a particle starts from rest and travels a distance s with uniform acceleration,then it travels a distance 2s with uniform speed,finally it travels a distance 3s with uniform retardation and comes to rest.if the complete motion of the particle is a straight line then the ratio of its average velocity to maximum velocity is
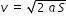 ......................(1)
......................(1)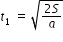 ................(2)
................(2)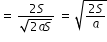 ................(3)
................(3)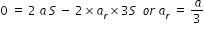
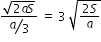 .......................(4)
.......................(4)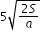 ..............................(5)
..............................(5)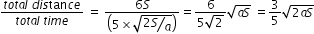 ...................(6)
...................(6)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
You have rated this answer /10
Browse free questions and answers by Chapters
- 1 Thermodynamics
- 2 Gravitation
- 3 Electromagnetic Waves
- 4 Communication Systems
- 5 Laws of Motion
- 6 Current Electricity
- 7 Work, Energy and Power
- 8 Kinematics
- 9 Physics and Measurement
- 10 Rotational Motion
- 11 Properties of Solids and Liquids
- 12 Kinetic Theory of Gases
- 13 Oscillations and Waves
- 14 Electrostatics
- 15 Magnetic Effects of Current and Magnetism
- 16 Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents
- 17 Optics
- 18 Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
- 19 Atoms and Nuclei
- 20 Electronic Devices
