CBSE Class 11-science - Illustrations of Bodies in SHM Videos
Oscillations
This video explains the kinematics and dynamics of a spring in simple harmonic motion.
- Two bodies P and Q of equal masses are suspended from two separate springs of constants K1 and K2 respectively. If the two bodies oscillate vertically such that their maximum velocities are equal, then what is the ratio of the amplitudes of vibration of P and Q?
- What is the frequency of oscillation of a simple pendulum mounted in a cabin that is freely falling under gravity?
- Will a pendulum gain or lose time, when taken to the top of a mountain?
- Plot a graph between the time period (T) for a simple pendulum and its length (L)?
- A graph was plotted taking log10T Vs log10l for a simple pendulum. What is the nature of the graph and what is its slope?
- (a) On what factors, does the energy of simple harmonically vibrating particle depend? (b) A spring of force constant k is broken into n equal parts (n>0). What will be the spring factor of each part?
- Two identical springs of force constant k each are connected in series. What will be the spring factor of the combination when they are connected in (i) Series (ii) Parallel
-
A particle is vibrating in S.H.M. When the distances of the particle from the mean position are y1 and y2 it has velocities v1 and v2 respectively. Prove that the time period is,
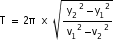
-
A tray of mass 9 kg is supported by two springs, each of force constant K as shown in the figure. On pressing the tray slightly downwards and then releasing it, it executes SHM of period 1s. When a block of mass M1 is placed in the tray, the period increases by 2s. Calculate the mass of the block.
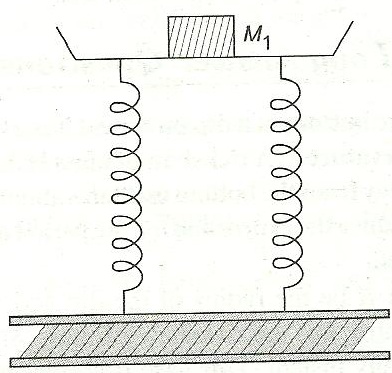
-
Two identical, springs each of spring factor K, may be connected in the following different ways..
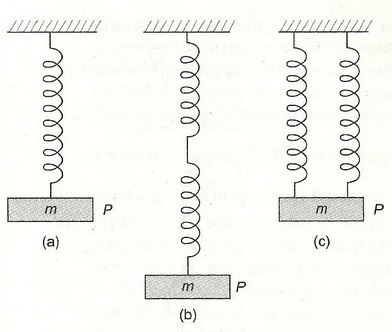 Deduce the spring factor for oscillations of the body P of mass m in each case.
Deduce the spring factor for oscillations of the body P of mass m in each case.

