CBSE Class 11-science Answered
Molecular orbital theory can give us information about both ionic and covalent molecules and naturally predicts which molecules will be ionic and which will be covalent.
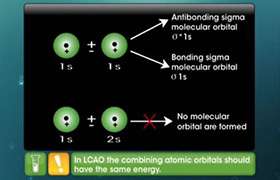
When two atomic orbitals overlap, they can be in phase (added) or out of phase (subtracted). When they overlap in phase, constructive inter-action occurs in the region between the nuclei, and a bonding orbital is produced. The energy of the bonding orbital is always lower (more stable) than the energies of the combining orbitals. When they overlap out of phase, destructive interaction reduces the probability of finding electrons in the region between the nuclei, and an antibonding orbital is produced. This is higher in energy (less stable) than the original atomic orbitals. The overlap of two atomic orbitals always produces two MOs: one bonding and one anti-bonding.
In a bonding molecular orbital, the electron density is high between the two atoms, where it stabilizes the arrangement by exerting a strong attraction for both nuclei. By contrast, an anti-bonding orbital has a node (a region of zero electron density) between the nuclei; this allows for a strong net repulsion between the nuclei, which makes the arrangement less stable. Electrons are more stable (have lower energy) in bonding molecular orbitals than in the individual atoms. Placing electrons in antibonding orbitals, on the other hand, requires an increase in their energy, which makes them less stable than in the individual atoms.
Regards
Topperlearning Team.



 4.IF7
5.
4.IF7
5. B.Explain anti bonding and bonding hybridised orbitals.
C._________on hydrolysis gives ethyne while ______ on hydrolysis gives methane.
D.Explain why the colour of Bayer's reagent gets discharged when treated with an alkene.
E.i) State and explain Le Chatelier’s principle. On the basis of this principle discuss the conditions for obtaining the maximum yield of SO3 in the following reaction. 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌2SO3(g); ∆𝐻= - 42k.cal.(ii) Calculate the pH value of 0.01M CH3 COOH if it is 5% dissociated.
B.Explain anti bonding and bonding hybridised orbitals.
C._________on hydrolysis gives ethyne while ______ on hydrolysis gives methane.
D.Explain why the colour of Bayer's reagent gets discharged when treated with an alkene.
E.i) State and explain Le Chatelier’s principle. On the basis of this principle discuss the conditions for obtaining the maximum yield of SO3 in the following reaction. 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌2SO3(g); ∆𝐻= - 42k.cal.(ii) Calculate the pH value of 0.01M CH3 COOH if it is 5% dissociated.