Class 10 FRANK Solutions Biology Chapter 6 - Photosynthesis
Get access to Frank Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 6 Photosynthesis at our study portal. TopperLearning helps you ace your Biology board exam by giving you all the necessary chapter resources including textbook solutions. Our Frank Solutions for learning photosynthesis include topics like plant pigments, photolysis, heterotroph, chlorophyll, chloroplasts etc.
Also, learn the chemical equation of photosynthesis with our textbook solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology. Practice tests, sample papers and previous years’ papers are some of the other online learning resources that you can use to study chapter concepts.
74
75
76
77
78
Photosynthesis Exercise 74
Solution 2
(i) Plant pigments - Plant pigments are a variety of different kinds of molecules present in plants that absorb certain wavelengths of light while reflecting others.
(ii) Quantum - Quantum are the discrete packets which stores energy and these particles can be changed from one form to another.
(iii) Organic food - The food that is produced by using methods that do not involve synthetic inputs such as synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers is called organic food.
(iv) Light reaction - The reaction of photosynthesis which takes place in the presence of light is called light reaction.
(v) Photolysis in photosynthesis - The process of splitting of water by sunlight during light reaction of photosynthesis is called photolysis in photosynthesis.
(ii) Quantum - Quantum are the discrete packets which stores energy and these particles can be changed from one form to another.
(iii) Organic food - The food that is produced by using methods that do not involve synthetic inputs such as synthetic pesticides and chemical fertilizers is called organic food.
(iv) Light reaction - The reaction of photosynthesis which takes place in the presence of light is called light reaction.
(v) Photolysis in photosynthesis - The process of splitting of water by sunlight during light reaction of photosynthesis is called photolysis in photosynthesis.
Solution 3
Solution 4
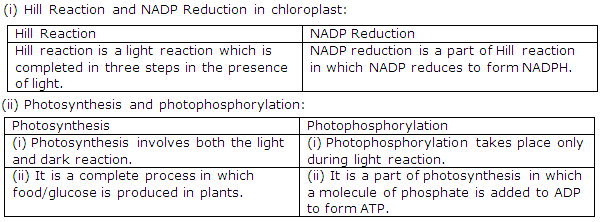
Solution 5
(i) The aim of the experiment is to prove that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis.
(ii) Potassium hydroxide absorbs CO2 from the surrounding. It is placed to remove CO2 within the conical flask.
(iii) The leaf inside the conical flask would be tested for the presence of starch by the application of iodine.
(iv) The expected result of the above test is - No change in the colour will be observed.
(v) Yes, it is necessary to similarly test on the outer leaf also to show that leaves present in CO2 show photosynthesis.
(ii) Potassium hydroxide absorbs CO2 from the surrounding. It is placed to remove CO2 within the conical flask.
(iii) The leaf inside the conical flask would be tested for the presence of starch by the application of iodine.
(iv) The expected result of the above test is - No change in the colour will be observed.
(v) Yes, it is necessary to similarly test on the outer leaf also to show that leaves present in CO2 show photosynthesis.
Solution 6
(i) 1 - Upper Epidermis; 2 - Palisade layer / chloroplast; 3 - Xylem; 4 - Phloem; 5 - Guard cell
(ii) The two arrows show the release of oxygen and water vapours during the daytime and carbon dioxide and very less amount of oxygen is released during the night.
(iii) Yes, one more arrow can be added to show the absorption of carbon dioxide by the leaf.
(iv) One vein has been shown in this section.
(ii) The two arrows show the release of oxygen and water vapours during the daytime and carbon dioxide and very less amount of oxygen is released during the night.
(iii) Yes, one more arrow can be added to show the absorption of carbon dioxide by the leaf.
(iv) One vein has been shown in this section.
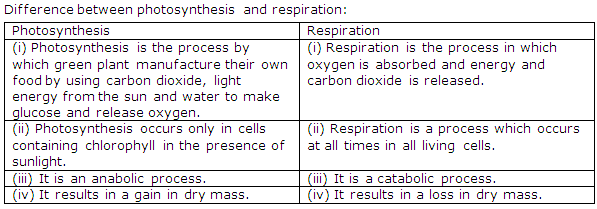
Solution 7
Solution 8
Solution 9
Solution 1
Photosynthesis Exercise 75
Solution 15
Solution 16
Coelus and mushroom.
Solution 17
It is because the upper surfaces of broad leaves are directly exposed to sunlight which leads to maximize the rate of photosynthesis.
Solution 18
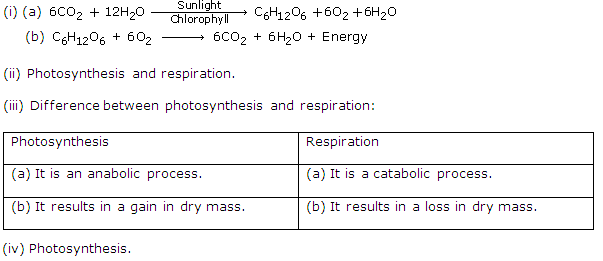
Solution 19
Chlorophyll.
Solution 20
True
Solution 21
False
Solution 22
During the day transpiration and photosynthesis are interlinked as the stomata opens to facilitate the inward diffusion of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis which also leads to loss of water vapours to the outside during transpiration.
Solution 10
(i) The objective of this experiment is to prove that oxygen is released during photosynthesis.
(ii) Hydrilla
(iii) Oxygen
(iv) The rate of photosynthesis will increase and the rate of bubbling also increases when sodium bicarbonate is added.
(v) Photosynthesis will not take place.
(ii) Hydrilla
(iii) Oxygen
(iv) The rate of photosynthesis will increase and the rate of bubbling also increases when sodium bicarbonate is added.
(v) Photosynthesis will not take place.
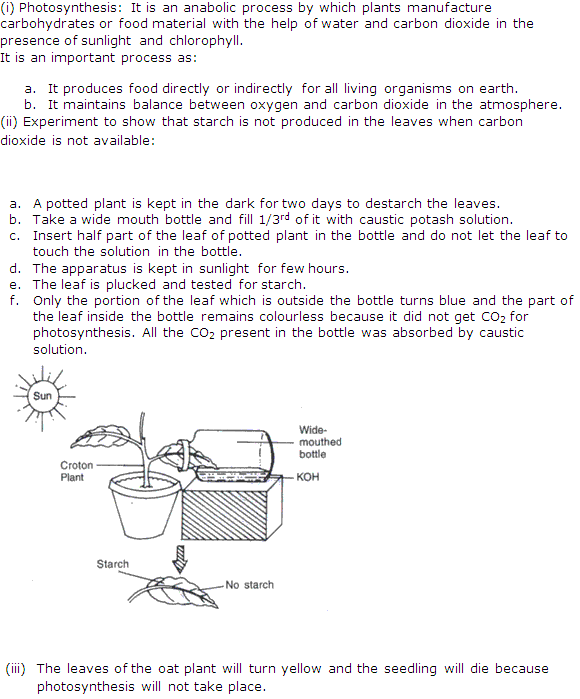
Solution 11
(i) The leaf is then treated with iodine solution.
(ii) The leaf from first plant will not show starch test while the leaf from second plant will become blue-black showing the presence of starch.
(iii) It is necessary to grease the glass sheet to prevent the entry of air containing CO2.
(iv) The hypothesis that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis is being tested in this experiment.
(ii) The leaf from first plant will not show starch test while the leaf from second plant will become blue-black showing the presence of starch.
(iii) It is necessary to grease the glass sheet to prevent the entry of air containing CO2.
(iv) The hypothesis that CO2 is necessary for photosynthesis is being tested in this experiment.
Solution 12
Light intensity is directly proportional to sunlight. Increase in intensity of light increases the rate of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is maximum in red light followed by blue light and is least in green light.
Solution 13
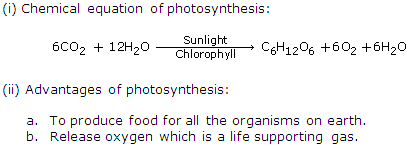
(i) Advantages of photosynthesis:
(a) To produce food for all the organisms on earth.
(b) Release oxygen which is a life supporting gas.
(ii) Respiration is a catabolic process while photosynthesis is an anabolic process. During respiration oxygen is taken and carbon dioxide is given out while during photosynthesis carbon dioxide is taken and oxygen is given out.
(iii) Chlorophyll is a green coloured pigment found in green plants. it absorbs light energy which is utilized for the formation of ATP and reduction of NADP during photosynthesis.
(a) To produce food for all the organisms on earth.
(b) Release oxygen which is a life supporting gas.
(ii) Respiration is a catabolic process while photosynthesis is an anabolic process. During respiration oxygen is taken and carbon dioxide is given out while during photosynthesis carbon dioxide is taken and oxygen is given out.
(iii) Chlorophyll is a green coloured pigment found in green plants. it absorbs light energy which is utilized for the formation of ATP and reduction of NADP during photosynthesis.
Solution 14

Photosynthesis Exercise 76
Solution 23
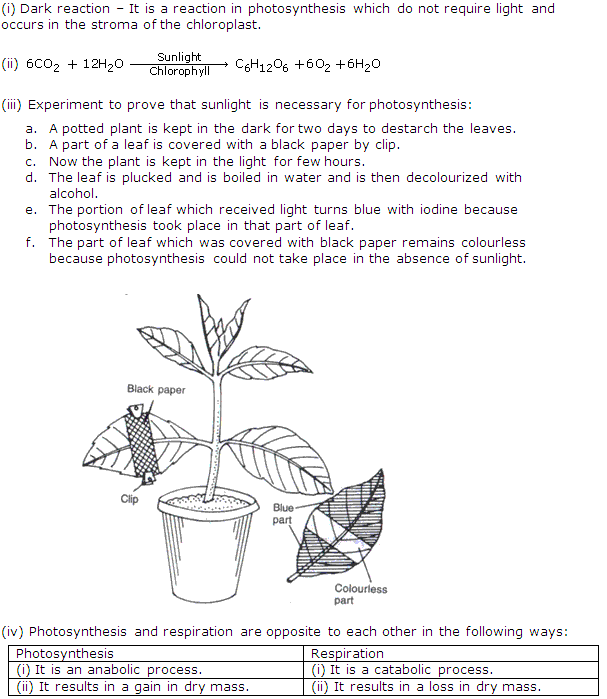
(i) Destarched plant is the plant which lacks starch. Destarching is done by keeping the plant in dark for 2-3 days or covering a part of a leaf with a black paper by clip.
(ii) (a) The leaf is plucked and is boiled in water and decolourized with alcohol.
(b) The portion of leaf which received light turns blue with iodine because photosynthesis took place in that part of leaf.
(c) The part of leaf which was covered with black paper remains colourless because photosynthesis could not take place in the absence of sunlight.
This shows that starch is not manufactured in the absence of light.
(ii) (a) The leaf is plucked and is boiled in water and decolourized with alcohol.
(b) The portion of leaf which received light turns blue with iodine because photosynthesis took place in that part of leaf.
(c) The part of leaf which was covered with black paper remains colourless because photosynthesis could not take place in the absence of sunlight.
This shows that starch is not manufactured in the absence of light.
Solution 24
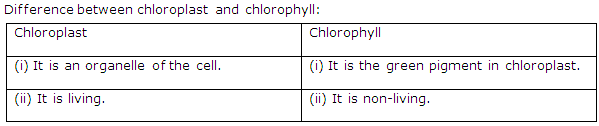
(i) Chloroplast.
(ii) Glucose and oxygen.
(iii) Fungi, insects and animals.
(iv) Photolysis.
(v) Magnesium.
(vi) Chloroplast.
(ii) Glucose and oxygen.
(iii) Fungi, insects and animals.
(iv) Photolysis.
(v) Magnesium.
(vi) Chloroplast.
Solution 25
(i) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) True
(v) True
(vi) True
(vii) False
(viii) False
(ix) True
(ii) True
(iii) False
(iv) True
(v) True
(vi) True
(vii) False
(viii) False
(ix) True
Solution 26
(i) Photosynthesis
(ii) Atmosphere
(iii) Glucose
(iv) Yellow
(v) Chloroplast
(vi) Glucose and oxygen
(vii) Stomata
(ii) Atmosphere
(iii) Glucose
(iv) Yellow
(v) Chloroplast
(vi) Glucose and oxygen
(vii) Stomata
Solution 27
(i) (d) During night
(ii) (e) Green plants
(iii) (f) Oxygen
(iv) (b) Light reaction
(v) (a) Decomposers
(ii) (e) Green plants
(iii) (f) Oxygen
(iv) (b) Light reaction
(v) (a) Decomposers
Solution 28
Chloroplasts are the cell organelles in green plants which have chlorophyll and thus serve as the main site of photosynthesis.
Solution 29
(i) Large surface area of leaves.
(ii) Presence of more stomata.
(iii) The thinness of leaves.
(ii) Presence of more stomata.
(iii) The thinness of leaves.
Solution 30
Carbon cycle is a series of chemical reactions in which atmospheric carbon dioxide is used by the organisms and returned to the atmosphere. Photosynthetic plants use carbon as carbon dioxide from the air synthesizing organic compounds. By respiration, burning, decay, etc. the carbon is returned to the atmosphere.
Solution 31
Carbon in the form of carbon dioxide enters living organisms and then goes back to the atmosphere through several pathways forming the true carbon cycle. Thus, it helps in maintaining the balance of nature.
Solution 32
The amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increasing due to increased human activities like burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, etc. which cause the rise in global temperatures. This global warming result in melting of polar ice caps, floods in coastal areas, disturbance in hydrogenic cycle etc. Thus "Human activities are harmful to the balance of nature".
Solution 33
Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by:
(i) Producers - Producers or green plants use carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. A small amount of carbon dioxide is used by chemosynthetic bacteria also.
(ii) Marine Organisms - Some amount of carbon dioxide is directly fixed by a few marine organisms and sea water absorbs carbon dioxide in the form of dissolved carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, carbonate and bicarbonates.
(i) Producers - Producers or green plants use carbon dioxide through photosynthesis. A small amount of carbon dioxide is used by chemosynthetic bacteria also.
(ii) Marine Organisms - Some amount of carbon dioxide is directly fixed by a few marine organisms and sea water absorbs carbon dioxide in the form of dissolved carbon dioxide, carbonic acid, carbonate and bicarbonates.
Photosynthesis Exercise 77
Solution 34
(a) Carbon dioxide is returned back to the atmosphere mainly through the following ways:
(i) Respiration - Animals and plants respire and release carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
(ii) Decay - Plants and animals decay organic matter with the help of bacteria and fungi and release carbon dioxide.
(iii) Combustion - Plants and animals which got buried under the soil changed into coal and oil and releases carbon dioxide when these are burnt.
(iv) Ocean water - Carbon dioxide occurs in the form of lime stone in molluscan shells and as by product of photosynthesis in marine water.
(b) (i) To show that sunlight is needed for photosynthesis.
(ii) Yes, the uncovered portion of the experimental leaf is the control.
(iii) To destarch the leaf.
(iv) 1. Boil the leaf in alcohol.
2. Wash the leaf in water to make it soft.
3. Add iodine solution on the leaf. The portion uncovered shows blue-black colour and the portion covered shows brown colour. This indicates that sunlight is needed for photosynthesis.
(i) Respiration - Animals and plants respire and release carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
(ii) Decay - Plants and animals decay organic matter with the help of bacteria and fungi and release carbon dioxide.
(iii) Combustion - Plants and animals which got buried under the soil changed into coal and oil and releases carbon dioxide when these are burnt.
(iv) Ocean water - Carbon dioxide occurs in the form of lime stone in molluscan shells and as by product of photosynthesis in marine water.
(b) (i) To show that sunlight is needed for photosynthesis.
(ii) Yes, the uncovered portion of the experimental leaf is the control.
(iii) To destarch the leaf.
(iv) 1. Boil the leaf in alcohol.
2. Wash the leaf in water to make it soft.
3. Add iodine solution on the leaf. The portion uncovered shows blue-black colour and the portion covered shows brown colour. This indicates that sunlight is needed for photosynthesis.
Solution 35
(i) (e) 5
(ii) (a) 1
(iii) (b) 2
(iv) (e) 5
(ii) (a) 1
(iii) (b) 2
(iv) (e) 5
Solution 36
(1) leaves
(2) water
(3) hydrogen ion
(4) photolysis
(5) hydrogen
(6) NADPH2
(7) ATP
(8) photophosphorylation
(9) glucose
(10) polymerization
(2) water
(3) hydrogen ion
(4) photolysis
(5) hydrogen
(6) NADPH2
(7) ATP
(8) photophosphorylation
(9) glucose
(10) polymerization
Solution 37
(i) (d) 3.5
(ii) (b) Oxygen
(iii) (c) Water
(iv) (c) Decrease because the temperature drops.
(v) (b) Increases because more photosynthesis occurs.
(ii) (b) Oxygen
(iii) (c) Water
(iv) (c) Decrease because the temperature drops.
(v) (b) Increases because more photosynthesis occurs.
Photosynthesis Exercise 78
Solution 39
(i) (d) To stop synthesis process in the leaves.
(ii) (c) Chloroplasts
(iii) (d) split water
(iv) (c) Palisade mesophyll
(v) (b) ADP
(vi) (b) liberate O2
(vii) (a) Grana
(viii) (b) Red light
(ix) (d) Carbon dioxide
(x) (d) water, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll and sunlight
(ii) (c) Chloroplasts
(iii) (d) split water
(iv) (c) Palisade mesophyll
(v) (b) ADP
(vi) (b) liberate O2
(vii) (a) Grana
(viii) (b) Red light
(ix) (d) Carbon dioxide
(x) (d) water, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll and sunlight
Solution 38


