Quadratic Equations
Quadratic Equations Synopsis
Synopsis
- An equation of the form ax2+bx +c = 0 is called a quadratic equation, where a, b, c are real numbers and a ≠ 0.
Roots of the quadratic equation
- The value of x that satisfies an equation is called the roots of the equation.
- A real number a is said to be a solution/root of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 if aa2 + ba + c = 0.
- A quadratic equation has at most two roots
Solving Quadratic Equation by:
- Splitting the middle term (or factorization) method
If ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ≠ 0, can be reduced to the product of two linear factors, then the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 can be found by equating each factor to zero.
Steps involved in solving quadratic equationax2 +bx+c = 0(a ≠0) by splitting the middle term (or factorization) method:
Step 1: Find the product ac.
Step 2: Find the factors of ‘ac’ that add up to b, using the following criteria:
i.If ac > 0 and b > 0, then both the factors are positive.
ii.If ac > 0 and b < 0, then both the factors are negative.
iii.If ac < 0 and b > 0, then larger factor is positive and smaller factor is negative.
iv.If ac < 0 and b < 0, then larger factor is negative and smaller factor is positive.
Step 3: Split the middle term into two parts using the factors obtained in the above step.
Step 4: Factorize the quadratic equation obtained in the above step by grouping method. Two factors will be obtained.
Step 5: Equate each of the linear factors to zero to get the value of x. - Completing the square method
Any quadratic equation can be converted to the form (x + a)2 – b2 = 0 or (x – a)2 + b2 = 0 by adding and subtracting the constant term. This method of finding the roots of quadratic equation is called the method of completing the square.
The steps involved in solving a quadratic equation by completing the square, are as follows:
Step 1: Make the coefficient of x2 unity.
Step 2: Express the coefficient of x in the form 2⨯ x ⨯ p.
Step 3: Add and subtract the square of p.
Step 4: Use the square identity (a + b)2 or (a – b)2 to obtain the quadratic equation in the required form (x + a)2 - b2 = 0 or (x – a)2 + b2 = 0.
Step 5: Take the constant term to the other side of the equation.
Step 6: Take the square root on both the sides of the obtained equation to get the roots of the given quadratic
equation. - Quadratic formula
The roots of a quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 (a ≠ 0) can be calculated by using the quadratic
formula: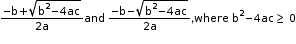
If b2 – 4ac < 0, then equation does not have real roots.
- Discriminant of a quadratic equation
For the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0, a ¹ 0, the expression b2 – 4ac is known as discriminant.
- Nature of Roots
Let f(x) = ax2 + bx + c = 0 be the quadratic equation, the discriminant D = b2 – 4ac. - Relation between roots and coefficients:
Let a, b be the roots of the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0 then
Note: Quadratic equation can be rewritten as.x2-(α+β) x+ α.β =0
- Equations reducible to Quadratic Equations
There are many equations which are not in the quadratic form but can be reduced to the quadratic form by simplifications.
Type I: ax2n + bxn + c = 0
Put xn = y
So, the equation reduces to ay2 + by +c = 0
Now solve for y and hence for x.
Type II: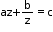 where a, b, c are constants
where a, b, c are constants
Make it az2 – cz + b = 0
Now, solve it for z.
Type III: (x+a) (x=b) (x+c) (x+d)+ k = 0,where the sum of two of the quantities is equal to the sum of the other tw)o.
Example:
(x+1)(x+2)(x+3)(x+4) + 1= 0
As sum of 1 and 4 is equal to sum of 2 and 3
⟹ [(x+1)(x+4)][(x+2)(x+3)+1 =0
⟹ (x2 + 5x +4 )(x2+5x+6)+1=0
Take x2+5x =y
⟹ (y+4)(y+6)+1=0
⟹ y2+10y+24+1=0
⟹ y2+10y +25 =0
⟹ (y+5)2 =0
⟹ y=-5
⟹ x2 +5x+5=0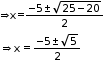
- Formation of Equations with given roots
Suppose the given roots are α and β
Therefore x = α and x =β
⟹ (x- α) = 0 and (x- β ) =0
The equation forms will be
(x- α)(x- β)=0
⟹ x2 –( α+ β)x+ α β=0
⟹ x2-(sum of roots)x + Product of roots =0
- Applications of quadratic equations
- The applications of quadratic equation can be utilized in solving real life problems.
- Following points can be helpful in solving word problems:
- Every two digit number ‘xy’ where x is a ten’s place and y is a unit’s place can be expressed as. Xy= 10x +y.
- Downstream: It means that the boat is running in the direction of the stream
Upstream: It means that the boat is running in the opposite direction of the stream
Thus, if
Speed of boat in still water is x km/h
And the speed of stream is y km/h
Then the speed of boat downstream will be (x + y) km/h and in upstream it will be (x − y) km/h.
If a person takes x days to finish a work, then his one day's work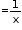
Download complete content for FREE 



