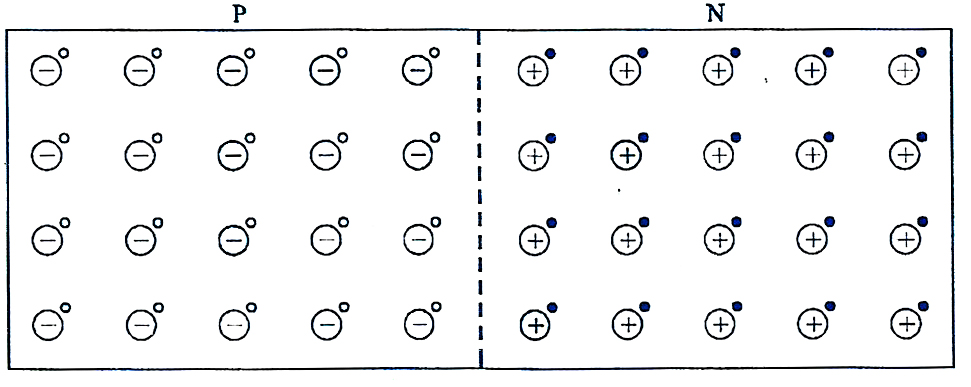
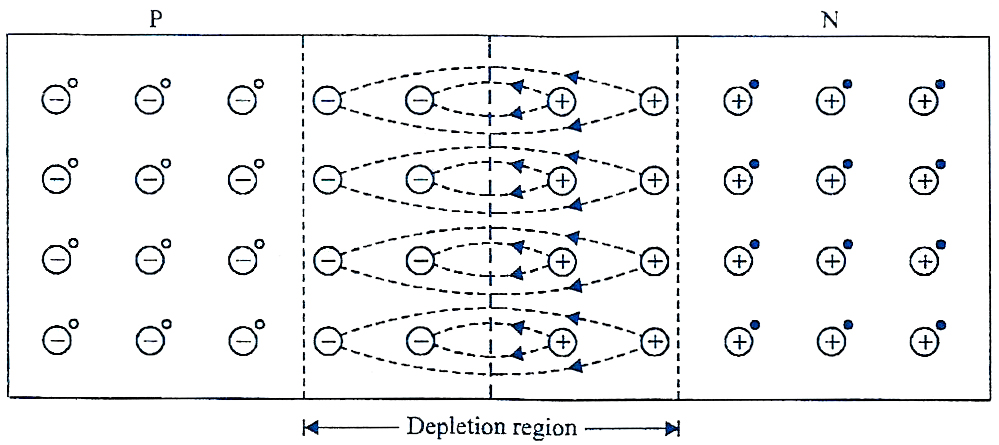
"The depletion region of unbiased pn junction contains only fixed ions".Sir, isn't this statement true?I've found in a mcqs book(arihant publications) that the depletion region of unbiased pn junction contains both es and holes. i got confused .please give me an answer sir.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
You have rated this answer /10
Browse free questions and answers by Chapters
- 1 Electric Charges and Fields
- 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
- 3 Current Electricity
- 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism
- 5 Magnetism and Matter
- 6 Electromagnetic Induction
- 7 Alternating Current
- 8 Electromagnetic Waves
- 9 Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
- 10 Wave Optics
- 11 Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
- 12 Atoms
- 13 Nuclei
- 14 Semiconductor Electronics
- 15 Communication Systems
