Class 8 MAHARASHTRA STATE TEXTBOOK BUREAU Solutions Science Chapter 8: Pollution
Pollution Exercise Exercise
Solution 1
a. Air pollution (due to smog)
b. Water pollution (due to contaminated food and water)
c. Air pollution (due to pollen)
d. Soil pollution (due to excessive chemicals)
e. Air pollution (due to traffic)
Solution 2
Nilesh is a student of std. VIII and lives in urban area. It takes about an hour to go to the school by bus. He faces heavy traffic of two wheelers, four wheelers, rickshaws, buses while going to school (Air pollution). He is facing the problem of asthma since last few days (Air pollution). Doctors recommended him to stay away from urban area. Since then, his mother sent him to the village of his maternal uncle. Nilesh saw heaps of garbage at many places in village (Air pollution and soil pollution). Foul smell of human and animal wastes was present at many places (Air pollution). Blackish water with foul smell was flowing in a stream (Water pollution). He developed some abdominal disease within few days (Water pollution).
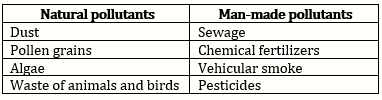
Solution 3
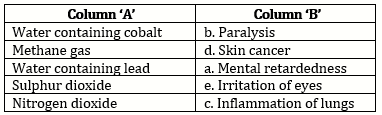
Solution 4
- False. (Even if washing of soiled clothes is done in running water, it will cause water pollution as the dirt will be added to water.)
- True. (Most of the electricity is generated in India by burning coal. More the electricity used by using more appliances, more will be the pollution due to excessive burning of fossil fuels.)
Solution 5.a
Contamination of natural environment which can have a harmful impact on the ecosystems is called pollution.
Solution 5.b
Factors affecting the natural functions of an ecosystem and causing harmful effects on abiotic and biotic factors are called pollutants.
Examples: Carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, smoke, dust.
Solution 5.c
- Oxides of sulphur and nitrogen are released into the atmosphere through burning of coal, timber and fuel oils.
- These oxides mix with rain water and form acids like sulphuric acid, nitric acid and nitrous acid.
- These acids mix with rain drops and snowflakes and come down as rain, called acid rain.
Solution 5.d
Gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitric oxide and nitrous oxide in the atmosphere act as greenhouse gases. Their increased concentration in the atmosphere prevents the escape of heat, which warms the air. This is called greenhouse effect.
Solution 5.e
Pollutants which can be seen easily with the naked eyes are called visible pollutants.
Examples: Sewage, plant waste, animal waste, sand, pesticides, plastic.
Solution 5.f
Pollutants which are completely dissolved in water or mixed in air, and hence, cannot be seen with the naked eyes are called invisible pollutants.
Examples: Gases like carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, bacteria, viruses and fungi.
Solution 6.a
Air pollution:
1. Emissions of harmful gases from vehicles on the road.
2. Lot of construction activities which produce dust.
Water pollution:
1. Plastic waste thrown in water bodies.
2. Urinating or defecating in or near water bodies.
Soil pollution:
1. Dumping of garbage in open areas.
2. Excessive use of pesticides and insecticides on plants.
Solution 6.b
- Vehicles run on fuels like petrol and diesel.
- These fuels are burnt in vehicles to produce energy which results in the production of smoke.
- This smoke contains harmful gases like carbon monoxide, hydrogen, nitrogen oxide, particulate matter, ammonia and sulphur dioxide.
- Therefore, vehicles are said to be the major contributors to air pollution.
- Bicycles, vehicles which run on CNG, electric cars and metros are vehicles which causes least or no pollution.
Solution 6.c
Natural reasons for water pollution:
- Presence of aquatic weeds in water bodies.
- Excessive growth of algae in water bodies.
- Mud and sludge which are added to water bodies due to river currents and their diversions.
- Growth of microbes like bacteria and fungi on dead and decaying matter present in water bodies.
Solution 6.d
Preventive measures for air pollution:
1. Minimise the use of fossil fuels and use cleaner sources suchas CNG.
2. Use public transport or carpooling.
3. Industries must fix tall chimneys fitted with electrostaticprecipitators and filters.
4. Garbage and plastics should not be burnt in the open.
5. Nuclear wastes should be disposed of safely.
6. Plants should be grown along the roadsides.
7. Fines should be charged and penalties should be enforced for those who break laws amended to control air pollution.
Solution 6.e
There is an increase in the global temperature due to greenhouse effect. The heat on the Earth remains trapped due to envelope of greenhouse gases. The percentage of carbon dioxide and methane is constantly increasing and hence, there is also an increase in temperature. Thus, greenhouse effect is directly related to the global warming.
Effects of this relation between greenhouse effect and global warming are as follows:
- Polar ice caps and glaciers at both the poles are melting due to increased temperature.
- The oceans' water is rising due to this melted ice. The sea level rise is causing coastal land submergence. The islands at various regions are at the risk of drowning.
- Many species of living organisms are already extinct due to global warming. The rest are also threatened. Polar bear is endangered. Wild animals are showing weird migrations.
- The increased temperature of the oceanic water is causing several changes in tides and currents. This has resulted in an increased occurrence of cyclones, hurricanes and cloud bursting. Natural disasters are also on the rise in the last decade.
- Agricultural production is decreasing. Regions with less rainfall are facing draughts.
Solution 6.f
Air pollution:
1. Go green to breathe clean.
2. Stop being mean, and keep the air clean. ·
Water pollution:
1. Be aware and handle water with care
2. Polluted water will make life harder. Keep it purest, water is dearest.
Soil pollution:
1. Lend a hand to save the land.
2. Don't spoil the soil. It is more valuable than oil.
Solution 7