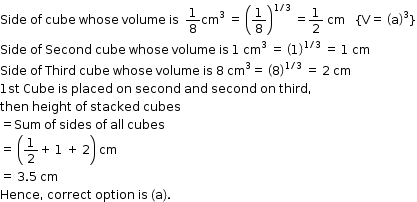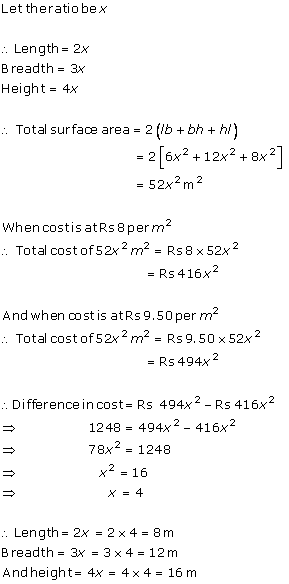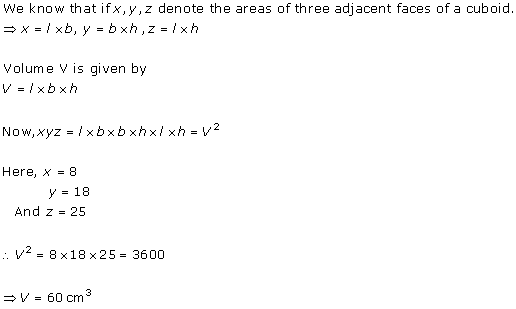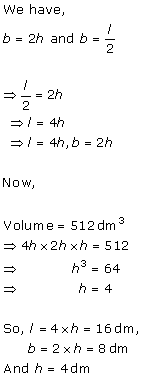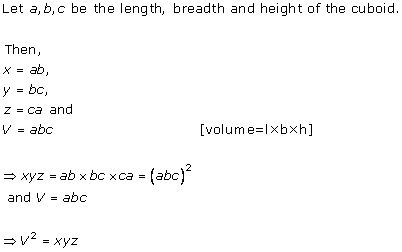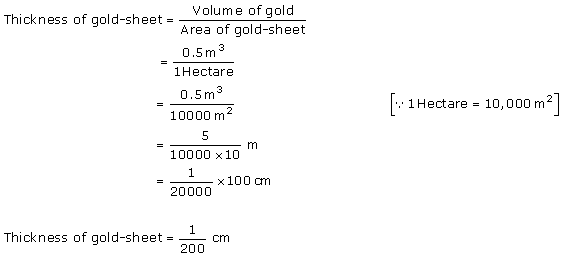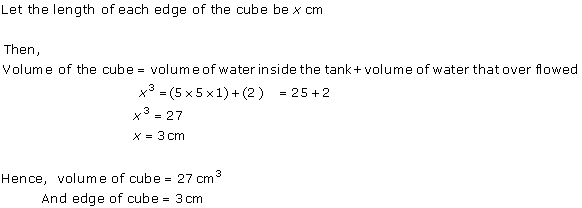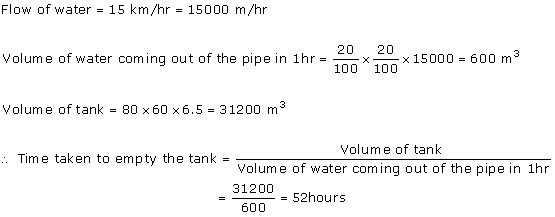Class 9 RD SHARMA Solutions Maths Chapter 18 - Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube
Ex. 18.1
Ex. 18.2
18.35
18.36
18.37
Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube Exercise Ex. 18.1
Solution 1

Solution 2
Solution 3
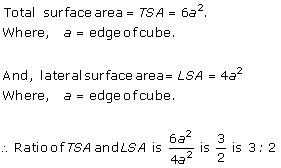
Solution 4

Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9

Solution 10
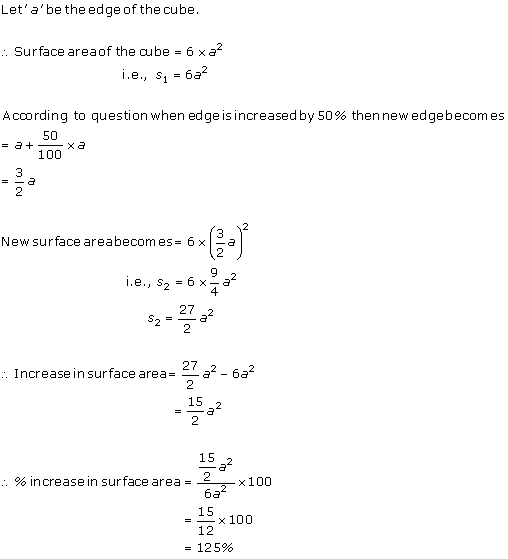
Solution 11
Solution 12
Length of shelter = 4 m
Breadth of shelter = 3 m
Height of shelter = 2.5 m
The tarpaulin will be required for top and four sides of the shelter.
Area of Tarpaulin required = 2(lh + bh) + lb
= [2(4 2.5 + 3
2.5 + 3  2.5) + 4
2.5) + 4 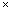 3] m2
3] m2
= [2(10 + 7.5) + 12] m2
= 47 m2
Breadth of shelter = 3 m
Height of shelter = 2.5 m
The tarpaulin will be required for top and four sides of the shelter.
Area of Tarpaulin required = 2(lh + bh) + lb
= [2(4
= [2(10 + 7.5) + 12] m2
= 47 m2
Solution 13
Solution 14
Solution 15
Total surface area of one brick = 2(lb + bh + lh)
= [2(22.5 × 10 + 10 × 7.5 + 22.5 × 7.5)]cm2
= 2(225 + 75 + 168.75)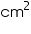
= (2 × 468.75) cm2
= 937.5 cm2
Let n number of bricks be painted by the container.
Area of n bricks = 937.5n cm2
Area that can be painted by the container = 9.375 m2 = 93750 cm2
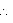 93750 = 937.5n
93750 = 937.5n
n = 100
Thus, 100 bricks can be painted out by the container.
= [2(22.5 × 10 + 10 × 7.5 + 22.5 × 7.5)]cm2
= 2(225 + 75 + 168.75)
= (2 × 468.75) cm2
= 937.5 cm2
Let n number of bricks be painted by the container.
Area of n bricks = 937.5n cm2
Area that can be painted by the container = 9.375 m2 = 93750 cm2
n = 100
Thus, 100 bricks can be painted out by the container.
Solution 16
Solution 17

Solution 18
Solution 19
External length (l) of bookshelf = 85 cm
External breadth (b) of bookshelf = 25 cm
External height (h) of bookshelf = 110 cm
External surface area of shelf while leaving front face of shelf
= lh + 2 (lb + bh)
= [85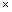 110 + 2 (85
110 + 2 (85 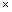 25 + 25
25 + 25 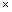 110)] cm2
110)] cm2
= 19100 cm2
Area of front face = [85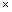 110 - 75
110 - 75 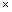 100 + 2 (75
100 + 2 (75 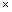 5)] cm2
5)] cm2
= 1850 + 750 cm2
= 2600 cm2
Area to be polished = (19100 + 2600) cm2 = 21700 cm2
Cost of polishing 1 cm2 area = Rs 0.20
Cost of polishing 21700 cm2 area = Rs (21700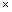 0.20) = Rs 4340
0.20) = Rs 4340
Now, length (l), breadth (b) height (h) of each row of bookshelf is 75 cm, 20 cm, and
External breadth (b) of bookshelf = 25 cm
External height (h) of bookshelf = 110 cm
External surface area of shelf while leaving front face of shelf
= lh + 2 (lb + bh)
= [85
= 19100 cm2
Area of front face = [85
= 1850 + 750 cm2
= 2600 cm2
Area to be polished = (19100 + 2600) cm2 = 21700 cm2
Cost of polishing 1 cm2 area = Rs 0.20
Cost of polishing 21700 cm2 area = Rs (21700
Now, length (l), breadth (b) height (h) of each row of bookshelf is 75 cm, 20 cm, and
30cm 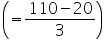 respectively.
respectively.
Area to be painted in 1 row = 2 (l + h) b + lh
= [2 (75 + 30)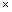 20 + 75
20 + 75 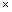 30] cm2
30] cm2
= (4200 + 2250) cm2
= 6450 cm2
Area to be painted in 3 rows = (3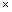 6450) cm2 = 19350 cm2
6450) cm2 = 19350 cm2
Cost of painting 1 cm2 area = Rs 0.10
Cost of painting 19350 cm2 area = Rs (19350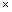 0.10) = Rs 1935
0.10) = Rs 1935
Total expense required for polishing and painting the surface of the bookshelf
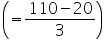 respectively.
respectively.Area to be painted in 1 row = 2 (l + h) b + lh
= [2 (75 + 30)
= (4200 + 2250) cm2
= 6450 cm2
Area to be painted in 3 rows = (3
Cost of painting 1 cm2 area = Rs 0.10
Cost of painting 19350 cm2 area = Rs (19350
Total expense required for polishing and painting the surface of the bookshelf
= Rs(4340 + 1935) = Rs 6275
Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube Exercise Ex. 18.2
Solution 1
Volume of tank = l 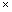 b
b 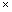 h = (6
h = (6 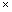 5
5 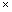 4.5) m3 = 135 m3
4.5) m3 = 135 m3
It is given that:
1 m3 = 1000 litres
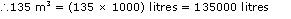
Thus, the tank can hold 135000 litres of water.
1 m3 = 1000 litres
Thus, the tank can hold 135000 litres of water.
Solution 2
Let height of cuboidal vessel be h.
Length (l) of vessel = 10 m
Width (b) of vessel = 8 m
Volume of vessel = 380 m3
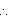 l
l 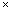 b
b 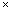 h = 380
h = 380
Length (l) of vessel = 10 m
Width (b) of vessel = 8 m
Volume of vessel = 380 m3
10
h = 4.75
Thus, the height of the vessel should be 4.75 m.
Solution 3
Length (l) of the cuboidal pit = 8 m
Width (b) of the cuboidal pit = 6 m
Depth (h) of the cuboidal pit = 3 m
Volume of the cuboidal pit = l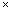 b
b 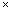 h = (8
h = (8 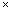 6
6 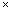 3)
3) 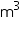 = 144 m3
= 144 m3
Cost of digging 1 m3 = Rs 30
Cost of digging 144 m3 = Rs (144 30) = Rs 4320
30) = Rs 4320
Width (b) of the cuboidal pit = 6 m
Depth (h) of the cuboidal pit = 3 m
Volume of the cuboidal pit = l
Cost of digging 1 m3 = Rs 30
Cost of digging 144 m3 = Rs (144
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13
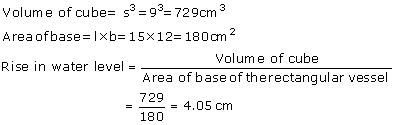
Solution 14
Solution 15
Solution 16
Length (l) of the cuboidal tank = 20 m
Breadth (b) of the cuboidal tank = 15 m
Height (h) of the cuboidal tank = 6 m
Capacity of tank = l × b × h = (20 × 15 × 6) m3 = 1800 m3 = 1800000 litres
Water consumed by people of village in 1 day = 4000 × 150 litres = 600000 litres
Let water of this tank lasts for n days.
Water consumed by all people of village in n days = capacity of tank
n × 600000 = 1800000
n = 3
Thus, the water of tank will last for 3 days.
Breadth (b) of the cuboidal tank = 15 m
Height (h) of the cuboidal tank = 6 m
Capacity of tank = l × b × h = (20 × 15 × 6) m3 = 1800 m3 = 1800000 litres
Water consumed by people of village in 1 day = 4000 × 150 litres = 600000 litres
Let water of this tank lasts for n days.
Water consumed by all people of village in n days = capacity of tank
n × 600000 = 1800000
n = 3
Thus, the water of tank will last for 3 days.
Solution 17
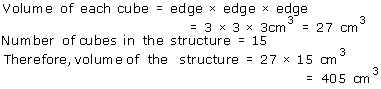
Solution 18
Length 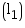 of the godown = 40 m
of the godown = 40 m
Breadth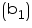 of the godown = 25 m
of the godown = 25 m
Height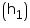 of the godown = 10 m
of the godown = 10 m
Volume of godown = l1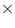 b1
b1 h1 = (40
h1 = (40  25
25  10)
10) 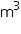 = 10000
= 10000 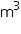
Length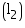 of a wooden crate = 1.5 m
of a wooden crate = 1.5 m
Breadth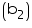 of a wooden crate = 1.25 m
of a wooden crate = 1.25 m
Height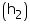 of a wooden crate = 0.5 m
of a wooden crate = 0.5 m
Volume of a wooden crate =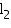
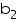
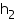 = (1.5
= (1.5 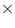 1.25
1.25 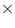 0.5) m3 = 0.9375
0.5) m3 = 0.9375 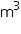
Let n wooden crates be stored in the godown.
Volume of n wooden crates = volume of godown
0.9375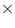 n = 10000
n = 10000
Breadth
Height
Volume of godown = l1
Length
Breadth
Height
Volume of a wooden crate =
Let n wooden crates be stored in the godown.
Volume of n wooden crates = volume of godown
0.9375
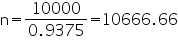
Thus, 10666 wooden crates can be stored in godown.
Solution 19
Solution 20
Solution 21
Solution 22
Rate of water flow = 2 km per hour 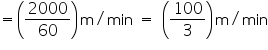
Depth (h) of river = 3 m
Width (b) of river = 40 m
Volume of water flowed in 1 min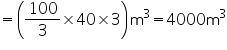
Thus, in 1 minute 4000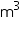 = 4000000 litres of water will fall into the sea.
= 4000000 litres of water will fall into the sea.
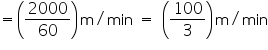
Depth (h) of river = 3 m
Width (b) of river = 40 m
Volume of water flowed in 1 min
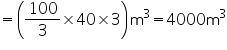
Thus, in 1 minute 4000
Solution 23
Solution 24
Solution 25
Solution 26
Solution 27
Solution 28
Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube Exercise 18.35
Solution 1

Solution 2
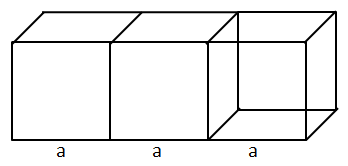

Solution 3
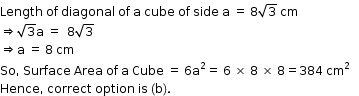
Solution 4
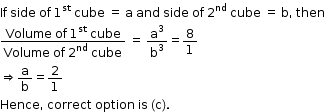
Solution 5
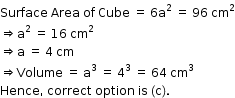
Solution 6
Let,
Length = 3x,
Width = 2x
Height = x
Volume = 48 cm3
L×W×H = 48 cm3
3x × 2x × x = 48 cm3
6x3 = 48 cm3
x3 = 8 cm3
x = 2 cm
Total Surface area
= 2(3x × 2x + 2x × x + 3x × x)
= 2(6x2 + 2x2 + 3x2)
= 2(11x2)
= 22x2
= 22(4)
= 88 cm2
Hence, correct option is (d).
Solution 7
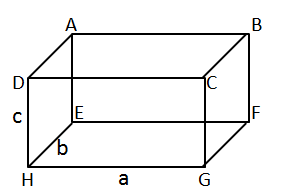

Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube Exercise 18.36
Solution 8
Let edge = a
Volume, V = a3
If a' = 2a, then
V' = (a')3 = (2a)3 = 8a3
V' = 8 V
Hence, correct option is (d).
Solution 9

Solution 10

Solution 11
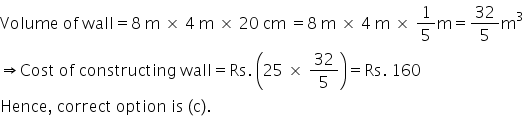
Solution 12
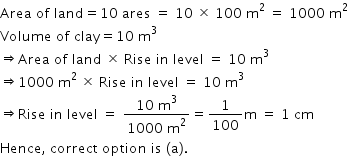
Solution 13
Let the dimensions of Cuboid be a, b, c respectively.
Volume, V = abc = 12 cm3
If a' = 2a, b' = 2b, c' = 2c, then
V' = a'b'c' = 8abc = 8 × 12 = 96 cm3
Hence, correct option is (d).
Solution 14
Let the edge of cube = a
Total no. of edge = 12
Sum of all edges = 12a
12a = 36cm
i.e. a = 3 cm
Volume = a3 = 33 = 27 cm3
Hence, correct option is (b).
Solution 15

Solution 16

Solution 17

Solution 18

Solution 19
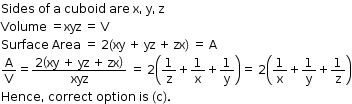
Solution 20

Solution 21
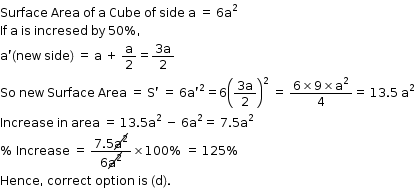
Surface Areas and Volume of a Cuboid and Cube Exercise 18.37
Solution 22