in the zygote.
iv. Mutations: Abnormalities in meiosis may bring about chromosomal mutations, some of which may be advantageous for the organism.
Solution 13
i. Drones of honey bee and lower plants such as Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra etc. are haploids. These produce haploid gametes by mitosis and not by meiosis.
ii. Spermatozoa and ova of higher animals, and microspores and megaspores of higher plants do not undergo cell division.
Solution 14
The 'S' or synthesis phase marks the period during which DNA synthesis or replication takes place. DNA replication is necessary for cell division, and cell division cannot happen without DNA replication.
Solution 15
Yes. DNA replication can take place without cell division.
DNA replication takes place in order to prepare for cell division. Cell division is the next logical step after DNA replication.
Solution 16
i. In the G1 phase, the number of chromosomes (N) per cell remains the same, and each chromosome is formed of one chromatid. In the S phase, each chromosome is formed of two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. The same condition continues in the G2 phase, while in the M phase, the sister chromatids separate and move to different cells, but the number of chromosomes remains the same in mitosis.
ii. In the G1 phase, the amount of DNA content (C) per cell remains the same, but in the S phase, it is doubled due to DNA replication. It remains double in the G2 phase but is halved in the M phase of the cell cycle.