C3 and C4 cycles........
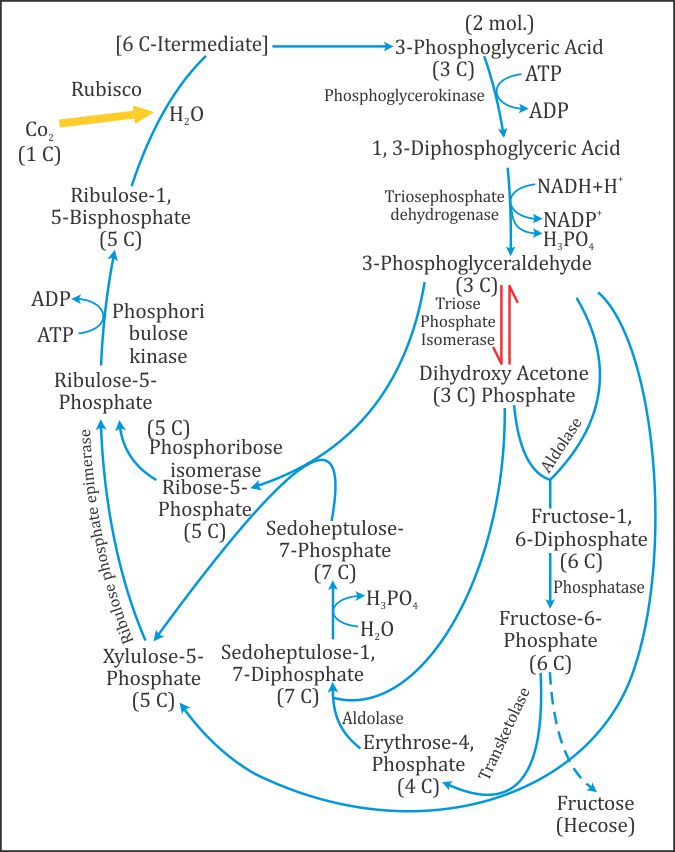
Carboxylation
- During carboxylation, CO2 combines with ribulose 1,5-biphosphate to produce an intermediate compound, which splits in the presence of water to form two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric
acid (PGA).
Reduction
- During reduction or the glycolytic reversal phase, carbohydrate is formed at the expense of the photochemically made ATP and NADPH.
Regeneration
- During regeneration, the CO2 acceptor ribulose 1,5-biphosphate is formed again so that the cycle is continuous.
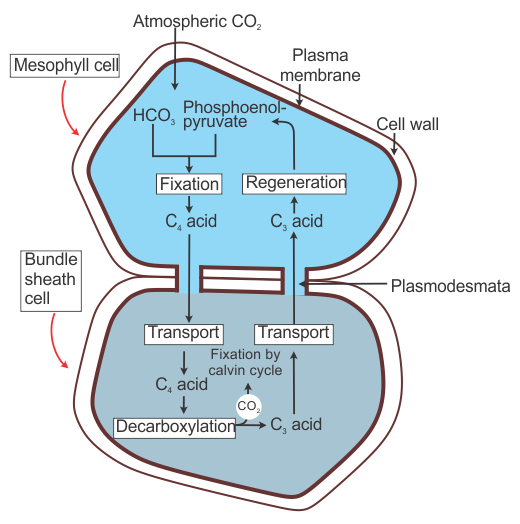
- C4 plants carry out double fixation of CO2—initial and final.
- The product of initial fixation in mesophyll cells is transported to bundle sheath cells for final fixation.
Initial Fixation
- Carbon dioxide is first fixed in the mesophyll cells to form a 3C compound—phosphoenol pyruvic acid (PEP), leading to the formation of a 4C compound, oxaloacetic acid (OAA).
- OAA is reduced to malic acid or transaminated to form aspartic acid.
Transport
- Malic acid or aspartic acid is transported to bundle sheath cells through plasmodesmata.
Final Fixation
- It occurs in two steps:
Release of CO2
- Inside the bundle sheath cells, malic acid is decarboxylated and aspartic acid is deaminated through the following reactions:
CO2 Assimilation
- CO2 released in bundle sheath cells is fixed through the Calvin cycle in which RUBP is the secondary or final acceptor of CO2 in C4 plants.
Regeneration of PEP
- Pyruvic acid or alanine formed in the bundle sheath cells return to the mesophyll cells.
- Alanine is deaminated through a transamination reaction to form pyruvic acid.
- Pyruvic acid is converted to phosphoenol pyruvic acid and inorganic phosphate with the help of ATP
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
You have rated this answer /10
Browse free questions and answers by Chapters
- 1 Biomolecules
- 2 Cell : The Unit of Life
- 3 Respiration in Plants
- 4 Animal Kingdom
- 5 Evolution
- 6 Ecosystem
- 7 The Living World
- 8 Biological Classification
- 9 Reproduction in Organisms
- 10 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- 11 Human Reproduction
- 12 Reproductive Health
- 13 Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- 14 Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- 15 Biotechnology : Principles and Processes
- 16 Biotechnology and its Applications
- 17 Human Health and Disease
- 18 Microbes in Human Welfare
- 19 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- 20 Organisms and Populations
- 21 Biodiversity and Conservation
- 22 Environmental Issues
- 23 Plant Kingdom
- 24 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- 25 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- 26 Structural Organisation in Animals
- 27 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- 28 Mineral Nutrition
- 29 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
- 30 Plant Growth and Development
- 31 Digestion and Absorption
- 32 Breathing and Exchange of Gases
- 33 Body Fluids and Circulation
- 34 Excretory Products and their Elimination
- 35 Locomotion and Movement
- 36 Neural Control and Coordination
- 37 Chemical Coordination and Integration
- 38 Transport in Plants
