CBSE Class 12-science Chemistry Carbohydrates
What are carbohydrates? How would you classify carbohydrates? TopperLearning’s Chemistry expert explains the answers to these questions in our concept videos. Revise CBSE Class 12 Science Chemistry Biomolecules – Carbohydrates by accessing our online learning materials. These well-prepared study materials for Chemistry include topic notes, chapter-wise NCERT solutions and sample paper solutions.
You can revise concepts such as reducing sugar, non-reducing sugar etc. by including our video lessons and topic notes in your study plan. To improve your answering skills, you can practise questions related to carbohydrates in the CBSE Class 12 Science Chemistry previous years’ question papers which are available online as part of our board exam study resources.
- difference between glucose and fructose?
- how many asymmetric carbon atoms are present gulose
- what are carbohydrate
- What are anomers?
- Mass of sucrose C12H22O11 produced by mixing 84 gm of carbon, 12 gm of hydrogen and 56 L. O2 at 1 atm & 273 K according to given reaction, is C(s) + H2(g) + O2(g) → C12H22O11(s)
- Give one example each for reducing and non-reducing sugars.
- Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?
-
An optically active compound having molecular formula C6H12O6 is found in two isomeric forms (A) and (B) in nature. When (A) and (B) are dissolved in water they show the following equilibrium:
(i) What are such isomers called? (ii) Can they be called enantiomers? Justify your answer. (iii) Draw the cyclic structure of isomer (A).
-
Despite having an aldehydic group:(a) Glucose does not give 2, 4-DNP test. What does this indicate?(b) Draw the howorth structure of
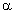 -D-(+)-Glucopyranose.(c) What is the significance of D and (+) here?
-D-(+)-Glucopyranose.(c) What is the significance of D and (+) here?
- Why are carbohydrates generally optically active?