CBSE Class 11-science Answered
describe glycolysis briefly( long question carring 7 marks)
Asked by hrushikesh.barik | 21 Feb, 2018, 09:15: PM
- Glycolysis is also called the EMP pathway because the steps of this biochemical pathway were worked out by the German scientists Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof and Jakub Parnas in 1930s
- Glycolysis is the common pathway seen in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
- In plants, glucose is derived from sucrose.
- Sucrose is converted into glucose and fructose in the presence of the enzyme invertase
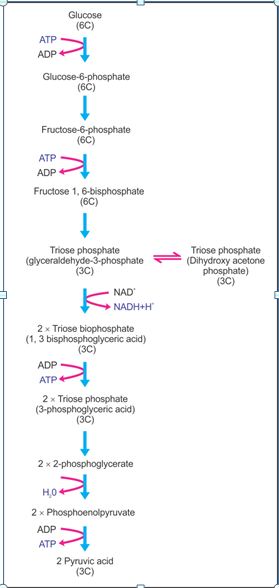
Steps in Glycolysis
- Glucose (6C) is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate (6C) in the presence of the enzyme hexokinase. One molecule of ATP is consumed during this step.
- Glucose-6-phosphate (6C) isomerises into fructose-6-phosphate (6C) in the presence of the enzyme phosphohexoisomerase.
- Fructose-6-phosphate (6C) is phosphorylated to fructose-1, 6-biphosphate (6C) in the presence of the enzyme phosphofructokinase (PFK). One molecule of ATP is used during this step.
- Fructose-1, 6-biphosphate (6C) splits into two 3C molecules—glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate (PGAL) (3C) and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) (3C)—in the presence of the
enzyme aldolase. - Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) (3C) is isomerised to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (PGAL) (3C) in the presence of the enzyme phosphotriose isomerase.
- Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is phosphorylated to form 1, 3-bisphosphoglyceric acid (3C).
- 1, 3-Bisphosphoglyceric acid (3C) transfers its one phosphate group to ADP and gets converted to 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3C). This results in the formation of ATP.
- 3-Phosphoglyceric acid (3C) is converted to 2-phosphoglycerate (3C) in the presence of the enzyme phosphoglyceromutase.
- 2-Phosphoglycerate loses its water molecule and forms phosphoenolpyruvate in the presence of the enzyme enolase.
- The high-energy phosphate group of phosphoenol pyruvate (3C) is transferred to ADP in the presence of the enzyme pyruvate kinase to form pyruvate (3C). This results in the formation of ATP.
Answered by Sivanand Patnaik | 22 Feb, 2018, 08:30: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by mohimpathak8638 | 12 Feb, 2021, 07:41: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by kaintkaku | 25 Apr, 2018, 12:14: AM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM
CBSE 11-science - Biology
Asked by Topperlearning User | 14 Jul, 2014, 12:03: PM