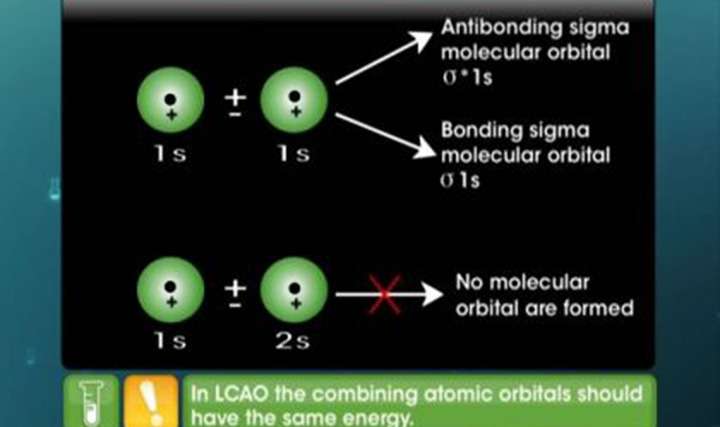
CBSE Class 11-science Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory
- why is O2 molecule paramagnetic
- what is paramagnetic
- which of the follwing do not exist He2 HeH+ Be2
-
A. give method and find hybridisation and shape of :
1. XeF2
2.SF2
3.
4.IF7 5.
B.Explain anti bonding and bonding hybridised orbitals. C._________on hydrolysis gives ethyne while ______ on hydrolysis gives methane. D.Explain why the colour of Bayer's reagent gets discharged when treated with an alkene. E.i) State and explain Le Chatelier’s principle. On the basis of this principle discuss the conditions for obtaining the maximum yield of SO3 in the following reaction. 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌2SO3(g); ∆𝐻= - 42k.cal.(ii) Calculate the pH value of 0.01M CH3 COOH if it is 5% dissociated.
- Molecular orbital theory explanation
- How many nodal planes do the SIGMA Pz ABMO.have and How?
- Write the molecular orbital diagram of N2+ and calculate their bond order
- why nitrogen have different structure of molecular orbital theory
- An atomic orbital is monocentric while a molecular orbital is polycentric. Explain
- What is the relationship between bond order and the dissociation energy of a molecule?