Class 9 LAKHMIR SINGH AND MANJIT KAUR Solutions Chemistry Chapter 4 - Structure Of The Atom
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 191
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
(b). Maximum of 8 e- can be accommodated in outermost shell of an atom.
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
(b). p+
(c). n
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 192
Solution 20
Solution 21
Solution 22
(a). 8 electrons are present in outermost shell of Neon.
(b). 7 electrons are present in outermost shell of Chlorine.Solution 23
(b). N shell can accommodate maximum of 32 e-.
Solution 24
(b). M shell can accommodate maximum of 18 e-.
Solution 25
(ii). Thomson discovered 'electron'.
(iii). Goldstein discovered 'proton'.
Solution 26
(b). Electron has relative charge of -1.
(c). Neutron has relative charge of 0.
Solution 27
(b) Mass number
(c) 11
(d) 23
(e) 20
(f) Nucleus
(g) Electrons
(h) Protons
(i) 8
(j) 18
(k) Neutron
(l) Negative; Positive; No
Solution 28
The relative mass of an electron is 1/1840 u.
A charge of -1 is carried by an electron.
Solution 29
Absolute mass of electron is 9 x 10-28 Kg.
Absolute charge on electron is 1.6 x 10-19 C.
Solution 30
Solution 31
Important information furnished about nucleus in Rutherford's alpha- particle scattering experiment is:
(i). Nucleus of an atom is positively charged.
(ii). Nucleus of an atom is very hard and dense.
(iii). Nucleus of an atom is very small as compared to the size of an atom as a whole.
Solution 32
Solution 33
Solution 34
(b). Atomic no. is characteristic for any particular element.
Solution 12
(b). True
(c). False
Solution 13
Solution 14
Solution 15
Solution 16
Solution 17
Solution 18
Solution 19
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 193
Solution 35
Relative mass of proton is 1u.
Relative charge of proton is +1 C.
Solution 36
Absolute charge of proton - 1.6 x 10-19 C
Solution 37
Difference between proton and neutron-
(1). Proton is positively charged while electron is negatively charged.
(2). Proton is much heavier than electron.
Solution 38
Two observations which shows that atom is not indivisible are-
(1). In J. J. Thomson's experiment, the stream of cathode rays in the gas discharge tube shows the presence of negatively charged subatomic particles called electrons.
(2). In Goldstein's experiment, the faint red glow in the gas discharge tube shows the presence of positively charged subatomic particles called protons.
Solution 39
(ii). Formation of anode rays tells about the presence of positively charged protons in all the atoms.
Solution 40
Electronic configuration of oxygen (atomic no. = 8) is (2,6)
Solution 41
So, K-2 ; L-8 ; M-2
Solution 42
(a). Nucleus is a small positively charged part at the center of an atom. Nucleus is positively charged.
(b). Rutherford discovered nucleus of an atom.Solution 43
Alpha - particles have +2 units of charge.
Solution 44
(b). Electronic configuration of given element- (2,8,3)
K-2 ; L-8 ; M-3
Solution 45
Electronic configuration - (2,8,8)
The special thing about the outermost shell is that it is completely filled with the electrons.
Solution 46
Solution 47
Electron has relative charge of -1u, proton has +1u and neutron has 0 relative charge.
Solution 48
Solution 49
Electron has relative charge of -1u while proton has +1u of relative charge.
Solution 50
Proton has relative charge of +1u and neutron has no relative charge.
Solution 51
Also, electron has relative mass of 1/1840 u and neutron has relative mass of 1 u.
Solution 52
Solution 53
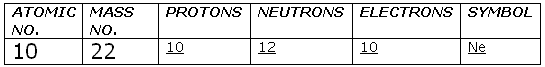
Solution 54
Solution 55
(b). When electricity at high voltage is passed through a gas at very low pressure taken in discharge tube, stream of minute particles are given out by the cathode. These stream of particles are called cathode rays.
(c). The conclusion is that all the atoms contain negatively charged particles called electrons.
Solution 56
(a). According to Thomson model of atom- An atom consists of a sphere of positive charge with negatively charged electrons embedded in it. The positive and negative charges in an atom are equal in magnitude.
Neutron was not present in the Thomson model of atom.
(b). When mass no. is 18 and no. of electrons is 7 then
(i). No. of protons = 7
(ii). No. of neutrons = 18 - 7 = 11
(iii). Atomic no. = 7
Solution 57
(a).Rutherford's model of atom-
1. An atom consists of positively charged, dense and very small nucleus containing all the protons and neutrons. Almost all the mass of atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
2. The nucleus is surrounded by negatively charged electrons. The electrons are revolving at very high speed round the nucleus in fixed circular orbits.
3. The electrostatic attraction between the positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons keep the atom held together.
4. An atom is electrically neutral.
5. Most of the space in an atom is empty.
The major drawback of Rutherford model of atom is that it does not explain the stability of the atom.
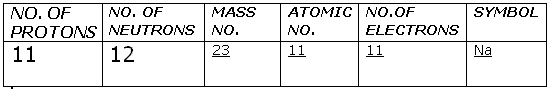
(b).Given: Mass no. = 23
No. of electrons = 11
Then, no. of protons = 11
No. of neutrons = 23 - 11 = 12
Atomic no. = 11
Solution 58
(a). Bohr's model of atom-
1. An atom is made up of three particles, namely electrons, protons and neutrons.
2.The protons and neutrons are located in the small nucleus at the center of atom.
3. Electrons revolve round the nucleus in fixed circular orbits.
4. Maximum no. of electrons for any given shell is fixed. Any shell cannot exceed that maximum value.
5. Each given shell is associated with fixed amount of energy.
6. There is no change in energy of electrons as long as they keep revolving in the same energy level, and the atom remains stable.
(b).Given: Atomic no. = 11
Mass no. = 23
Then, electronic configuration - (2,8,1)
Nuclear composition is - 11 protons and 12 neutrons
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 194
Solution 59
(a). (i). Atomic no. is the number of protons in one atom of an element.
(ii). Mass no. is the total number of protons and neutrons present in one atom of the element.
Example- The total no. of protons in a carbon atom is 6, so its atomic no. is 6.
Also, one atom of Na contains 11 protons and 12 neutrons, so its mass no. is 23.
(b). Mass No. = Atomic no. + No. of neutrons
(c). No. of neutrons = Mass No. - Atomic no.
= 24 - 12 = 12
Solution 71
(ii). Atomic no. = 15
(iii). E.C. = (2,8,5)
Solution 72
(a). E.C. - (2,8,7)
(b). Atomic No. = 17
(c). Non-metal
(d). Anion; X-
(e). X must be ChlorineSolution 73
(b). Mass no. = 3 + 4 = 7
(c). E.C. - (2, 1)
(d). Metal
(e). Cation will be formed; because outermost single electron can be easily donated.
(f). E+
(g). Lithium
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 195
Solution 74
(b). Atomic number
(c). No. of protons = 4
(d). No. of neutrons = 9 - 4 = 5
(e). No. of electrons = 4
(f). Electrons in outermost orbit = 2
(g). X2+
Solution 75
(b). Element Z is non-metal
(c). As the outermost shell of element Z is completely filled so, it will not form any ion.
(d). Outermost electronic shell is completely filled with electrons.
(e). Name of element 'Z' = Argon
Symbol is Ar
(f). Z belongs to the group 'Noble gases'.
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 210
Solution 1
E.C of Nitrogen = 2, 5
So, no. of valence electrons in Nitrogen atom = 5
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
One such isotope is Cobalt-60.
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13
Solution 14
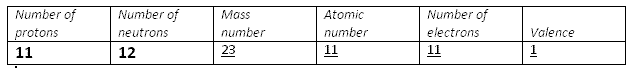
Solution 15
(a). M
(b). 3
(c). neutrons
(d). isotopes
Solution 16
(b). Mass no. = 6 + 5 = 11
(c). No. of electrons = 5
(d). No. of valence electrons, per atom = 3
Solution 17
E.C. = (2, 8, 7)
Valency = 8 - no. of valence electrons = 8 - 7 = 1
Solution 18
Atomic No. of X = 16
E.C. of X = (2, 8, 6)
Valency of X = 8 - no. of valence electrons = 8 - 6 = 2Structure Of The Atom Exercise 211
Solution 19
Valency shown by B (atomic no. 4) - 2
Valency shown by C (atomic no. 8) - 2
Valency shown by D (atomic no. 10) - 0
Valency shown by E (atomic no. 13) - 3
Solution 20
Cobalt-60 : This is used in the treatment of cancer.
Solution 21
Solution 22
Solution 23
For example- Cl-35 and Cl-37, show identical chemical properties as they have same no. of 7 valence electrons.
Solution 24
Solution 25
Solution 26
Deuterium, Protium and Tritium are isotopes.
Argon and Calcium are isobars.
Solution 27
(ii). All of them have 1 electron and 1 proton, so, they are electrically neutral.
Solution 28
Solution 29
Solution 30
D - 1 proton, 1 electron and 1 neutron.
T - 1 proton, 1 electron and 2 neutrons.
Solution 31
Atomic No. = 7
E.C = 2, 5
Valency of given element = 3
Given element is NITROGEN.
Solution 32
Valence electrons are situated in the outermost shell.
(b). There are 3 valence electrons present in the element with atomic no. 13.
Valence shell of this atom is M.
Solution 33
(a). Isotopes are the atoms of the same element having the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
For example - 35Cl17 and 37Cl17 are isotopes of chlorine.
(b). Similarity - A pair of isotopes have same atomic number.
Difference - A pair of isotopes have different mass numbers.
(c). In 35Cl17 - 17 protons, 17 electrons and 18 neutrons.
In 37Cl17 - 17 protons, 17 electrons and 20 neutrons.
Solution 34
(a).The isotopes which are unstable due to presence of extra neutrons in their nuclei and emit various types of radiations, are called radioactive isotopes or radioisotopes.
For example: Carbon - 14 , Arsenic - 74
(b). Uses of isotopes-
(i). They are used in the treatment of cancer.
(ii). Radioactive isotopes are used as 'tracers' in medicine to detect the presence of tumors and blood clots in human body.
(c). Average atomic mass = 35.5 u
Let % amount of 35Z17 be y, then amount of 37Z17 is (100 - y).
Then-
Solution 35
(a). The capacity of an atom of an element to form chemical bonds is known as its valency.
Valency of an atom with atomic no. 14 is 4.
(b). The valency of an element is either equal to the number of valence electrons in its atom or equal to the number of electrons required to complete eight electrons in the valence shell.
Valency of metal = No. of valence electron in its atom
Valency of a non-metal = 8 - No. of valence electron in its atom
For example- Valency of sodium (metal) is 1 and that of chlorine (non-metal) is also 1.
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 212
Solution 52
(a). E.C of Na+ = 2, 8
So, no. of valence electrons in sodium ion, Na+ = 8
(b). E.C of O2- = 2,8
So, no. of valence electrons in oxide ion, O-2 = 8
Solution 53
Atom A - 209A82
Atom B - 209B83
(i). A has 82 protons.
(ii). B has 83 protons.
(iii). No, A and B are not isotopes.
Structure Of The Atom Exercise 213
Solution 54
(ii). 79X35 and 80Y35 - these are isotopes as they have same atomic number.
Solution 55
(i). Subscripts represent atomic number whereas superscripts represent atomic mass.
(ii). Number of neutrons is responsible for the change in the superscripts.
(iii). Isotopes is the usual name for the given atoms of the element.
(iv). Nuclear composition of 18O8 is:-
No. of protons = 8
No. of neutrons = 18 - 8 = 10
Solution 56
A and B are the example of isobars. This is because they have same number of nucleons.
Solution 57
The two species are isobars.
A represents Argon (Atomic no. = 18) while B represents Calcium (Atomic no. = 20).
Solution 58
Solution 59
Solution 60
(ii). Mass number of Y = 8 + 9 = 17
(iii). X and Y are isotopes.
(iv). X and Y represent Oxygen.

