Class 10 LAKHMIR SINGH AND MANJIT KAUR Solutions Biology Chapter 2 - Control and Coordination
Control and Coordination Exercise 92
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9
(b) Gravity.
(c) Chemical.
(d) Water.
(e) Touch.
Solution 10
(b) Geotropism.
(c) Chemotropism.
(d) Hydrotropism.
(e) Thigmotropism.
Control and Coordination Exercise 93
Solution 11
Solution 12
(b) Stem.
Solution 13
Solution 14
(b) Stem.
Solution 15
(b) Light.
Solution 16
(b) Geotropism.
(c) Light.
(d) Gravity.
(e) Touch.
(f) Earth, gravity.
(g) Geotropism.
(h) Auxin.
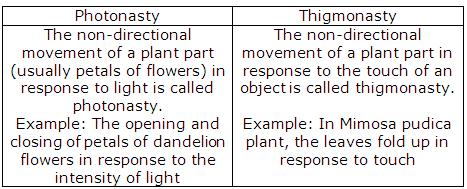
(i) Photonasty.
Solution 17
(b) Folding up of leaves of a sensitive plant on touching.
Solution 18
The four types of plant hormones are:
(i) Auxins - It promotes cell enlargement and cell differentiation in plants.
(ii) Gibberellines - It helps in breaking the dormancy in seeds and buds.
(iii) Cytokinins - It promotes cell division in plants.
(iv) Abscisic acid - It promotes the dormancy in seeds and buds.
Solution 19
(b) Stem bends towards the light; positive phototropism.
Solution 20
(b) Root bends away from light; negative phototropism
Solution 21
(b) (i) A dandelion flower opens up in the morning in bright light. This phenomenon is known is positive photonasty.
(ii) At night, the dandelion flower closes and this phenomenon is known as negative photonasty.
Solution 22
(b) (i) During the daytime the petals of moon flower close when there is bright light.
(ii) At night, when it is dark the petals of moon flower opens up. This phenomenon is known as photonasty.
Solution 23
Solution 24
Example even if a seed is planted upside down, its root will grow downwards into earth because it is positively geotropic.
Solution 25
Solution 26
| Tropic movements | Nastic movements |
| 1. These movements are always in the direction of the stimulus. 2. These movements are slow. 3. These movements are exhibited by all parts of a plant. For example, movement of shoot towards the light and not towards gravity. |
1. These movements are neither away nor towards the stimulus. 2. These movements are fast. 3. These movements are exhibited by the flat organs (like leaves and petals of flowers) of a plant. For example, the bending and drooping of leaves in 'Touch-me-not' plant. |
Solution 27
(a) The movement of a plant part in response to an external stimulus in which the direction of response is not determined by the direction of stimulus is called nastic movement.
Example: The folding up of the leaves of a sensitive plant on touching is an example of thigmonasty.
(b)
Control and Coordination Exercise 94
Solution 28
(b) Geotropism.
Solution 29
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Auxin
(d) Abscisic Acid
Solution 30
(b) Root
(c) Stem
(d) Root
Solution 31
Solution 32
Solution 33
Example - The bending of plant stem towards light is an example of positive phototropism.
(b) Different types of tropisms are:
(i) Phototropism - The movement of a plant part in response to light is called phototropism. Its stimulus is light.
(ii) Geotropism - The movement of a plant part in response to gravity is called geotropism. Its stimulus is gravity.
(iii) Chemotropism - The movement of a plant part in response to a chemical stimulus is called chemotropism. Its stimulus is chemical.
(iv) Hydrotropism - The movement of a plant part in response to a water stimulus is called hydrotropism. Its stimulus is water.
(v) Thigmotropism - The movement of a plant part in response to a touch stimulus is called thigmotropism. Its stimulus is touch.
(c)
| Tropisms | Nasties |
| 1. These movements are always in the direction of the stimulus. 2. These movements are slow. 3. These movements are exhibited by all parts of a plant. For example, movement of shoot towards the light and not towards |
1. These movements are neither away nor towards the stimulus. 2. These movements are fast. 3. These movements are exhibited by the flat organs (like leaves and petals of flowers) of a plant. For example, the bending and dropping of leaves in 'Touch-me-not' plant. |
Solution 35
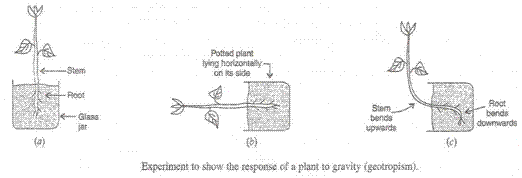
Example - Roots grow towards gravity.
(b) If the plant part moves towards the direction of gravity, it is called positive geotropism.
Example - Roots.
If the plant part moves against the direction of the gravity it is negative geotropism.
Example - Stem
(c) Tendrils.
Solution 36
(b) (i) Light - Phototropism.
(ii) Gravity - Geotropism.
(iii) Chemical - Chemotropism.
(iv) Water - Hydrotropism.
(v) Touch - Thigmotropism.
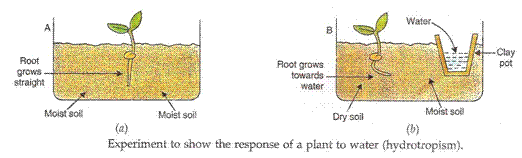
(c) The movement of a plant part in response to water is called hydrotropism.
Example: The roots of a plant always go towards water, this is positive hydrotropism.
Solution 37
(a) The growth of a plant part in response to a stimulus is called positive tropism and if the growth of a plant part is away from the stimulus, then it is called negative tropism.
Example: The roots of a plant go towards earth in response to gravity is an example of positive geotropism whereas stem grows away from earth against gravity is an example of negative geotropism.
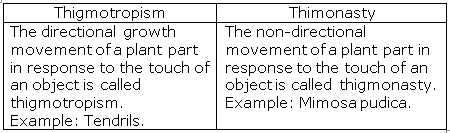
(b) The directional growth movement of a plant part in response to the touch of an object is called thigmotropism.
Example: Tendrils grow towards any support which they happen to touch and wind around it.
(c)
Tendrils grow towards a stimulus hence it is a directional movement which shows that it is a case of thigmotropism whereas, the folding of leaves in mimosa plant does not depend on the direction of stimulus (touch) which shows that it is an example of thigmonasty.
Exercise
Solution
Solution
Solution
Control and Coordination Exercise 115
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
(b) Axon.
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13
(b) Progesterone and oestrogen.
Solution 14
(b) Thermoreceptors.
(c) Phonoreceptors.
(d) Olfactory receptors.
(e) Gustatory receptors.
Solution 15
Solution 16
Solution 17
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
(b) Salivary glands.
(c) Pancreas.
Solution 21
Solution 22
Solution 23
Solution 24
Solution 25
Solution 26
(b) Hormone.
Solution 27
Solution 28
(ii) Sneezing.
(iii) Coughing.
Solution 29
Solution 30
Solution 31
(b) Nervous; sensory; motor.
(c) Sensory.
(d) Motor.
Control and Coordination Exercise 116
Solution 32
(b) A receptor is a cell (or a group of cells) in a sense organ which is sensitive to a particular type of stimulus (or a particular type of change in the environment). Example: Photoreceptors and Phonoreceptors.
An effecter is the part of the body which can respond to the stimulus according to the instructions sent from the nervous system (spinal cord and brain).
Example: Muscles and glands.
Solution 33
(b) The medulla controls various involuntary actions such as heart beat, breathing, blood pressure and peristaltic movements of the elementary canal. It is also the controlling centre for reflexes such a swallowing, coughing, sneezing, secretion of saliva and vomiting.
Solution 34
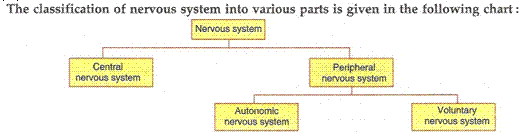
(a) The three types of nerves which make up the peripheral nervous system are: spinal nerves, cranial nerves and visceral nerves.
(b)
(c) When the agarbatti burns, it produces vapours having a characteristic pleasant smell which is detected by the olfactory receptors present inside our nose. The action of smell of agarbatti or receptors sets off chemical reactions which generate electrical impulses. The sensory neurons carry these electric al impulses to the sensory area of fore brain called cerebrum. This makes us detect the smell of burning agarbatti.
Solution 35
(b) Receptors are the special cells present in our sense organs which detect all the information from our environment and feed it to the nervous system.
An effector responds to electrical impulses sent from the nervous system through motor nerves.
Solution 36
(b) The function of testosterone hormone is to control the development of male sex organs and male features such as deeper voice, moustache, body hairs etc. The function of oestrogen is to control the development of female sex organs and female features such as feminine voice, soft skin and mammary glands.
Solution 37
(i) Pons: It takes part in regulating respiration.
(ii) Cerebellum: It helps in maintaining posture and balance of the body. It enables us to make precise and accurate movements.
(iii) Medulla: The medulla controls various involuntary actions such as heart beat, breathing, blood pressure and peristaltic movements of the elementary canal. It is also the controlling centre for reflexes such a swallowing, coughing, sneezing, secretion of saliva and vomiting.
(b) Function of cerebrum: It is the main thinking part of the brain. It is the site of our faculties such as learning, reasoning, intelligence, personality and memory. All our thoughts, sensation, actions and movements are controlled by cerebrum.
Solution 38
(b) Cranium is a bony box in the skull in which the brain is present. Its function is to protect the brain.
Solution 39
(b) Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxine hormone which regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins so as to produce the best balance for the growth. Iodised salt is advisable as it contains appropriate amounts of iodine compounds needed by the thyroid gland to make sufficient thyroxine hormone for the body and hence goitre disease can be prevented.
Solution 40
Solution 41
| Nervous System | Endocrine System |
| It is a system to coordinate the activities of bodies. It helps all other system of our body to work together. It receives information from the surroundings, processes it, interprets it and then responds accordingly. | It is a group of endocrine glands which produces various hormones that helps in coordinating the activities of our body. The hormones produced by the endocrine glands act as messengers between the nervous system and the organs of our body. |
Solution 43
(i) Pineal gland
(ii) Hypothalamus
(iii) Pituitary
(iv) Thyroid
(v) Parathyroid
(vi) Thymus
(vii) Pancreas
(viii) Adrenal glands
(ix) Testes (in males)
(x) Ovaries (in females).
Pancreas, testes and ovaries function as exocrine glands.
Solution 44
(ii) c
(iii) e
(iv) a
(v) b
Solution 45
Solution 46
Solution 47
Solution 48
| Receptor | Effector |
|
A receptor is a cell (or a group of cells) in a sense organ which is sensitive to a particular type of stimulus (or a particular type of change in the environment). Example: Photoreceptors and Phonoreceptors. |
An effector is the part of the body which can respond to the stimulus according to the instructions sent from the nervous system (spinal cord and brain). Example: Muscles and glands. |
| Cerebrum | Cerebellum |
| (i) It is a part of forebrain. (ii) It is the main thinking part of the brain. All our thoughts, sensation, actions and movements are controlled by cerebrum. |
(i) It is a part of hindbrain. (ii) It helps in maintaining posture and balance of the body. It enables us to make precise and accurate movements. |
Solution 49
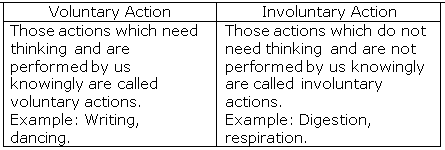
Digestion is an involuntary action as it does not involve the thinking process and is performed unknowingly by our digestive system.
Solution 50
(ii) (a) Cerebrum (b) Spinal cord.
Solution 51
(b) Insulin.
(c) Testosterone.
(d) Oestrogen.
Control and Coordination Exercise 117
Solution 55
(ii) It helps all other systems of our body to work together.
(iii) It receives information from the surroundings, processes it, interprets it and then responds accordingly.
(b) The main organs of the nervous system are; brain, spinal cord and nerves.
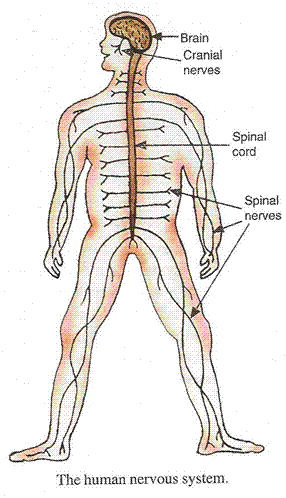
(c) When the sense organ in our body is affected, it sends the message to the brain in the form of electrical impulses through the sensory neurons. The brain analyses this message and decides the action to be taken. The brain then sends out instructions to the muscles of the concerned body parts through motor nerves and the concerned body part acts accordingly.
Solution 56
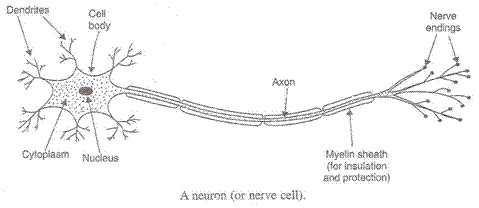
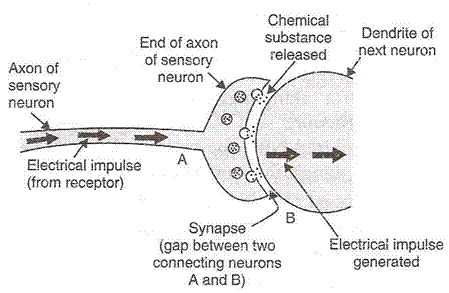
(a) The unit which makes up the nervous system is called a neuron.
(b) A microscopic gap between a pair of adjacent neurons over which nerve impulses pass when going from one neuron to the next is called a synapse. Synapse between two neurons acts as a one way valve which allows electrical impulses to pass in one direction only. This happens as follows: When an electrical impulse coming from the receptor reaches the end of the axon of sensory neuron, then the electrical impulse releases tiny amount of a chemical substance called neuro transmitter substance into the synapse between two adjacent neurons. This substance crosses the synapse and starts a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of the next neuron. In this way, the electrical impulses passes from one neuron to the next across the synapse.
Solution 57
(b) The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. The work of the CNS is to direct incoming messages to the motor neurons that are connected to the part of the body which will respond to a stimulus. It is involved in complicated responses where both (brain and spinal cord) work. It enables a person to give a more appropriate and more intelligent response to various situations.
(c) (i) The brain receives information carrying nerve impulses from all the sensory organs of the body.
(ii) It responds to the impulses brought in by sensory organs by sending its own instructions through motor nerves to the muscles and glands causing them to function accordingly.
(iii) It correlates the various stimuli from different sense organs and produces the most appropriate and intelligent response.
(iv) It coordinates the body activities so that the mechanisms and chemical reactions of the body work together efficiently.
(v) It stores information so that behavior can be modified according to the past experience.
Solution 58
(ii) Thyroid - Thyroxine.
(iii) Pancreas - Insulin.
(iv) Adrenal - Adrenaline.
(v) Testes - Testosterone.
(b) The endocrine glands do not have ducts to secrete their hormones. They release hormones directly into the blood of a person and reach the concerned body part through the blood and act on it.
(c) Hypothalamus.
(d) The adrenaline hormone prepares our body to function at maximum efficiency during emergency situations like danger, anger etc. This adrenaline hormone increases our heartbeat, breathing rate, blood flow into muscles and causes liver to put more stored glucose into our blood. All these actions produce a lot of energy in our body and help us to cope up the emergency situations. Thus, when adrenaline is secreted in large amounts it prepares our body for action.
(e) Goitre - The neck of the person appears to be swollen due to the enlargement of thyroid gland located in the neck.
Solution 52
(b) Receptors (Olfactory).
(c) Effector (Salivary glands).
Solution 53
(a) Te structural and functional unit of nervous system is neuron.
(b)
(c) Autonomic nervous system means self governing nervous system. Its function is to control and regulate the functions of the internal organs of our body involuntarily.
(d) The voluntary nervous system is a system which helps us to take voluntary actions which are under the conscious control of the brain.
Example: If a student is getting late for school and sees his watch. He starts walking fast. In this process, the eyes see the time and send the information to the brain through the sensory nerves. The brain analyses the information and sends the instructions to walk faster to the muscle of our legs through the motor nerves. The muscles of the legs act accordingly and make the student walk faster.
Solution 54
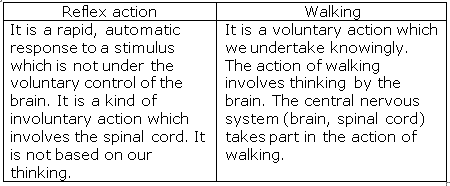
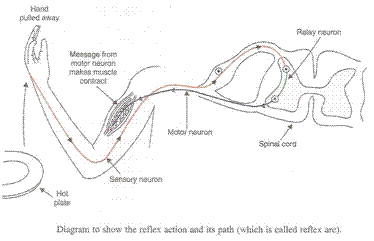
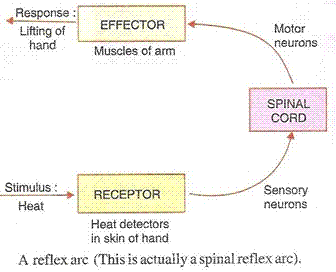
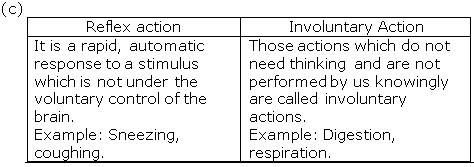
(a) The rapid, automatic response to a stimulus which is not under the voluntary action of the brain is called reflex action.
Example: Moving our hand away on touching a hot plate.
(b) The pathway taken by the nerve impulses in our reflex action is called the reflex arc.