Class 11-science H C VERMA Solutions Physics Chapter 9 - Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision Exercise 159
Solution 1
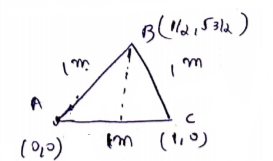
Take A as origin (0,0)
then C= (1,0)
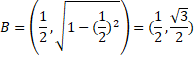
![]()
![]()
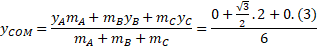
![]()
![]() if we take AC as
x-axis.
if we take AC as
x-axis.
Similarly, if we take AB as x-axis,
![]()
Solution 2
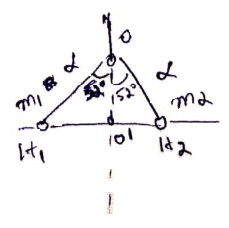
O![]() Ao
Ao
Take ![]() as origin.
as origin.
then ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
=0
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Distance from O-atom= ![]()
=![]()
![]() m
m
![]() m
m
Solution 3
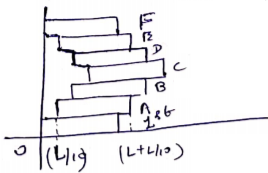
take O as (0,0)
brick A and E is from ![]()
brick B and D is from ![]()
brick C is from ![]()
![]() ,F are from (0 to L)
,F are from (0 to L)
For ![]() and F
bricks, C.O.M=
and F
bricks, C.O.M=![]()
For B and D,
C.O.M=![]()
(as they are displaced by ![]() )
)
Similarly,
For A and E
C.O.M=![]()
For C, C.O.M=![]()
![]() of all bricks
of all bricks
![]()
![]()
Solution 4
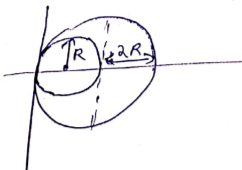
C.O.M of 2R disc =(2R,0)
C.O.M of R disc=(R,0)
C.O.M of system=![]()
![]() }
}
{![]() }
}
C.O.M of system=![]()
=![]()
Distance of C.O.M (system) from C.O.M of 2R disc
=![]()
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision Exercise 160
Solution 5
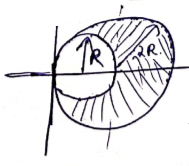
C.O.M of 2R disc =(2R,0)
C.O.M of R disc=(R,0)
C.O.M of shaded area=![]()
=![]()
From C.O.M of 2R disc, it is ![]() distance away.
distance away.
Solution 6
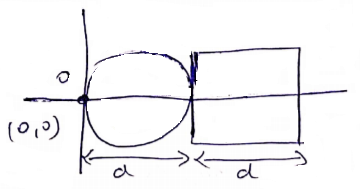
Area density of square=![]()
(Mass/unit area)
Mass/unit area of circle=![]()
![]()
![]()
C.O.M of square = (![]() )
)
C.O.M of circle = (![]() )
)
C.O.M of the whole system= ![]()
=![]()
=![]()
From C.O.M of disc it is
![]()
=![]() distance away.
distance away.
Solution 7
Velocity coordinates of 1Kg![]()
For another 1Kg![]()
For 1.2Kg![]()
For 1.5Kg![]()
For 0.5Kg![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
COM= (0.13487, -0.13915)
Solution 8
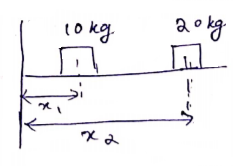
Initially, let
10Kg be ![]() cm
away
cm
away
20Kg be ![]() cm
away
cm
away
![]()
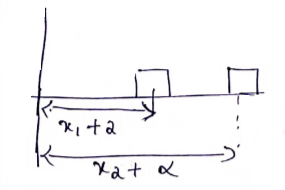
Let 20Kg be moved by distance of 2cm.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() cm
cm
20Kg should move 1cm towards left.
Solution 9
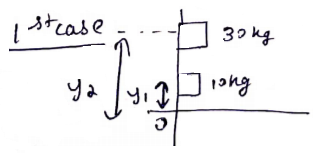
![]()
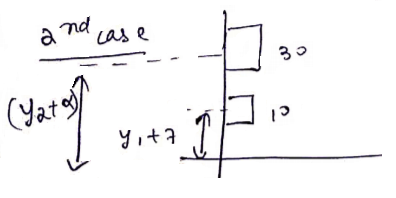
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() cm
cm
![]() should be moved 1cm
downward.
should be moved 1cm
downward.
Solution 10
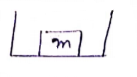
As ice melts, COM would no shift, as there is no external force (not even gravity).
Solution 11
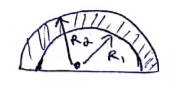
C.O.M of shaded region=![]()
![]()
![]()
{![]() =density
of material}
=density
of material}
{l=thickness of disks}
![]()
![]()
![]()
C.O.M of shaded area
=![]()
=![]()
=![]()
=![]() above center
above center
Solution 12
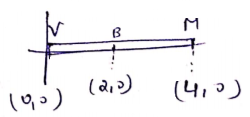
V-Verma
M-Mathur
B-Boat
![]()
![]() m
m
When they come to center
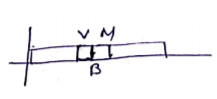
![]()
![]() m
m
Shift in ![]()
![]()
![]() m
m
So, the boat would shift 0.13m so that COM of system remains same.
Solution 14
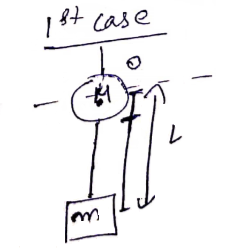
Let balloon be at origin.
![]()
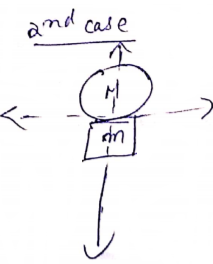
Both monkey and balloon are at origin.
![]()
Shift=![]()
=![]()
So, the balloon descends by ![]() distance.
distance.
Solution 15
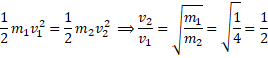
![]()
![]()
Solution 16
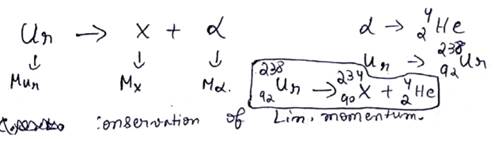
![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Solution 17
Conservation of lin. Momentum (C.O.L.M)
![]()
M-Man
E-Earth
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Solution 18
n![]()
![]() Kg-m/s
Kg-m/s
![]() Kg-m/s
Kg-m/s
(a)
If ![]() and
and ![]() are along same direction.
are along same direction.
Resultant
velocity, ![]()
![]() in same direction.
in same direction.
C.O.L.M
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
(b) If ![]() ,
, ![]() or
or ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision Exercise 161
Solution 19
When he throws a bag to left, momentum is conserved.
![]()
![]() velocity
of bag
velocity
of bag
![]() speed
of man
speed
of man
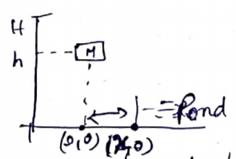
Let pond start from (![]() )
)
Time to reach height h=![]()
Time to reach ground, ![]()
Time taken by man=![]()
=![]()
COM of the system will be at (0,0)
after he reaches ground (let bag reach ![]() from origin) (
from origin) (![]() )
)
![]()
![]()
From law of kinematics
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 20
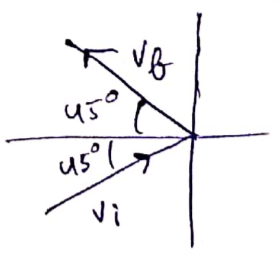
![]()
![]()
(a) change in momentum
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() kg-m/s
kg-m/s
(b) change in momentum magnitude
![]()
Solution 21
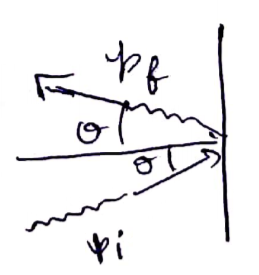
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 22

resultant velocity of 2 particles moving along x and y-axis
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
C.O.L.M
![]()
![]()
So,
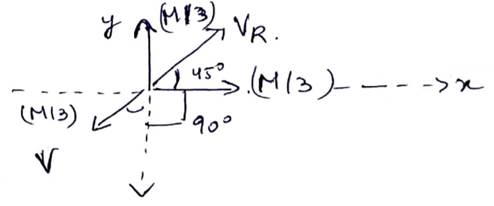
V is along ![]() below x-axis.
below x-axis.
Solution 23
In a closed spaceship, there is no external force (not even gravity). So the spaceship will move with a constant speed of 15m/s.
Solution 24
Volume of 1 hailstorm
![]()
![]()
Mass=![]()
![]() kg
kg
Mass of 2000 hailstorms=![]()
![]() kg
kg
average force on 1![]() roof
roof
![]() N
N
Average force on 10m×10m (100![]() )roof
)roof
![]() N
N
Solution 25
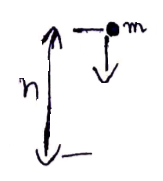
![]()
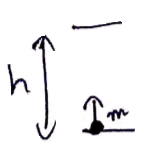
![]()
![]()
For falling down,
Time taken ![]()
![]()
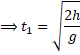
For bouncing up (back)
![]()
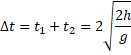
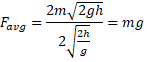
Solution 26
C.OL.M
![]() velocity
with which man in car approaches.
velocity
with which man in car approaches.
![]()
![]()
Solution 27
After 1 bullet,
C.O.L.M![]()
![]()
After 2nd bullet C.O.L.M![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
(after 2nd shot)
Solution 28
After left person jumps,
![]()
![]()
u is left, ![]() is right
is right
After right person jumps
![]()
![]()
u is left, ![]() is right
is right
(as ![]() is left)
is left)
Net velocity=![]()
=![]() towards left
towards left
Solution 29
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision Exercise 162
Solution 30
C.O.L.M (conservation of linear momentum)
![]() s-school boy, b-bugghi
s-school boy, b-bugghi
![]() m/s
m/s
Solution 31
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Solution 32
![]()
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
![]()
![]()
=1200J
Solution 33
Use C.O.L.M, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 34

Use C.O.L.M,
![]()
![]()
Solution 40
K.E. of nucleus=![]()
Decrease in internal energy
![]()
![]()
Solution 41
We know that for the spring,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Use law of kinematics,
![]()
![]()
![]() m
m
x=10cm
Solution 42
FBD of block after collision
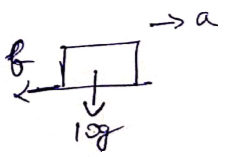
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Use law of kinematics,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 43

e=co-efficient of restitution
![]()
After collision with ground,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is the equation of trajectory.
is the equation of trajectory.
![]()
{y=0 at second projectile after it falls down from 1st projectile}
![]()
From starting point, it falls after distance.
![]()
![]()
Solution 44
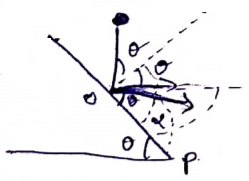
After falling down, ball will have a projectile motion.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Equation of trajectory
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 46
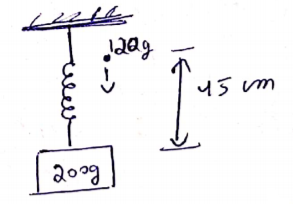
At equilibrium ![]()
(before 120g falls) ![]() N/m
N/m
![]() m/s
m/s
Use C.O.L.M,
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
If spring is stretched extra by ![]()
According to conservation of energy,
![]()
![]()
![]() cm
cm
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision Exercise 163
Solution 35
Use C.O.L.M
v=initial velocity
![]() final
velocities
final
velocities
![]() -(1)
-(1)
Given
![]()
![]() -(2)
-(2)
Solve (1) and (2)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 36
(a) Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]()
![]()
For maximizing, take derivative.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
![]()
![]() J
J
(b) ![]() v
v
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 37
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]() J
J
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
When ![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
![]() when
when ![]() or
or ![]()
if ![]()
if ![]()
as ![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Solution 39
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 45
![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
![]()
=10m/s
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
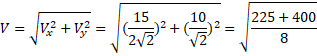
![]() m/s
m/s
Angle of reflection![]()
Angle of projection![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
l=18.5m
Solution 47
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]()
From C.O.E.L (conservation of energy law)
![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Solution 48
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
From C.O.E.L,
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
![]() m/s
m/s
Solution 49
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be travelled by
be travelled by ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
![]() {integrate}
{integrate}
Use C.O.E.L,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Similarly,![]()
Solution 50
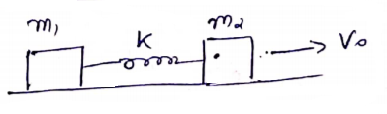
(a) ![]()
(b) Use C.O.E.L
![]()
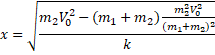
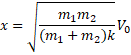
Solution 51
If ![]() and
and ![]() is travelled by
is travelled by ![]() under F
under F
Work done![]()
Use C.O.E.L ![]()
![]()
Use C.O.L.M ![]()
![]()
Solution 52

![]()
![]()
Net force of ![]()
![]()
Net force of ![]()
![]()
Use C.O.E.L,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 53
![]() ft/s
ft/s
(velocity of pillow w.r.t man)
![]()
Use C.O.L.M,
![]()
![]() {
{![]() ft/s}
ft/s}
![]()
![]()
![]() ft/s
ft/s
Time taken for going down=![]()
![]() sec
sec
Total time taken (up+ down) =![]() sec
sec
Solution 54
Use C.O.L.M,
![]()
When B reaches man,
Use C.O.E.L,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Use C.O.L.M of whole system
![]()
![]()
Solve (1) and (2) to get
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Use ![]()
![]()
![]()
Block's initial velocity![]()
Solution 55
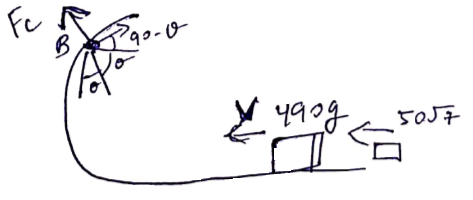
Use C.O.L.M,
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
![]() (
(![]() =velocity
at position B)
=velocity
at position B)
![]()
Use C.O.E.L
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Angle of projection=
Angle of projection=![]()
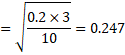
Distance in horizontal direction
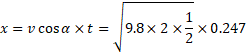
![]() m
m
Vertical direction distance=![]()
Total distance=![]()
=0.22m
Solution 56
(a) For initial velocities,
Use C.O.E.L
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]()
![]() -(1)
-(1)
Since collision is elastic, e=1
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() -(2)
-(2)
Solve (1) and (2),
![]()
Similarly, ![]()
(b) Use C.O.E.L
![]()
![]()
![]()
For mass m, use C.O.E.L,
![]()
![]()
![]()
2m will rise up to, ![]()
m will rise up to, ![]()
Solution 57
Consider ![]() Mass
per unit length of chain
Mass
per unit length of chain
![]()
![]()
After chain's release,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Weight of chain due to x length
![]() {M'=Mass
of x length}
{M'=Mass
of x length}
Total force=![]()
Solution 58
(a) Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]() -(1)
-(1)
Use C.O.E.L,
![]() -(2)
-(2)
Solving (1) and (2)
![]()
![]()
If ![]()
![]()
Use kinematics law,
![]()
![]() m
m
(b) If it is inelastic,
C.O.L.M![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
![]()
![]() m
m
Solution 59
Using work energy principle
V=velocity of 2kg near collision
![]()
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
Use C.O.L.M, {![]() =final
velocities}
=final
velocities}
![]()
![]() - (1)
- (1)
As collision is elastic, e=1
![]() - (2)
- (2)
Solving (1) and (2)
![]()
![]() m/s
m/s
![]() m/s
m/s
Use C.O.E.L for 1st block,
![]()
![]() cm
cm
Use C.O.E.L for 2nd block,
![]()
![]() cm
cm
Distance between them=4+1=5cm
Solution 60
Along x-direction ![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()
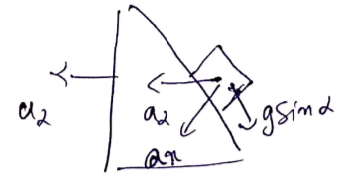
![]() =resultant
=resultant
![]()
![]()
Vertical distance travelled by m=![]()
Use law of kinematics, ![]()
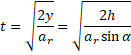
![]() {velocity
of M block}
{velocity
of M block}
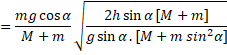
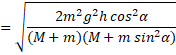
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision Exercise 164
Solution 61
(a) Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]()
(b) Use C.O.E.L
![]()
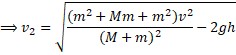
(c) ![]() {resultant
velocity}
{resultant
velocity}
![]()
![]()
Use C.O.E.L
![]()
![]()
Total height=![]()
![]()
=![]()
(d) time for flight
![]()
Total time=![]()
![]()
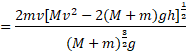
Solution 62
b-block
e-earth
Use C.O.L.M
![]()
![]()
Use C.O.E.L
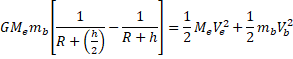
![]()
![]()
![]()
h<<R
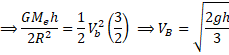
Solution 63
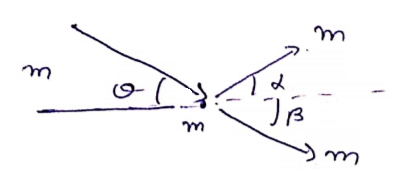
If m is not colliding head-on, along x-axis, use C.O.L.M
![]() -(1)
-(1)
Along y-axis, ![]() -(2)
-(2)
Use C.O.E.L
![]()
Squaring (1) and (2) and add them,
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Solution 64
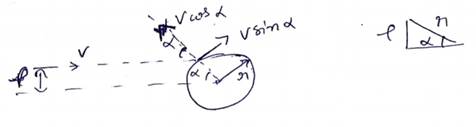
![]()
![]() {after
collision}
{after
collision}
![]()
Centre of Mass, Linear Momentum, Collision Exercise 169
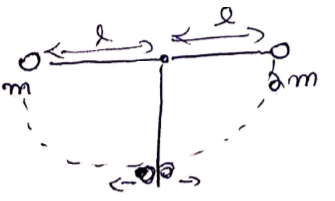
Solution 13
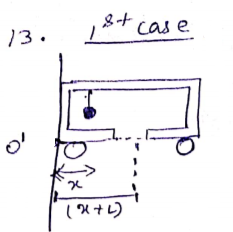
Take![]() as origin
as origin
![]()
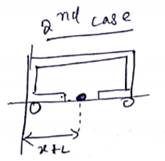
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Cart should be displaced ![]() cm for
COM of system to be same.
cm for
COM of system to be same.

