CBSE Class 8 Answered
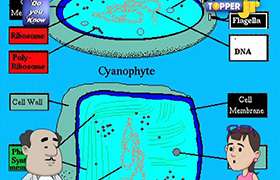
Different organelles present in a cell are as follows:
|
CELL ORGANELLES |
||
|
NATURE AND OCCURRENCE |
MAIN CHARACTERISTICS |
MAIN FUNCTIONS |
|
Plasma membrane/Cell membrane |
||
|
1. Forms the outermost covering in animal cells 2. Lies next to the cell wall in plant cells
|
1. Very thin, flexible, delicate, living membrane 2. Possesses tiny pores
|
1. Separates cellular material from its surroundings 2. Acts as an effective barrier and regulates the entry of substances, in and out of the cell 3. Maintains shape of the cell (in animal cells) |
|
Cell wall (In plant cells only) |
||
|
1. Non-living rigid protective covering situated just outside the plasma membrane
|
1. Mainly composed of cellulose
|
1. Gives rigidity and shape to the plant cells 2. Allows substances in solution to enter and leave the cell, without any obstruction 3. Provides protection
|
|
Cytoplasm |
||
|
1. Content inside the plasma membrane, excluding the nucleus
|
1. Transparent jelly-like material 2. Contains a mixture of water and soluble organic and inorganic compounds and various cell organelles |
1. Different organelles contained in it perform different functions 2. Centre of all metabolic activities
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) |
||
|
1. Irregular network of tubular double membrane
|
1. Continuous with the plasma membrane on the outside and nuclear membrane on the inside 2. May be smooth (SER) or rough (RER) |
1. Supportive framework of the cell 2. RER synthesizes proteins, while SER secretes lipids 3. Provides pathway for the distribution of nuclear material |
|
Mitochondria |
||
|
1. Have varied shapes, but usually are sausage-like
|
1. Tiny rod-shaped or spherical organelles 2. Double walled, inner wall thrown into folds, called cristae |
1. Release and store energy 2. Synthesis of respiratory enzymes 3. Synthesis of energy-rich compounds |
|
Golgi Apparatus (In animal cells) Dictyosomes (In plant cells) |
||
|
1. Stacks of flattened membrane sacs
|
1. Exist as an extensive network near the nucleus in an animal cell and are freely distributed in plant cells |
1. Synthesis and secretion of enzymes, hormones, etc. 2. Involved in the synthesis of plasma membrane, cell wall, etc. |
|
Ribosomes |
||
|
1. Dense, spherical, small granules, either scattered in the cytoplasm or attached to the outside of ER |
1. Single walled, dense spherical bodies, composed mainly of RNA and proteins |
1. Synthesis of proteins
|
|
Lysosomes |
||
|
1. Simple, tiny, single membrane bound sacs 2. Evenly distributed in cytoplasm |
1. Membranous sacs budded out from Golgi bodies 2. Contain 40 different types of enzymes |
1. Intracellular digestion 2. Suicide bags of the cell. Rapidly destroy organelles, in case of cell ageing or injury |
|
Centrosome (In animal cells only) |
||
|
1. Region surrounding centrioles located near nucleus |
1. Contain one or two centrioles |
1. Initiates and regulates cell division
|
|
Plastids (In plant cells only) |
||
|
1. Have their own genome
|
1. Different kinds, chromoplasts, chloroplasts and leucoplasts 2. Possess disc-like structures called thylakoids containing chlorophyll |
1. Chromoplasts- Impart colour to flowers and fruits 2. Chloroplasts- Trap solar energy for photosynthesis 3. Leucoplasts- Store starch |
|
Nucleus |
||
|
1. Centrally located spherical cellular component
|
1. Largest cell organelle 2. Mostly spherical and dense 3. Nuclear membrane with pores, which allow substances to enter and leave the nucleus |
1. Regulates cell functions 2. Cell dies, in the absence of nucleus 3. Contains chromosomes, made up of genes, that control hereditary characteristics |
|
Nucleolus |
||
|
1. Embedded within the nucleus of the cell
|
1. One or more in number 2. Round-shaped |
1. Produces ribosomes 2. Participates in proteins synthesis by forming and storing RNA |
|
Chromatin fibres |
||
|
1. Embedded within the nucleus of the cell |
1. Network of thread-like structures, made up of DNA |
1. Chromosomes carry hereditary information or genes |
|
Vacuoles |
||
|
1. Fluid-filled or solid-filled and membrane-bounded spaces 2. Kind of storage sacs
|
1. Non-living structures 2. Clear spaces with water or other substances in solution 3. Larger in plant cells and fewer and smaller in animal cells |
1. Storage of water and other substances, food, pigments and waste products 2. Gives turgidity to the cells
|
|
Granules |
||
|
1. Non-living structures
|
1. Small particles, crystals or droplets
|
1. Starch (in plant cells), glycogen (in animal cells)and fat-containing granules serve as food for the cell |