CBSE Class 12-science Chemistry Integrated Rate Equation
Study better with TopperLearning’s CBSE Class 12 Science Chemistry Chemical Kinetics – Integrated Rate Equation learning resources such as practice tests, NCERT solutions etc. Learn to derive the integrated rate equation with the step-wise explanation provided by an experienced Chemistry expert in our concept videos. Our topic notes for Chemistry will enable you to have a quick look at key concepts related to the integrated rate equation.
Practise our CBSE Class 12 Science Chemistry textbook solutions to learn to use the half-life formula for the calculations involving the first-order, second-order or zero-order reactions. To make sure that you remember the problem-solving methods in your board exam, take mock exams using our sample papers and previous years’ Chemistry papers.
-
Please ans both part

- Explain why the rate of a chemical reaction does not remain uniform throughout the reaction?
-
For a chemical reaction X
Y, The rate increases by the factor 2.25 when concentration of X is increased by 1.5. Derive or suggest the rate law equation and find the order of reaction.
- A gas phase decomposition of xy follows the rate law r = k[xy]n. what are the units of its rate constant?
-
The reaction A + 3B
 2C obeys the rate equation: Rate = k[A]1/3 [B]3/2. Find out the order of this reaction?
2C obeys the rate equation: Rate = k[A]1/3 [B]3/2. Find out the order of this reaction?
-
The experimental data for the reaction:
2A + B2 → 2AB is:
Write the rate equation for the reaction?
- The half-life of a first order decomposition of nitramide is 2.1 hour at 25o C. Determine the time taken for the compound to decompose 99% of its original amount, rate constant = 0.2303 per hour.
- The rate of reaction between A and B increases by a factor of 100. Calculate the order of the reaction when the concentration of A is increased 10 times.
-
Calculate the rate of reaction from the rate law:
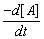 = k[A] [B]2, when the concentration of A and B are 0.01 M and 0.02 M respectively and k = 5.1 x 10-3 L2 mol-2 s-1.
= k[A] [B]2, when the concentration of A and B are 0.01 M and 0.02 M respectively and k = 5.1 x 10-3 L2 mol-2 s-1.
- Derive an equation for calculating the half life of a first order reaction




