CBSE Class 11-science Answered
derive Cp -Cv =R with full explanation in lucid language
Asked by ppratim02 | 01 Feb, 2016, 06:33: PM
Consider one mole of an ideal gas contained in a cylinder ftted with friction less piston. Let A be the area of piston, P be pressure, V be volume and T be temperature of the gas respectively. Suppose that heat is supplied to the gas at constant volume, so that its temperature increases by dT. If dQ is the amount of heat supplied then,
dQ = 1×Cv×dT = CvdT
Now suppose that heat is supplied to the gas at constant pressure to again increase its temperature through dT. If dQ' is the amount of heat supplied then,
dQ' = 1×Cp×dT = CpdT
When the gas is heated at constant pressure, the piston moves outward and work (say dW) is performed by the gas. As the increase in temperature is the same (dT) in two cases,
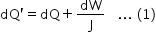
where dQ/J is the heat equivalent of the work. If the piston moves out through a small distance dx, then
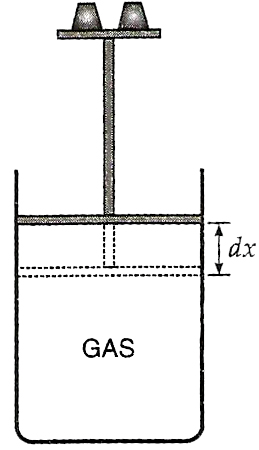
dW = force×distance = (pressure×area of the piston)×distance = (PA) dx = P dV,
where dV(=A×dx) is the small increase in volume of the gas when heated at constant pressure.
Substituting for dQ, dQ' and dW in eqn (1), we have,
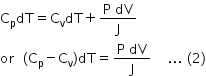
According to the perfect gas equation, PV = RT
The heat dQ' is supplied to the gas at constant pressure P. Therefore, differentiating both the sides of the above equation by treating P as constant, we have,
P dV = R dT
Substituting for P dV in equation (2), we get
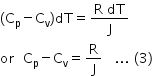
As R is always positive, it follows that Cp>Cv. Since R/J is constant, Cp-Cv is always constant.
If Cp and Cv are measured in the units of work and R is also in the units of work (or energy) then,
Cp - Cv = R
Answered by Faiza Lambe | 02 Feb, 2016, 09:58: AM
Concept Videos
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by arjunsah797 | 01 Mar, 2022, 03:01: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by sanjanapujar80 | 12 Jun, 2021, 10:29: AM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by shubhamgoyal1722 | 15 Dec, 2020, 11:18: AM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by Venkeylkm | 16 Jul, 2020, 04:12: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by pgskgokul | 06 Jul, 2020, 02:50: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by abhilashkulgude111 | 07 Jun, 2019, 09:05: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 01:23: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 13 Apr, 2015, 03:28: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 13 Apr, 2015, 03:19: PM
CBSE 11-science - Physics
Asked by Topperlearning User | 13 Apr, 2015, 03:20: PM




