explains Boyle's Law and charle's law on basis of kinetic molecular theory of gases
Boyls Law:
At constant temperature, the volume of a given mass of a dry gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
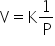
K = constant
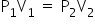
Charles's Law
At constant pressure, the volume of a given mass of a dry gas increases or decreases by of its
original volume at 0°C for each degree centigrade rise or fall in temperature.
At temperature T (K) and Volume V (cm3 )
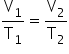
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
You have rated this answer 2/10
Browse free questions and answers by Chapters
- 1 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- 2 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- 3 States of Matter
- 4 Equilibrium
- 5 Hydrogen
- 6 Hydrocarbons
- 7 Environmental Chemistry
- 8 Solutions
- 9 Chemical Kinetics
- 10 Surface Chemistry
- 11 Biomolecules
- 12 Polymers
- 13 Chemistry in Everyday Life
- 14 Atomic Structure
- 15 Chemical Thermodynamics
- 16 Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
- 17 p-Block Elements
- 18 d - and f - Block Elements
- 19 Some Basic Principles of Organic Chemistry
- 20 Organic Compounds Containing Halogens
- 21 Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen
- 22 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen
- 23 Co-ordination Compounds
- 24 Purification and Characterisation of Organic Compounds
- 25 s-Block Element (Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals)
- 26 Solid State
- 27 Some Basic Concepts in Chemistry
- 28 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Metals
- 29 Principles Related to Practical Chemistry
