Volume and Surface Area of Solids
Volume and Surface Area of Solids Synopsis
Synopsis
Introduction to Surface area and Volume
- Surface area of a solid is the sum of the areas of all its faces.
- The space occupied by a solid object is the volume of that object.
- Cuboid
If l, b, h denote respectively the length, breadth and height of a cuboid, then:
- Lateral surface area or Area of four walls = 2(ℓ + b) h
- Total surface area = 2(ℓb + bh + hℓ)
- Volume = ℓ x b x h
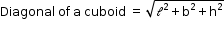
- Cube
If the length of each edge of a cube is 'a' units, then:
- Lateral surface area = 4 x (edge)2
- Total surface area = 6 x (edge)²
- Volume = (edge)3
- Diagonal of a cube =
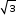 x edge
x edge
- Cylinder
Right circular cylinder
If r and h respectively denote the radius of the base and the height of a right circular cylinder, then:
- Area of each end or Base area = pr²
- Area of curved surface or lateral surface area = perimeter of the base x height = 2p rh
- Total surface area (including both ends) = 2prh + 2pr² = 2pr (h + r)
- Volume = Area of the base x height = pr²h
- Hollow cylinder
If R and r respectively denote the external and internal radii of a right circular hollow cylinder and h denotes its height, then:
- Area of each end = pR² - pr²
- Area of curved surface = 2p(R + r)h
- Total surface area = (Area of curved surface) + 2(Area of each end)
= 2p(R + r)h + 2 (pR² - pr²)
- Right circular cone
If r, h and l respectively denote the radius, height and slant height of a right circular cone, then:
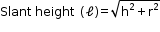
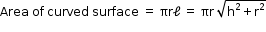
- Total surface area = Area of curved surface + Area of base = prℓ + pr² = pr (ℓ + r)
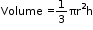
- Sphere
- If r is the radius of a sphere, then:
- Surface area = 4pr²
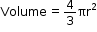
- Hemisphere
If r is the radius of a hemisphere, then: - Area of curved surface = 2pr²
- Total surface Area = Area of curved surface + Area of base
= 2pr² + pr²
= 3pr²
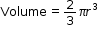
- Combination of Solids
- The total surface area of the solid formed by the combination of solids is the sum of the curved surface area of each of the individual solids.
- The volume of the solid formed by the combination of basic solids is the sum of the volumes of each of the basic solids.
- Frustum of the cone
- If a right circular cone is cut off by a plane parallel to its base, then the portion of the cone between the plane and the base of the cone is called a frustum of the cone.
- If h is the height, l is the slant height, R and r are the radii of the upper and lower ends of a frustum of a cone, then:
- Curved surface area = p (R + r) ℓ
- Total surface area = p(R + r) ℓ +p[R² + r²]
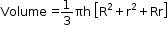
Conversion of Solids
- When a solid is melted and converted to another, volume of both the solids remains the same, assuming there is no wastage in the conversions. However, the surface area of the two solids may or may not be the same.
- The solids having the same curved surface do not necessarily occupy the same volume and vice versa.
Download complete content for FREE 

