Class 10 LAKHMIR SINGH AND MANJIT KAUR Solutions Biology Chapter 1 - Life Processes
Life Processes Exercise 23
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Parasitic - Plasmodium.
Holozoic - Human Beings.
Solution 7
Life Processes Exercise 24
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
(b) Oxygen.
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13
Solution 14
(b) Green.
Solution 15
Solution 16
Solution 17
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
Solution 21
(ii) Carnivores.
(iii) Omnivores.
Solution 22
(ii) Herbivores.
(iii) Omnivores.
Solution 23
Solution 24
Solution 25
Solution 26
Solution 27
Solution 28
Solution 29
Solution 30
(ii) Large Intestine.
Solution 31
Solution 32
Solution 33
Solution 34
Solution 35
Solution 36
Solution 37
Solution 38
Solution 39
(b) Heterotrophs.
(c) Autotrophs, heterotrophs.
(d) Carbon dioxide, water.
(e) Starch.
Exercise
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Solution
Life Processes Exercise 25
Solution 52
(b) Enzymes help in the breaking down of complex organic food materials into simpler forms.
Solution 53
(i) Makes the acidic food coming from the stomach alkaline so that the pancreatic enzymes can act on it.
(ii) Bile salts breaks the fats present in the food into small globules making it easy for the enzymes to act and digest them.
(b) Trypsin: It is a pancreatic enzyme present in the pancreatic juice. Its function is to digest the proteins.
Solution 54
Solution 55
(ii) - (a)
(iii) - (d)
(iv) - (b)
Solution 56
(b) Heterotrophs.
(c) Autotrophs.
(d) Chloroplast.
(e) Guard cells.
(f) Pepsin.
Solution 57
(ii) - (d)
(iii) - (a)
(iv) - (b)
Solution 40
(b) (i) Glucose
(ii) Starch.
Solution 42
(b) The conditions necessary for autotrophic nutrition are sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water.
Solution 43
| Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
| It is that mode of nutrition in which an organism makes its own food from the simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide and water present in the surroundings (with the help of sunlight energy) Example: Green Plants |
It is that mode of nutrition in which an organism cannot make its own food from simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide and water, and depends on other organisms for its food. Example: Animals. |
Solution 44
(b) The various types of Heterotrophic nutrition are:
(i) Saprotrophic nutrition.
(ii) Parasitic nutrition.
(iii) Holozoic nutrition.
Solution 45
(b) The photosynthesis takes place in the following three steps; (i) Absorption of sunlight energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy into chemical energy and splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen by light energy.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen to form carbohydrates like glucose by utilising the chemical energy
Solution 46
(b) Plants need nitrogen to make proteins and other compounds. They take up nitrogen from the soil in the form of inorganic salts called nitrates (or nitrites), or in the form of organic compounds which are produced by bacteria from the atmospheric nitrogen.
Solution 47
Example: Fungi and many bacteria obtain food by saprophytic nutrition.
(ii) Parasitic nutrition: It is that nutrition in which an organism derives its food from the body of another living organism (called its host) without killing it.
Example: Plasmodium and round worms obtain food by parasitic nutrition.
(iii) Holozoic nutrition: It is that nutrition in which an organism takes the complex organic food materials into its body by the process of ingestion; the ingested food is digested and then absorbed into the body cells of the organism.
Example: Human beings obtain food by holozoic nutrition
Solution 48
Example: Fungi and some bacteria.
(b) Parasite: A parasite is an organism (plant or animal) which feeds on another living organism called its host.
Example: Plasmodium and round worm.
Solution 49
(b) The water required by the plants for photosynthesis is absorbed by the roots of the plants from the soil through the process of osmosis. The absorbed water is then transported upward through the xylem vessels to the leaves where it reaches the photosynthetic cells and utilized in photosynthesis.
Solution 50
(a) Hydrochloric acid: It makes the medium of gastric juice acidic so that the enzyme pepsin can digest the proteins properly and also kills any bacteria that might have entered the stomach with food.
(b) Pepsin: The enzyme pepsin digests the proteins present in the food and converts them into smaller molecules.
(c) Mucus: The mucus helps to protect the stomach wall from its own secretions of hydrochloric acid.
Life Processes Exercise 26
Solution 58
(b) (i) Proteins (ii) Starch (iii) Proteins (iv) Fats.
(c) Absorption of digested foods occurs mainly in the small intestine due to the presence of a large number of finger like projections called villi.
Solution 59
(b) If mucus is not secreted, hydrochloric acid will cause the erosion of inner lining of stomach leading to the formation of ulcers in the stomach.
(c) The contraction and expansion movements of oesophagus also called peristaltic movements pushes the food down into the elementary canal.
Solution 60
(b) Plant kept in continuous light will live longer because it will be able to produce oxygen required for its respiration by the process of photosynthesis.
Solution 61
(b) When photosynthesis occurs during the day, the carbon dioxide released by plants by respiration is all used up and not released. Similarly, some of the oxygen produced during photosynthesis is used up in respiration. Since the plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen even during the day, it means that no photosynthesis is taking place.
Solution 62
(b) (i) Decreases in morning but increases in the afternoon
(ii) Decreases.
(iii) Decreases.
Solution 64
(b) The conditions for photosynthesis are sunlight, chlorophyll, carbon dioxide and water.
(c) Factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis are (i) Light (ii) Carbon dioxide (iii) Water (iv) Temperature (v) Mineral elements.
Solution 63
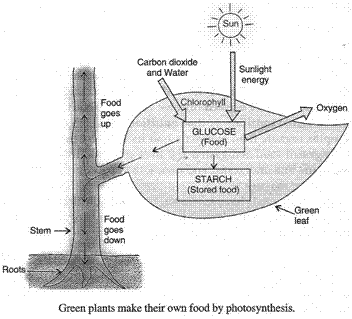
(a)
The process by which green plants make their own food (like glucose) from carbon dioxide and water by using sunlight energy in the presence of chlorophyll is called photosynthesis.
(c) The process of photosynthesis takes place in the green leaves of a plant. The carbon dioxide gas required for making food is taken by the plant leaves from the air which enters the leaves through tiny pores called stomata. Water required for making food is taken from the soil which is transported to the leaves from the soil through the roots and the stem. The sunlight provides energy required to carry out the chemical reactions involved in the preparation of food. The green pigment called chlorophyll absorbs sunlight energy. The photosynthesis takes place in three steps:
(i) Absorption of sunlight energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy into chemical energy and splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen by light energy.
(iii) Reduction of carbon dioxide by hydrogen to form carbohydrates like glucose by utilising the chemical energy.
Solution 68
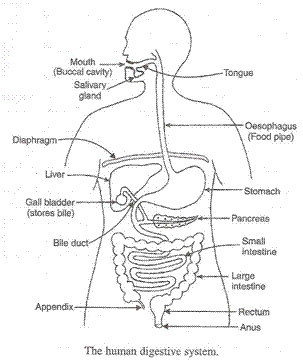
(a) Digestion of food in human beings: Digestion of food begins in the mouth. The mouth cavity contains teeth, tongue and salivary glands. The teeth cut the food into small pieces, chew and grind it. This is called physical digestion. Salivary glands produce saliva which mixes with the food. This involves chemical digestion of food. The saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase which digests the starch and converts it into maltose sugar. Mouth opens into a small funnel shaped area called pharynx which leads to a long tube called oesophagus. It carries the food down into the stomach. The wall of oesophagus is muscular. When the slightly digested food enters the food pipe, the walls of the oesophagus starts contraction and expansion movements called peristaltic movements which push the food into the stomach. Digestion does not take place in the oesophagus.
The glands present on the walls of the stomach secrete gastric juice that contains hydrochloric acid, the enzyme pepsin and mucus. A small amount of gastric lipase is also present that breaks down the fats present in the food. Gastric juice is acidic due to the presence of HCl which is necessary for the pepsin to become active and converts the proteins into peptones. The mucus protects the stomach walls from HCl. From the stomach, the partially digested food goes into the small intestine through sphincter muscle. Small intestine is divided into two parts: Duodenum and Ileum.
Duodenum receives the secretions of two glands, liver and pancreas through a common duct. Liver secretes bile which is alkaline and contains salts to emulsify the fats (or lipids). The bile secreted by the liver is stored in the gall bladder. Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which contains trypsin, lipase and pancreatic amylase. Trypsin digests the proteins, lipase emulsifies the fats and pancreatic amylase breaks down the starch. Thus, small intestine is the site of complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The walls of ileum secrete succus entericus which completes the digestion process.
(b) The walls of small intestine has finger like projections like villi which increases the surface area for absorption.
(c) Peristaltic movements.
Solution 69
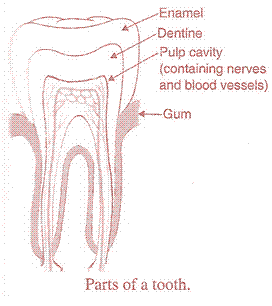
(b) The formation of small cavities (or holes) in the teeth due to the action of acid forming bacteria and improper dental care is called dental caries. This happens as follows: When we eat sugary food, the bacteria in our mouth act on sugar to produce acids. These acids dissolve the calcium salts from the tooth enamel and then from dentine forming small cavities in the tooth over a period of time in our mouth act on sugar to produce acids. These acids dissolve the calcium salts from the tooth enamel and then from dentine forming small cavities in the tooth over a period of time.
(c) If the teeth are not cleaned regularly, they become covered with the sticky, yellowish layer of food particles and bacteria cells called dental plaque. It causes tooth decay. It can be prevented by brushing the teeth regularly as it neutralises the acids.
Solution 70
(b) (i) Carbohydrates - The digestion of carbohydrates begins in the mouth. The human saliva contains an enzyme called salivary amylase which digests the starch present in the food into maltose sugar. The slightly digested carbohydrates when reaches the small intestine, pancreatic amylase present in the pancreatic juice breaks down the starch. The intestinal juice of the small intestine completes the digestion of carbohydrates and finally coverts it into glucose.
(ii) Fats - The process of digestion of fats begins in the stomach. The glands of stomach secrete a small amount of gastric lipase that breaks down the fats present in the food. From the stomach the partially digested food goes into small intestine where the pancreatic lipase breaks down the emulsified fats. The walls of small intestine secrete intestinal juice which converts the fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
(iii) Proteins - The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach. The glands of the stomach secrete gastric juice which contains an enzyme called pepsin. Pepsin converts the proteins into peptones. Pancreatic juice contains trypsin which digests the proteins into peptides and the intestinal juice completes the process of digestion of proteins thus converting it into amino acids.
Solution 66
Example: Goat and cow.
(ii) Carnivores - Those animals which eat only other animals as food are called carnivores.
Example: Tiger and Lion.
(iii) Omnivores - Those animals which eat both plants and animals are called omnivores.
Example: Human Being and dog.
(b)
| Lion | Carnivore |
| Man | Omnivore |
| Dog | Omnivore |
| Goat | Herbivore |
| Crow | Omnivore |
| Elephant | Herbivore |
| Snake | Carnivore |
| Hawk | Carnivore |
| Rabbit | Herbivore |
| Deer | Herbivore |
(c) The five steps involved in the process of nutrition in animals are (i) Ingestion (ii) Digestion (iii) Absorption (iv) Assimilation (v) Egestion.
Solution 65
(b) There are mainly two modes of nutrition:
(i) Autotrophic - Autotrophic nutrition is that mode of nutrition in which an organism makes its own food from the simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide and water present in the surroundings (with the help of sunlight energy).
Example: Green plants obtain food by autotrophic nutrition.
(ii) Heterotrophic - Heterotrophic nutrition is that mode of nutrition in which an organism cannot make its own food from simple inorganic materials like carbon dioxide and water, and depends on other organisms for its food.
Example: All animals obtain food by heterotrophic nutrition.
(c) The mode of nutrition in (i) round worm and (ii) plasmodium is parasitic nutrition.
Life Processes Exercise 46
Solution 1
Solution 2
Solution 3
Solution 4
Solution 5
Solution 6
Life Processes Exercise 47
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
(b) Photosynthesis.
Solution 12
Solution 13
Solution 14
Solution 15
Solution 16
Solution 17
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
Solution 21
Solution 22
Solution 23
Solution 24
(b) Carbon dioxide.
Solution 25
(b) True.
(c) False.
Solution 26
(b) Alveoli.
(c) Alveoli.
(d) Anaerobic, aerobic.
(e) Fish.
Solution 27
Solution 28
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
|
(i) Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen.
|
(i) Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.
(ii) Partial break down of food occurs in anaerobic respiration.
|
(b) Yeast and some bacteria.
Solution 29
(b) Lactic acid.
Solution 30
Solution 31
(b) Aerobic respiration in humans.
(c) Anaerobic respiration in muscle tissue of animals.
Solution 32
Difference between breathing and respiration:-
| Breathing | Respiration |
| (i) Breathing is a simple process. (ii) Breathing involves taking in oxygen from the air and releasing carbon dioxide into the air. (iii) Breathing is a physical process. |
(i) Respiration is a complex process. (ii) Respiration includes breathing as well as the oxidation of food in the cells of the organism to release energy. (iii) Respiration is a bio-chemical process. |
Life Processes Exercise 48
Solution 34
Solution 35
Solution 36
(a) Respiration in amoeba: Amoeba depends on simple diffusion of gases for breathing. The diffusion of gases takes place through the thin cell membrane of amoeba. Amoeba lives in water which contains dissolved oxygen. The oxygen from water diffuses into the body of amoeba through its cell membrane. The oxygen spreads quickly into the whole body and is used for respiration inside the amoeba cell. The process of respiration produces carbon dioxide which diffuses out through its cell membrane into the surrounding water.
(b) It is aerobic respiration.
Solution 38
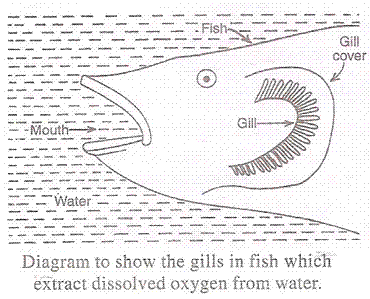
Respiration and fish: The fish has special organ of breathing called gills on both the sides of its head. The gills are covered by gill covers. The fish lives in water which contains dissolved oxygen. The fish breathes by taking in water through its mouth and sending it over the gills. When water passes over the gills, the gills extract dissolved oxygen from the water. The extracted oxygen is absorbed by the blood and carried to all the parts of the fish. The carbon dioxide produced by respiration is brought back by the blood into the gills for expelling into the surrounding water.
Solution 39
Solution 40
(b) Respiration in stems: The stems of herbaceous plants takes place through stomata. The oxygen from the air diffuses into the stem of a herbaceous plant through stomata and reaches all the cells for respiration. The carbon dioxide produced diffuses out through stomata. In woody stems, the bark has lenticels for the exchange of gases.
(c) Respiration in leaves: The leaves of a plant has tiny pores called stomata through which the exchange of respiratory gases takes place by diffusion. Oxygen from air diffuses into a leaf through stomata and reaches all the cells, where it is used for respiration and the carbon dioxide produced diffuses out from the leaf into the air through stomata.
Solution 41
(b) The aquatic animals use the oxygen dissolved in water to carry out respiration. The terrestrial animals obtain oxygen from air.
Solution 42
Solution 43
Solution 44
Solution 45
Solution 46
Solution 47
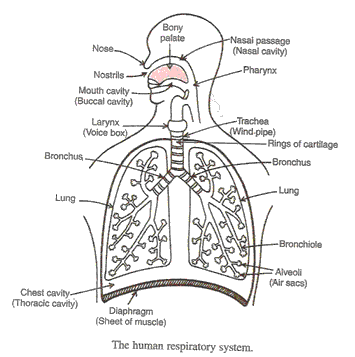
(a) The function of respiratory system is to breathe in oxygen for respiration (producing energy from food), and to breathe out carbon dioxide produced by respiration.
(b) The major organs of respiratory system in human beings are: (i) Nose (ii) Nasal Passage (iii) Trachea (iv) Bronchi (v) Lungs and (vi) diaphragm.
Solution 48
(b) Trachea does not collapse even when there is no air in it because it is supported by rings of soft bones called cartilage.
(c) During the process of 'breathing in' the air sacs or alveoli of the lungs get filled with air containing oxygen. The alveoli are surrounded by capillaries carrying blood so the oxygen of air diffuses from the alveoli walls into the blood from where it is carried to all the parts of the body.
As the blood passes through the tissues of the body, the oxygen present in it diffuses into the cells. This oxygen combines with the digested food to release energy. Carbon dioxide gas is produced as a waste product during respiration in the cells of the body tissues which diffuses into the blood. Blood carries the carbon dioxide back to the lungs where it diffuses into the alveoli.
(d) The human lungs have been designed to maximise the exchange of gases as there are millions of alveoli in the lungs which provides a large surface area for the exchange of gases.
Solution 49
| Respiration in plants | Respiration in Animals |
| (i) All the parts of the plants perform respiration individually. (ii) During respiration in plants there is a little transport of respiratory gases from one part of the plant to the other. (iii) The respiration in plants occurs at a slow rate. |
(i) An animal perfomrs respiration as a single unit. (ii) Respiratory gases are usually transported over long distances inside an animal during respiration. (iii) The respiration in animals occurs at a much faster rate. |
(b) (i) During daytime when photosynthesis occurs, oxygen is produced. The leaves use some of this oxygen for respiration and the rest of oxygen diffuses out into the air. Carbon dioxide produced by respiration is all used up in photosynthesis by leaves during the daytime. Even more carbon dioxide is taken in from air. Thus, the net gas exchange in leaves during daytime is: Oxygen diffuses out; Carbon dioxide diffuses in.
(ii) At night time, when no photosynthesis occurs and hence no oxygen is produced, oxygen from air diffuses in leaves to carry out respiration. Carbon dioxide produced by respiration diffuses out into air. So, the net gas exchange in leaves at night is: Oxygen diffuses in; Carbon dioxide diffuses out.
(c) Exhaled air contains more carbon dioxide because during the respiration process when oxygen breaks down glucose, then a lot of carbon dioxide is produced hence the exhaled air has a higher proportion of the same.
Solution 50
(b)
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| (i) Aerobic respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen. (ii) Complete breakdown of food occurs in aerobic respiration. (iii) The end products in aerobic respiration are carbon dioxide and water. (iv) Aerobic respiration produces a considerable amount of energy. Example: Human Beings. |
(i) Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. (ii) Partial breakdown of food occurs in anaerobic respiration. (iii) The end products in anaerobic respiration are ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast) and lactic acid (in animal muscles). (iv) Much less energy is produced in anaerobic respiration. Example: Yeast. |
(c) (i) Anaerobic respiration.
(ii) Aerobic respiration.
Solution 51
(b) Large organisms contain a respiratory pigment called haemoglobin which carries the oxygen from the lungs to all the body cells very efficiently.
(c) A terrestrial animal has an advantage over an aquatic animal in regard to obtaining oxygen for respiration that it is surrounded by an oxygen rich atmosphere from where it can take any amount of oxygen.
Life Processes Exercise 72
Solution 1
(b) Xylem.
Solution 2
(b) Food.
Solution 3
Solution 4
(b) Veins.
Solution 5
Solution 6
Solution 7
(i) The largest artery in the human body is 'Aorta'.
(ii) The largest vein in the human body is 'Vena Cava'.Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 10
Solution 11
Solution 12
Solution 13
(b) Xylem.
Life Processes Exercise 73
Solution 14
Solution 15
Solution 16
Solution 17
(b) Xylem.
Solution 18
Solution 19
Solution 20
Solution 21
(b) Carbon dioxide.
Solution 22
Solution 23
(b) False.
Solution 24
Stomata in the leaves and lenticels in the stems are two parts through which a plant releases its gaseous waste products into the air.
Solution 25
Solution 26
Solution 27
Solution 28
Solution 29
(b) Nephron.
(c) Kidneys.
(d) Lymph.
(e) White, red.
Solution 31
Solution 32
(b) The transport of food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant is called translocation.
(c) Phloem.
Solution 33
(a) (i)?
(ii)
(b)
Solution 34
| i | c |
| ii | a |
| iii | d |
| iv | e |
| v | b |
Solution 35
Solution 36
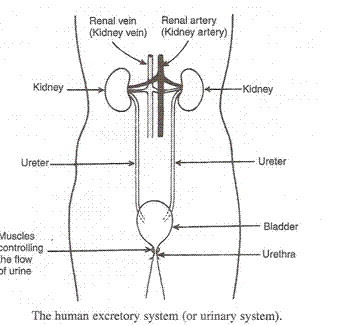
(b) Urea.
(c) Ureters.
(d) Urinary bladder is a bag which stores the urine temporarily till it is excreted out.
Solution 37
Solution 38
Platelets help in the coagulation of blood in a cut or wound.
Life Processes Exercise 74
Solution 39
(b) Heart needs valves to prevent the backflow of blood so that the blood flows only in one direction.
Solution 40
(ii) Water, glucose, salts in similar concentration to those in normal blood.
(iii) Urea.
Solution 41
| Artery | Vein | Capillary |
| (i) It is a thick walled blood vessel. | It is a thin walled blood vessel. | It is an extremely narrow blood vessel having very thin walls. |
| (ii) It carries blood from the heart to different parts of the body. | It brings blood from the different parts of the body to the heart. | They form an extensive network throughout all living cells in the body and connect arteries and veins. |
| (iii) It can dilate or constrict depending on the regulatory requirement of the body. | It cannot dilate or constrict. | It can dilate or constrict according to the requirement of the tissue. |
| (iv) It does not contsin any valve. | It contains simple valves which permit blood flow only towards the heart. | It does not contain any valves. |
Solution 42
(b) Ventricles
(c) Capillaries
(d) (i) Right side (ii) Left side
Solution 43
(a) Thevarious methods used by the plants to get rid of their waste products are (i) the plants get rid of gaseous waste products through stomata in leaves and lenticels in stems.
(ii) They get rid of solid and liquid waste by shedding off leaves, peeling of bark and falling of fruits.
(iii) Secreting gums and resins.
(iv) Plants excrete some waste substances into the soil around them.
(b) Excretion in amoeba: In amoeba, the waste material carbon dioxide is removed by diffusion through the cell membrane, but nitrogenous waste and excess water are removed by contractile vacuole.
Solution 44
(i) It takes part in the nutritive process of the body.
(ii) It protects the body by killing the germs drained out of the body tissues with the help of lymphocytes contained in the lymph nodes, by making antibodies.
(iii) It helps in removing the waste products like fragments of dead cells etc.
(b) If the blood pressure of a person is 120/80 it means that the systolic pressure is 120 mm Hg and diastolic pressure is 80 mm Hg.
Solution 45
Solution 46
(i) Plasma: It carries all the dissolved substances such as proteins, digested food, common salt etc from one part to another part of the body.
(ii) Red blood corpuscles (RBC): It carries oxygen from the lungs to all the cells of the body.
(iii) White blood corpuscles (WBC): It fights infection and protects us from diseases.
(iv) Platelets: It helps in the coagulation of blood in a cut or wound.
Solution 47
(ii) Excretory system.
(iii) Respiratory system.
(iv) Digestive system.
Solution 48
The minimum pressure in the arteries during relaxation phase of the heart is called the diastolic pressure.
The normal blood pressure values are:
Systolic pressure: 120 mm Hg.
Diastolic pressure: 80 mm Hg.
Solution 49
(b) The heart beats faster when a person runs for a while because the body needs more energy under these conditions.
Solution 50
(b) Functions of blood:
(i) It carries oxygen from the lungs to different parts of the body.
(ii) It carries carbon dioxide from the body cells to the lungs for breathing out.
(iii) It carries digested food from the small intestine to all the parts of the body.
(iv) It carries waste product called urea from the liver to the kidneys for excretion in the form of urine.
(v) It protects the body from diseases.
(c) Lymph.
Solution 51
(a) Human circulatory system is a system which is responsible for the transport of materials inside the body. The various organs of the circulatory system in humans are: heart, arteries, veins and capillaries.
(b)
(c) Single circulation is a type of circulatory system in which the blood passes through the heart only once in one complete cycle of the body.
Double circulation is a circulatory system in which the blood travels twice through the heart in one complete cycle of the body.
Solution 52
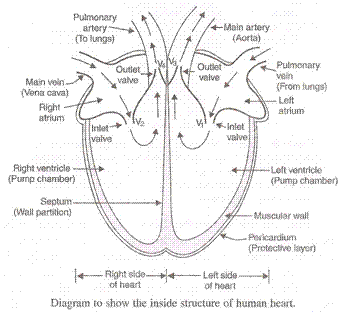
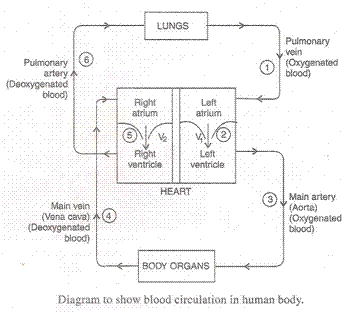
(i) When the muscles of all the four chambers are relaxed, the pulmonary vein brings the oxygenated blood from the lungs in the left atrium of the heart.
(ii) When the left atrium contracts, the oxygenated blood is pushed into the left ventricle through valve V1.
(iii) When the left ventricle contracts, the oxygenated blood enters the main artery called aorta from which it goes to the different body organs through small branches called arterioles and capillaries.
(iv) The main artery carries the blood to all the organs of the body head, arms etc except the lungs. The oxygenated blood gives off oxygen, digested food and dissolved materials to the body cells. The carbon dioxide produced in the cells enters the blood. The deoxygenated blood enters main vein called vena cava which carried it to the right atrium of the heart.
(v) When the right atrium contracts, the deoxygenated blood enters right ventricle through valve V2.
(vi) When the right ventricle contracts, the deoxygenated blood enters the lungs through pulmonary artery and releases carbon dioxide and absorbs fresh oxygen from air. The blood becomes oxygenated again and is sent to the left atrium of heart by pulmonary vein for circulation in the body. This whole process is repeated continuously.
Solution 53
(b) It is necessary to separate the oxygenated blood from mixing with deoxygenated blood as mammals and birds have high energy needs because they constantly require energy to maintain their body temperature.
(c) (i) Three chambered heart.
(ii) Four chambered heart.
(iii) Two chambered heart.
(d) The fish has a two chambered heart. Oxygenation of the blood takes place in the gills. The oxygenated blood from the gills is supplied to the body parts of the fish where oxygen is utilized and carbon dioxide enters into it making it deoxygenated. The deoxygenated blood returns to the heart to be pumped into gills again.
Solution 54
Functions of lymphatic system: (i) It takes part in the nutritive process of the body. (ii) It protects the body by killing the germs drained out of the body tissues with the help of lymphocytes contained in the lymph nodes, by making antibodies. (iii) It helps in removing the waste products like fragments of dead cells etc.
(b) Blood pressure: The pressure at which the blood is pumped around the body by the heart is called blood pressure. The two factors which expresses the blood pressure a person are systolic pressure and diastolic pressure.
(c) Urea is the main nitrogenous waste in human blood. It is removed from the body in the form of urine through the kidneys.
Solution 55
(a) The excretory system of human beings consists of the following main organs: two kidneys, two ureters, bladder and urethra.
(c) The excretory system removes the poisonous waste substances from the body in the form of urine and maintains ionic balance called osmoregulation.
Solution 56
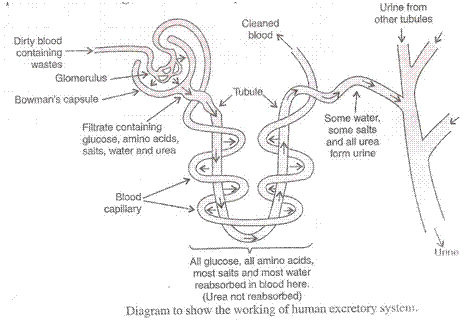
(b) Urinary bladder.
(c) Urethra is a tube which passes out the urine from the body collected in the urinary bladder.
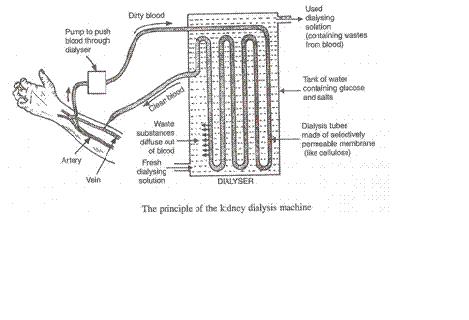
Solution 57
(b) Principle of Dialysis: The blood from an artery in the patients arm is made to flow into the dialyser of a dialysis machine made of long tubes of selective permeable membrane (like cellulose) which are coiled in a tank containing dialysing solution. The dialysing solution contains water, glucose and salts in similar concentrations to those in normal blood. As the patient's blood passes through the dialysing solution most of the waste like urea present in it pass through the selectively permeable cellulose tubes into the dialysing solution. The clean blood is pumped back into a vein of the patients arm.
Solution 58
(a) Transport in organisms (plants and animals) is necessary as it absorbs all essential substances and transports them to all parts so that they reach each and every cell of the body.
(b) Special tissues and organs are needed for the transport of substances in plants and animals because these tissues and organs can pick up the essential substances like food, oxygen, water, etc at one end of their body and carry them to all other parts.
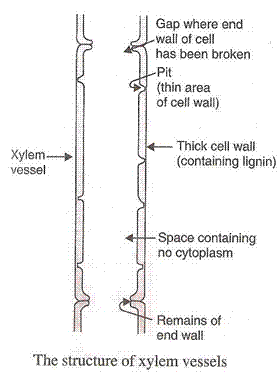
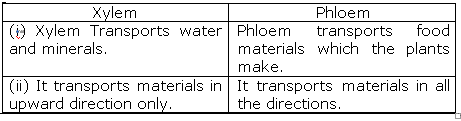
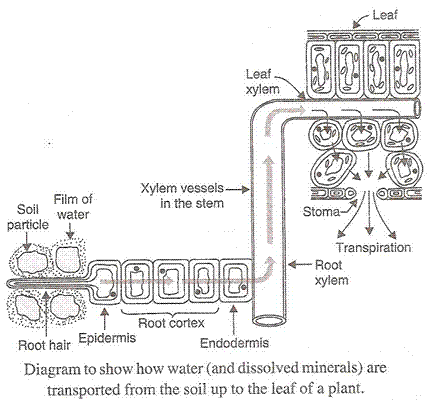
(c) Water and minerals are transported to various parts of the plant by xylem tissues called xylem vessels and tracheids. Plants take in water from the soil through the roots. The water containing minerals called cell sap is carried by the xylem vessels to all the parts of the body. The roots have root hairs to absorb water and minerals from the soil by diffusion and then pass from cell to cell by osmosis through epidermis, root cortex, endodermis and then reach the root xylem. The water enters the root xylem into the stem xylem and then reaches the leaves from the petioles.
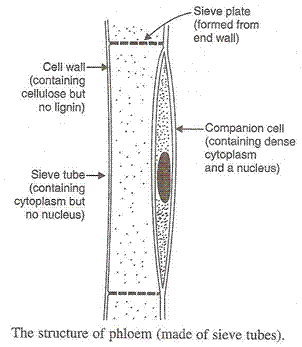
(d) Transportation of food in plants: The transport of food from the leaves to other parts of the plant is called translocation. Phloem tissue transports the food from the leaves to the other parts of the plant. The movement of food in phloem takes place by utilising energy. The sugar made in the leaves is loaded into the sieve tubes of phloem by using ATP. Water enters the sieve tube containing sugar which causes high pressure and pushes the food to all the parts of the plant having low pressure. This is how the food is transported according to the needs of the plant.