Class 11-science H C VERMA Solutions Physics Chapter 18 - Geometrical Optics
Geometrical Optics Exercise 412
Solution 1
By using mirror equation,
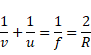
Hence,
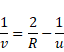
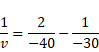
v=-60cm
Solution 2
We know that,
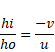
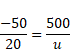
u=-200cm
Now by using mirror formula,
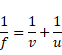
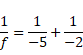
f=-1.44m
Solution 3
There are two possible cases:
(i) u=-u, v=2u, f=-20cm
By using mirror formula,
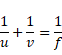
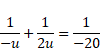
u=10cm
(ii) u=-u, v=-2u, f=-20cm
By using mirror formula,
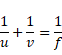
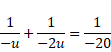
u=30cm
Solution 4
Using mirror equation,
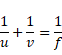
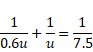
As,
{m=![]() }
}
{0.6=![]() }
}
u=5cm
Solution 5
Focal length
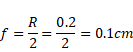
Now by using mirror formula,
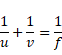
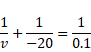
v=0.1cm
and magnification,
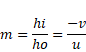
![]()
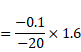
hi = 0.008cm
Solution 6
By using mirror formula ,
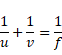
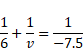
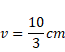
And,
![]()
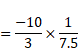
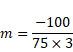
Also,
![]()
So,
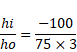
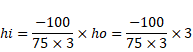
hi=1.33cm
Solution 7
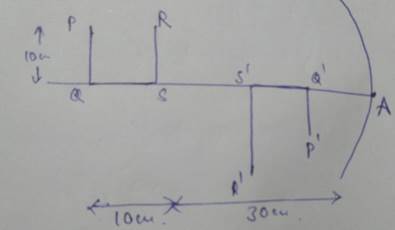
For PQ,
U=AQ=40cm
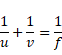
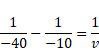
v=-13.3cm
Also,
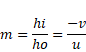
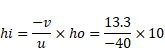
![]()
For RS
U=-30cm
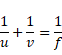
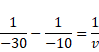
v=-15cm
Also,
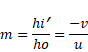
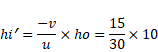
![]()
Now,
Q'S'=AS'-AQ'
=15-13.3
=1.7cm
Thus, total image length is,
3.3+5+1.7=10cm
Solution 8
As we know that,
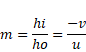
![]()
![]()
Now,
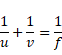
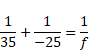
f=-87.5cm
Geometrical Optics Exercise 413
Solution 9
By using mirror formula,
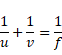
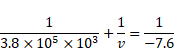
![]()
Now,
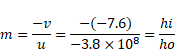
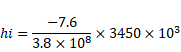
![]()
Solution 10
By using mirror formula,
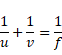
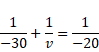
![]()
Also,
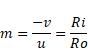
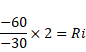
![]()
Solution 11
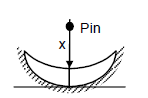
Let x be height of object above water.
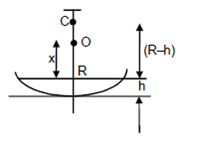
We know,
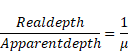
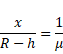
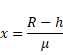
Solution 12
Both mirror produces one image in following two cases:
(A) When Source is at distance =2f or at center of curvature then image is produce at v=2f+2f=4f
(B) When source is at distance f then rays become parallel after reflecting through one mirror, then it is reflected through other mirror and only one image is formed
V=f + f=2f
Solution 13
By using mirror formula, for reflection,
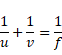
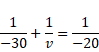
![]()
Now, for 2nd reflection,
u=60-(30+x)=30-x
Using Mirror equation,
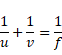
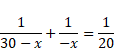
X2+10x-600=0
Solving equation we get,
X=20cm or x=-30cm
Therefore,
Total distance is 20+30=50cm
Solution 14
We know that,
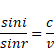
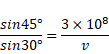
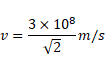
Distance
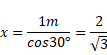
And time taken,
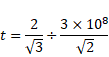
Total time taken
![]() s
s
Solution 15
Length of Shadow =0.5+0.5 tan r
Also,
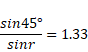
sin r=0.53
and
cos r=![]()
=0.85
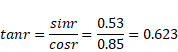
Length of shadow =0.5(1+tan r)
=0.5(1+0.623)
=81.5cm
Solution 16
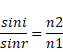
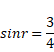
![]()
According to figure,
![]()
x=2.8m
Solution 17
Shift,
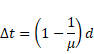
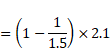
![]()
Solution 18
Shift due to water,
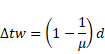
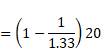
![]()
Shift due to oil,
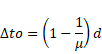
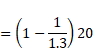
![]()
Adding Shift of water and oil,
![]()
=5+4.6
=9.6cm
Apparent depth =40-∆t
=40-9.6
=30.4cm
Solution 19
Shift is given as:
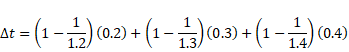
![]()
Shift of 0.2cm above P point takes place due to 3 sheets.
Solution 20
Total shift due to 'k ' no. of slabs is:
![]() …………
(1)
…………
(1)
Where
t1, t2, t3…………tkre thickness and ![]() are refractive index
are refractive index
![]() ………………….(2)
………………….(2)
Comparing equation(1) and (2)
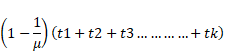
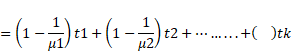
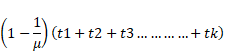
![]()
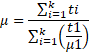
Solution 21
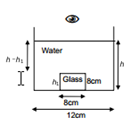
When glass piece is inserted inside water then volume of cylindrical water column becomes,
![]()
62×h=800+42×8
h=25.7cm
Now, shift due to glass block is,
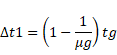
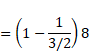
![]()
Now, shift due to water is,
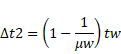
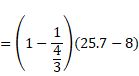
![]()
Net shift
![]()
=2.26+4.44
![]()
Geometrical Optics Exercise 414
Solution 22
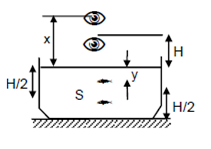
(A) We know ,
![]()
![]()
Distance =
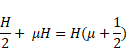
Image through mirror
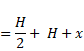
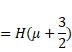
(B) We know that,
![]()
![]()
Direct image= H+y
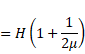
Real depth
=![]()
Apparent depth
= ![]()
Distance
of image=![]() =H
=H![]()
Solution 23
By above diagram,
![]() (1)
(1)
Also,
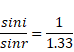
Sin r=1.33 × sin i
Sin r=4/5
Then, cot r=3/4 (2)
Comparing equation (1) and (2),
![]()
x=2.25cm
Ration
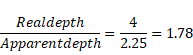
Solution 24
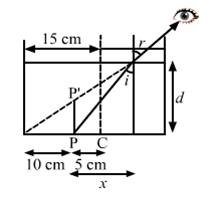
We know,
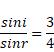
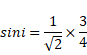
As![]()
Let x= distance between P and X
Now
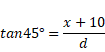
d=x+10
Also,
![]()
{![]() }
}
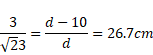
Solution 25
According to fig,
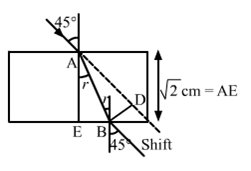
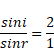
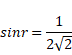
And ![]()
![]()
=24°
Shift
= AB sin![]()
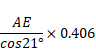
=0.62cm
Solution 26
We know,
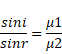
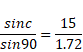
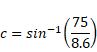
Solution 27
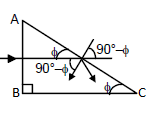
We know,
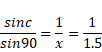
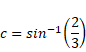
And
![]()
![]()
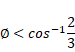
Hence,
![]() is the largest possible angle.
is the largest possible angle.
Solution 28
When light ray travels from glass to air then total internal reflection takes place. In this refracted angle is more than 90° for reflection to occur. Thus, maximum angle is 90°.
Solution 29
We know,
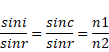
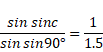
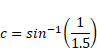
![]()
Angle increases from 0° to 40°48' then to 45° angle decreases.
Solution 30
(i) CASE I: When light passes through normal ,
![]()
![]()
Angle
of deviation ![]()
(ii) CASE II: When light is incident at critical angle
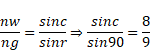
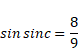
C=62.73°
Angle of deviation
=90°-c
=90°-62.73°
=37.27°
Range 0 to cos-1(8/9)
Solution 31
We know that,
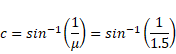
![]()
Maximum Deviation = 90°-41.8°
=47.2°
Thus, total internal reflection will take place.
In reflection deviation is given as:
D=180°-2i
i=45°
Solution 32
(a)As per figure,
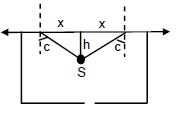
![]()
Also,
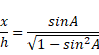
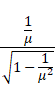
{![]() }
}
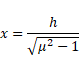
(b)
Angle A= sin-1(1/![]() )
)
Solution 33
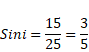
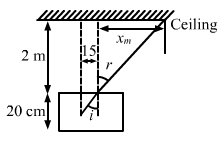
And also,
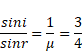
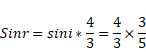
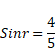
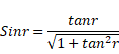
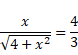
x=2.667m
Total radius= 2.667+0.15=2.817m
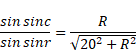
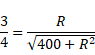
![]()
Solution 34
Angle of minimum deviation is given as :
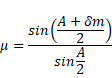
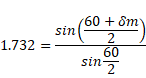
![]()
As we know,
![]()
![]()
Solution 35
We know that,
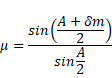
As angle is small,
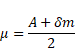
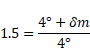
![]()
Solution 36
We know that,
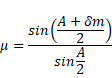
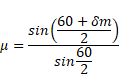
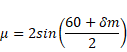
As ,
![]() =30°
=30°
![]()
![]()
Solution 37
We know,
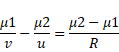
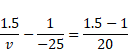
![]()
Solution 38
We know,
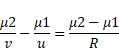
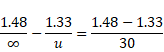
![]()
Geometrical Optics Exercise 415
Solution 39
We know that,
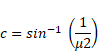
And
![]() =2
=2
Therefore,
c=30°
I > c
Therefore, rays reflected internally.
We know,
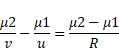
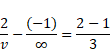
![]()
Solution 40
(a) Image distance from left =-(5-3.5)
=-3.5cm
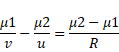
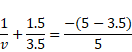
v=-3cm
Image will be formed at 2cm left from center.
(b) Image distance from right u=-(5+1.5)
=-6.5cm
We know,
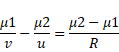
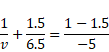
![]()
Image will be formed at 2.65 cm towards left from center
Solution 41
When rays refract through A then,
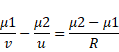
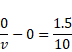
v=30cm
Now fro second refraction,
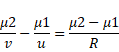
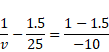
![]()
Solution 42
Focused at the surface
We know,
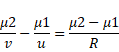
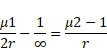
![]()
Focused at the center
We know,
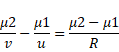
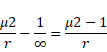
![]()
This is not possible. Thus, image cannot be focused at the center of the sphere.
Solution 43
We know,
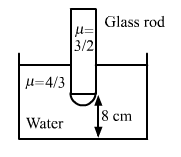
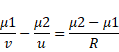
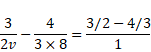
![]()
Solution 44
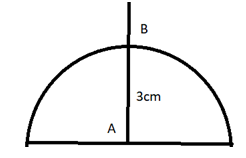
When image is refracted by A
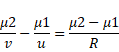
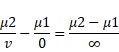
![]()
Now when image is refracted at B,
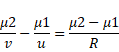
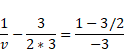
![]()
Solution 45
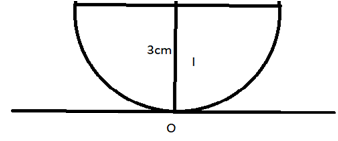
Shift in image is given as:
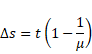
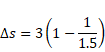
![]()
Solution 46
When refraction takes place from ACB then,
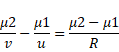
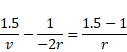
![]()
Now, refraction takes of reflected image above so v=f=r/2 and u= -3r/2
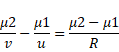
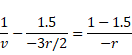
Hence,
![]()
Therefore, Image is formed at E.
Solution 47
For 1st refraction,
We know
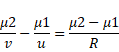
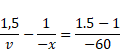
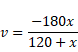
By using mirror formula,
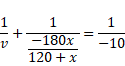
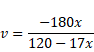
Now, for 2nd refraction,
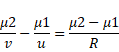
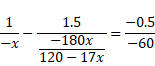
![]()
Solution 48
We know,
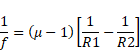
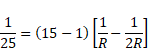
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 49
Air :
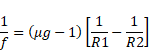
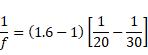
f=100cm
Air :
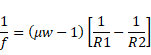
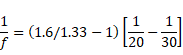
f=300cm
Solution 50
There are four types of lenses:
We know that,
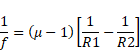
(1) If R1=+ve and R2= -ve
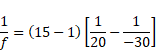
![]()
(2) If R1=-ve and R2= -ve
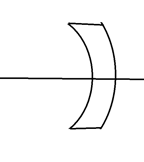
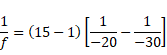
![]()
(3) If R1=-ve and R2= +ve
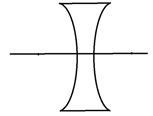
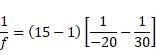
![]()
(4) If R1=+ve and R2= +ve
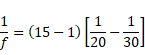
![]()
Solution 51
Beam is incident on lens, so,
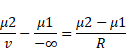
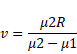
Now beam is refracted second time,
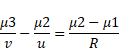
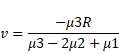
Therefore,
Image is formed at![]()
Image
formed when rays are incident from medium with refractive index ![]() is:
is:
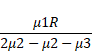
Solution 52
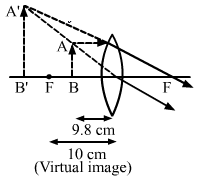
(a) We know,
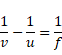
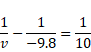
![]()
And magnification m=v/u=-490/-9.8=50cm
As m > 1 Then, Image is virtual and erect.
(b) We know,
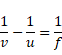
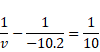
![]()
And magnification m=v/u=510/-9.8=-52.04cm
As m < 1. Then, Image is real and inverted.
Solution 53
In case of projector,
![]()
![]()
![]()
We know,
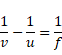
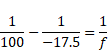
![]()
Solution 54
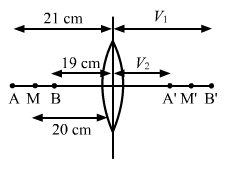
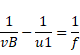
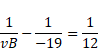
![]()
When object is at A, then
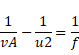
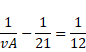
![]()
Now, Amplitude of vibration is given as:
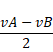
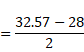
Amplitude=2.28cm
Solution 55
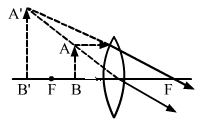
We know,
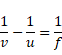
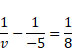
![]()
As image formed on left side.
Therefore, Virtual image
Solution 56
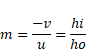
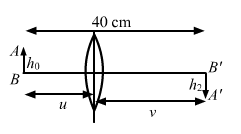
![]()
![]() (1)
(1)
And
![]() (2)
(2)
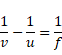
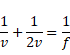
![]() (3)
(3)
From equation (1) and (2)
![]()
![]()
![]()
And from eq.(3)
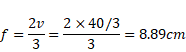
From eq (1) and (3)
![]()
Geometrical Optics Exercise 416
Solution 57
We know,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now,
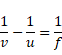
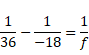
![]()
When the image is tripled then,
We know,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now,
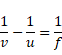
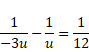
![]()
Solution 58
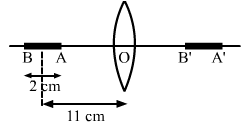
We know that,
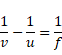
For OB'
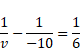
![]()
For OA'
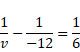
![]()
Now,
A'B'= OB'-OA'
=15-12
A'B'=3cm
Solution 59
We know,
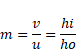
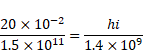
![]()
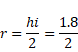
![]()
Solution 60
As given,
![]()
![]() (1)
(1)
And
![]() (2)
(2)
Now,
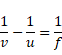
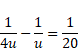
![]()
Object is at 15cm from the lens.
Solution 61
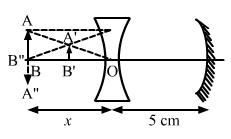
We know,
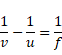
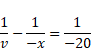
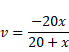
Therefore, For concave mirror,
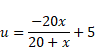
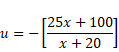
Now, Using mirror equation for concave mirror,
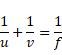
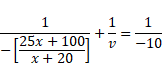
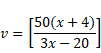
Now, in case of second refraction,
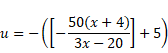
And
![]()
Therefore,
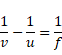
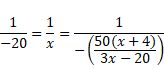
![]()
Solution 62
Let x be the object distance.
First using lens formula,
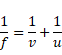
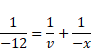
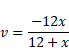
Now,
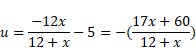
Now,
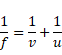
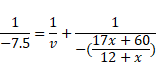
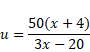
Now again it will refract through lens,
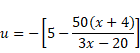
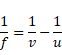
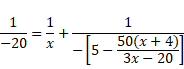
![]()
Solution 63
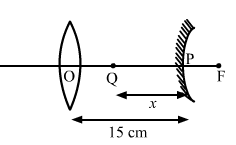
We know,
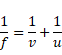
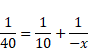
![]()
Therefore,
Object distance=15-40/3
=1.67cm
Solution 64
(I) Image formed due to direct transmission through lens.
We know,
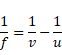
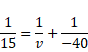
![]()
(II) Image due to reflection of rays by mirror and then transmission through lens.
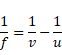
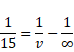
![]()
Solution 65
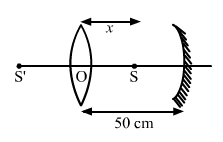
In case of lens,
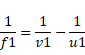
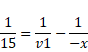
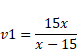
In case of mirror,
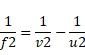
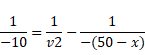
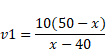
Now, distance between mirror and lens is,
![]()
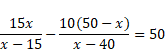
![]()
Solution 66
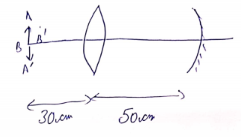
We know,
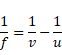
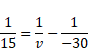
![]()
Image will be real and inverted and it will be at a distance of 20cm from mirror and f=10cm.
Hence,
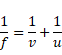
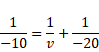
![]()
Now again rays will pass through lens, So
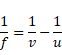
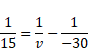
![]()
Therefore, Image is formed at the place of object. It real and inverted and of same size as object.
Solution 67
We know,
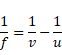
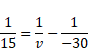
Now, shift of the image due to slab is:
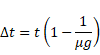
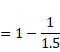
![]()
Image is formed at 30+0.33=30.33cm.
Solution 68
For convex lens,
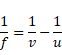
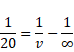
![]()
Therefore, For concave lens,
![]()
And
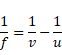
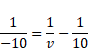
![]()
Thus, when rays pass through concave lens become parallel
According to fig.
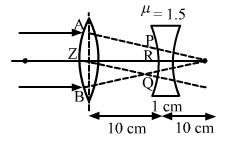
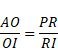
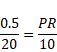
![]()
Solution 69
Net focal length is:
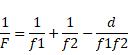
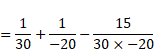
F=120cm
Equivalent lens is converging lens.
Now,
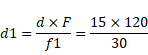
![]()
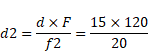
![]()
Distance of object from diverging lens is:
For d1 120-60= 60cm
For d2 120+90=210cm
Solution 70
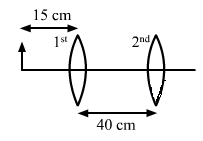
For lens I
We know,
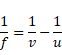
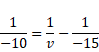
![]()
Magnification
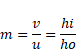
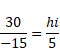
![]()
Image is inverted
Size of image is 10mm.
For lens II
We know,
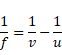
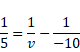
![]()
Magnification
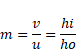
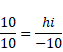
![]()
Image is real and erect.
Size of image is 10mm.
Solution 71
We know,
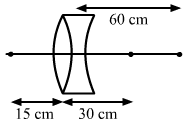
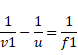
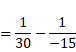
![]()
Also ![]()
V1=30cm
Now,
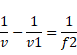
Hence
f=10 cm(convex lens)
F=60 cm(concave lens)
Solution 72
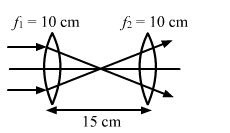
Beam will diverge after refracting from both lenses.
1st lens:
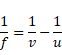
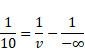
![]()
2nd lens:
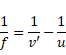
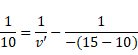
![]()
Therefore, Image is formed at distance of 5cm for 1st convex lens.
(c) Equivalent focal length is given as :
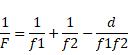
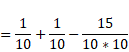
![]()
Solution 73
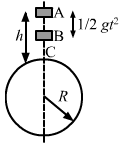
AB =![]()
And
BC=![]()
And
also u=-(![]() )
)
Now we know,
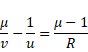
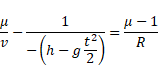
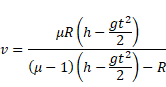
And velocity
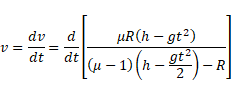
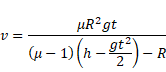
Solution 74
We know,
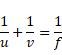
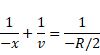
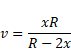
And velocity V=dv/dt
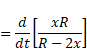
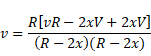
Solution 75
t < d/V
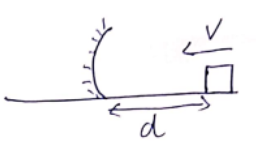
as we know,
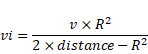
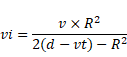
t > d/v
as we know that,
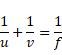
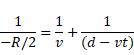
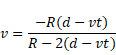
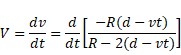
After solving we get,
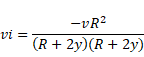
Absolute velocity is given as
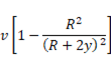
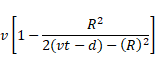
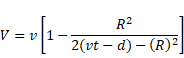
Solution 76
Recoil velocity is given as,
![]()
At
time 't' position =![]()
![]()
And u=kvt
Also,
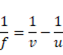
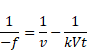
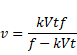
Velocity is given as:
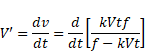
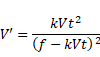
Thus velocity of separation is given as:
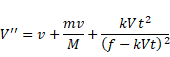
If t=0
![]()
Solution 77
In case of equilibrium,
mg=kx
x=mg/k=0.1cm
Thus, mean position =30+0.1=30.1cm
Max. Compression=8
And work done=KE2-KE1
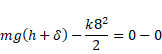
![]()
From fig2
Position of B=31.3cm
Amplitude=31.5-30.1=1.4
Position of A=30.1-1.4=28.7cm
For A,
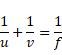
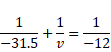
![]()
For B,
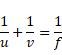
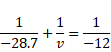
![]()
Therefore, Vibration length= 20.62-19.38=1.24cm
Solution 78
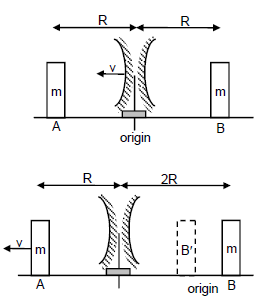
In time t=R/V the mass B must have moved vXR/v=R towards the mirror
For block B
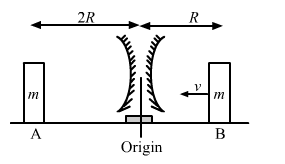
a)

b)
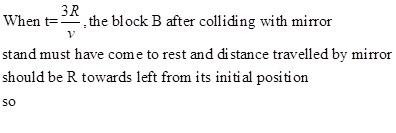
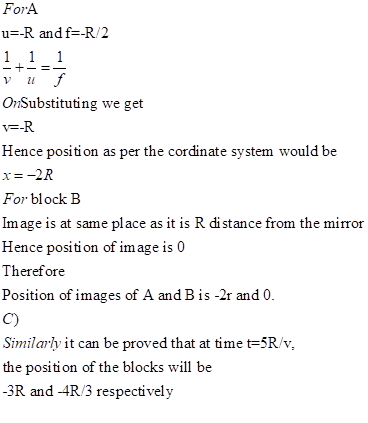
Geometrical Optics Exercise 417
Solution 79
According to given figure:
T-mg+ma-2m=0 (1)
And T-ma=0 (2)
From eq (1) and (2)
2ma-mg-2m=0
2ma=m(g+2)
A=10+2/2=6m/s2
And distance travelled is given as:
S=ut+at2/2
S=0+1/2×6×(0.2)2
S=12cm
Therefore u=-(42-12)
U=-30cm
We know,
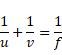
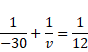
![]()

