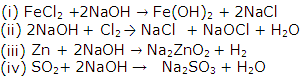Class 10 FRANK Solutions Chemistry Chapter 4 - Analytical Chemistry
Revise Chemistry concepts with our Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter 4 Analytical Chemistry. Learn to identify the given cations with clear answers by TopperLearning’s Chemistry experts. Relearn the concept of amphoteric oxides. Find out how to write balanced equations to explain the reaction of amphoteric oxides with a caustic alkali.
With our ICSE Class 10 Chemistry textbook solutions, you can practise MCQs, fill in the blanks and other scoring questions in Chemistry. For resolving doubts related to chemical equations or other topics, ask your questions at the ‘UnDoubt’ section of our website.
Analytical Chemistry Exercise 85
Solution 1
(b) Cupric salts = Blue
(c) Aluminium salts = Colourless
(d) Ferrous salts= Light green
(e) Ferric salts = Yellow
(f) Calcium salts = Colourless
Solution 2

Solution 3

Solution 4
Solution 5

Solution 6
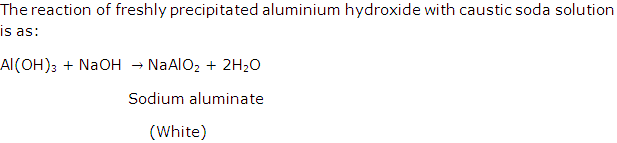
Solution 7

Solution 8

Solution 9
Solution 10

Solution 11
Analytical Chemistry Exercise 86
Solution 12

Solution 13
Solution 14

Solution 15
(b) Al2O3
(c) Na2ZnO2
Solution 16
(a) transition, Cr3+, Fe2+, MnO44-.
(b) Zn(OH)2
(c) NH4Cl
(d) Al2O3, Al
(e) NH4OH
Solution 17
(i) Green
(ii) ![]()
(iii) Colourless
(iv) H2
(v) Copper(II) salts
Analytical Chemistry Exercise 87
Solution 1992-1
(a) Addition of KCN
(b) Addition of excess of NaOH.
(c) Addition of excess of NH4OH.
Solution 1993-1

Solution 1995-1
(b) The cation present in solution B is Cu2+. The probable colour of solution B is blue.
Solution 1996-1

Solution 1996-2
(i) Solution of Calcium carbonate:
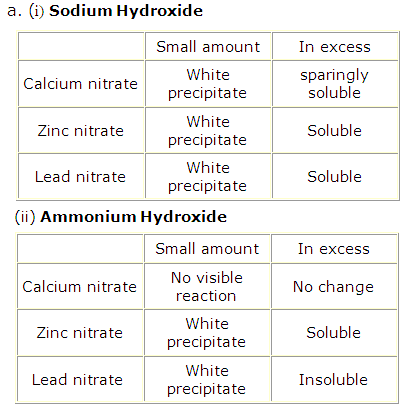
Calcium carbonate is CaCO3 and contains Ca2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Ca2+ since its addition to calcium carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Ca(OH)2 which are sparingly soluble in excess of NaOH.
(ii) Solution of Lead carbonate:
Lead carbonate is PbCO3 and contains Pb2+ ions. Ammonium hydroxide solution NH4OH can be used to identify Pb2+ since its addition to lead carbonate solution will give white precipitates of Pb(OH)2 which are insoluble in excess of NH4OH.
(iii) Solution of Zinc carbonate:
Zinc carbonate is ZnCO3 and contains Zn2+ ions. Sodium hydroxide solution NaOH can be used to identify Zn2+ since its addition to zinc carbonate solution will give white gelatinous precipitates of Zn(OH)2 which are soluble in excess of NaOH.
Solution 1996-3
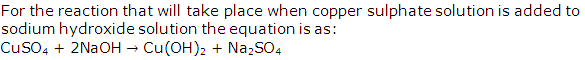
Solution 1997-1
Solution 1998-1

Analytical Chemistry Exercise 88
Solution 1999-1

Solution 2000-1
Solution 2001-1

Solution 2003-1
Solution 2003-2

Analytical Chemistry Exercise 89
Solution 2004-1

Solution 2005-1
(ii) C and F (Iron (III) chloride and Zinc chloride)
(iii) D (Lead nitrate)
(iv) A (Copper nitrate)
(v) F (Zinc chloride)
Solution 2006-1

Analytical Chemistry Exercise 90
Solution 2009-1
Solution 2009-2
(i) P is Ferric chloride
(ii) Q is an ammonium salt
(iii) R is ferrous sulphate
Solution 2009-3
(ii) When NaOH solution is added to the given solution, iron (II) chloride gives dirty green precipitate while reddish brown precipitate is obtained with iron(III) chloride.
Solution 2010-1
(i) Ammonia
(ii) Alkaline
(iii) Ammonium
(iv) Hydroxyl
(v) Dirty green
Solution 2010-2
![]()
Solution 2011-1
(i) Lead
(ii) Hydrogen sulphide
Analytical Chemistry Exercise 91
Solution 2013-1
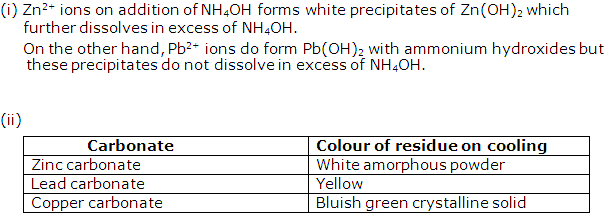
(i) (a) When NH4OH is added to copper (II) nitrate solution in small quantities, a pale blue precipitate is observed.
(b) When added in excess, NH4OH dissolves to give an inky blue solution forming a complex salt.
(ii) (a) When NH4OH is added to zinc nitrate solution in minimum quantity, it forms a gelatinous white precipitate.
(b) When added in excess, it dissolves to form a complex salt.
Solution 2014-1
(i) Iron (II):
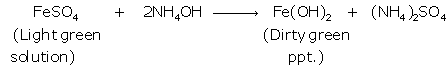
Iron (III):
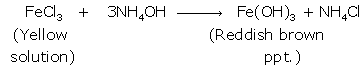
(ii) Pb(NO3)2+2 NH4OH → Pb(OH)2+2NH4NO3
On adding excess of NH4OH, chalky white ppt. of
insoluble Pb(OH)2 is formed.
ZnSO4 + 2NH4OH → Zn(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4
With excess of NH4OH, white gelatinous ppt. of soluble Zn(OH)2 is formed.
Solution 2016-1
i) When NH4OH is added to copper sulphate solution drop-wise, a pale blue ppt. is obtained.
CuSO4 + 2NH4OH → Cu(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4 + 4H2O
With excess of NH4OH, the ppt. dissolves to give a deep blue solution of tetra amine copper (II) sulphate.
Cu(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4 + NH4OH → [Cu(NH3)4]SO4 + H2O
ii) When NH4OH is added to zinc sulphate solution drop-wise, a white, gelatinous ppt. is obtained.
ZnSO4 + 2NH4OH → Zn(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4
With an excess of NH4OH, the ppt. dissolves to give a colourless solution of tetra amine zinc (II) sulphate.
Zn(OH)2 + (NH4)2SO4 + 2NH4OH → [Zn(NH3)4]SO4 + 4H2O
Solution 2017-1
Potassium sulphite on reacting with hydrochloric acid releases sulphur dioxide.
Solution 2017-2
Copper chloride