NEET Class neet Answered
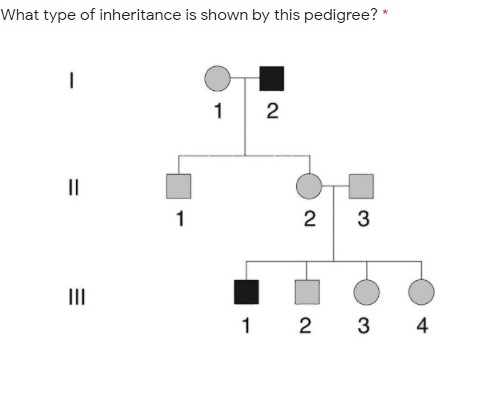
What type of inheritance is shown by this pedigree?
Asked by dhruvbaptu02 | 05 Sep, 2021, 01:29: PM
1st generation - Male is affected in this pedigree while female is normal.
2nd generation – Male and female both are normal.
3rd generation – One male is affected while the other male is normal. Both the females are normal.
The given pedigree shows X-linked inheirtance.
An X-linked trait is carried on the X chromosome. In pedigrees depicting X-linked inheritance, usually only males are affected and, although affected males may occur in consecutive generations, transmission is always through females. This is based on the fact that males have a single X chromosome (in addition to their Y chromosome), which they always inherit from their mother and will always pass on to their daughters but never to their sons. Females, on the other hand, have two X chromosomes. Therefore, they can be carriers of an X-linked mutation, but in most cases are phenotypically unaffected because they have a second (nonmutated) X chromosome, compensating for whatever loss of function is caused by the mutated gene.
Answered by Sheetal Kolte | 06 Sep, 2021, 11:50: AM
Concept Videos
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by prakhart.278 | 05 Jan, 2023, 01:44: PM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by 8709096763raj | 29 Mar, 2022, 10:00: PM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by dhruvbaptu02 | 05 Sep, 2021, 01:29: PM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by patra04011965 | 06 Aug, 2021, 08:50: PM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by 7085ankitsingh10a | 19 May, 2021, 10:45: AM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by sweety.agariya1010 | 20 Jan, 2021, 08:05: PM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by patra04011965 | 18 Jun, 2020, 09:10: PM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by m.shajahan1991 | 18 Jun, 2020, 03:56: PM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by arnavvidudala20050 | 24 Apr, 2020, 10:40: AM
NEET neet - Biology
Asked by dr_pradip27121972 | 22 Apr, 2020, 03:04: PM