Solid State
Solid State PDF Notes, Important Questions and Synopsis
SYNOPSIS
- Differences between crystalline solid and amorphous solid:
Crystalline Solid
Amorphous Solid
The internal arrangement of particles is well defined.
The internal arrangement of particles is not well defined.
There is regularity in the external form when crystals are formed.
There is no regularity in the external form when amorphous solids are formed.
These have a sharp melting point.
These melt over a range of temperatures.
These have characteristic heat of fusion.
These do not have characteristic heat of fusion.
Crystalline solids give a regular cut when cut with a sharp-edged knife.
Amorphous solids give an irregular cut.
Crystalline solids are regarded as true solids.
Amorphous solids are super-cooled liquids or pseudo solids.
These are generally incompressible.
These may be compressed to an extent.
- Classification of crystals into seven systems:
Crystal system
Unit cell dimensions and angles
Bravais Examples
Lattices
Cubic
a = b = c; α= β= γ= 90°
SC, BCC, FCC
NaCl
Orthorhombic
a ≠b ≠c; α= β= γ= 90°
SC, BCC, end
centred & FCC
SR (Rhombic sulphur)
Tetragonal
a = b ≠c; α= β= γ= 90°
SC, BCC
Sn, ZnO2
Monoclinic
a ≠b ≠c; α= γ= 90°≠β
SC, end centred
SM (Monoclinic sulphur)
Rhombohedral
a = b = c; α= β= γ = 90°
SC
Quartz
Triclinic
a ≠b ≠c; α≠β≠γ≠90°
SC
H3BO3
Hexagonal
a = b ≠c; α= β= 90°;γ= 120°
SC
Graphite
- Analysis of cubical system:
Property
SC
BCC
FCC
Atomic radius (r)
a = edge length
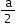
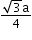
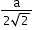
No. of atoms per
unit cell (Z)
1
2
4
C. No.
6
8
12
Packing efficiency
52%
68%
74%
No. of voids
(a) octahedral (Z)
(b) tetrahedral (2Z)
-
-
-
-
4
8
- Neighbourhood of a particle:
- Simple cubic (SC) structure:
Type of neighbour
Distance
No. of neighbours
nearest
a
6 (shared by 4 cubes)
(next)1
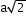
12 (shared by 2 cubes) (next)2
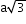
8 (unshared)
- Body-centred cubic (BCC) structure:
Type of neighbour
Distance
No. of neighbours
nearest
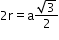
8
(next)1
=a
6
(next)2
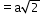
12
(next)3
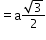
24
(next)4
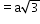
8
- Face-centred cubic (FCC) structure:
Type of neighbour
Distance
No. of neighbours
nearest
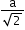
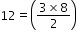
(next)1
a
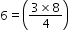
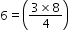
(next)2
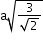
24
(next)3
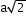
12
(next)4
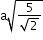
24
Packing of constituents in crystals:
|
Structure |
Packing pattern |
Coordination number |
Packing efficiency (%) |
Unit cell |
|
Simple cubic |
AAAA |
6 |
52 |
Primitive cubic |
|
Body-centred cubic or BCC |
ABAB |
8 |
68 |
Body-centred cubic |
|
Hexagonal closed packing |
ABAB |
12 |
74 |
Non-cubic |
|
Cubic closest packing or FCC |
ABCABC |
12 |
74 |
Face-centred cubic |
- Ionic crystals:
C. No.
Limiting radius ratio
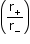
3
0.155 - 0.225 (triangular)
4
0.225 - 0.414 (tetrahedral)
6
0.414 - 0.732 (octahedral)
8
0.732 - 0.999 (cubic)
- Crystal defects (Imperfections):
- Stoichiometric effect:
-
Schottky defect:
- This defect is created when an ion leaves its correct lattice site and occupies an interstitial site. Examples: ZnS, AgCl, AgBr, AgI
Non-stoichiometric effect:
Metal excess defect:
- These defects arise due to anionic vacancies.
- This type of defect is exhibited by alkali halides. Examples: NaCl, KCl
Metal deficiency defect:
- These defects arise when a compound has metal deficiency due to the absence of a metal ion from its lattice site.
- This type of defect is generally found in compounds of transition metals. Examples: ZnO, CdS
Related Chapters
- Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- States of Matter
- Atomic Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Thermodynamics
- Solutions
- Equilibrium
- Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- Hydrogen
- s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- p-Block Elements
- d - and f - Block Elements
- Co-ordination Compounds
- Environmental Chemistry
- Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- Hydrocarbons
- Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- Polymers
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
- Principles Related to Practical Chemistry


