CBSE Class 11-science Answered
|
Hybridisation |
Overlapping |
|
It is defined as the process by which atomic orbitals of slightly different energies combine to form a new set of equivalent orbitals known as hybrid orbitals. |
It is defined as the process by which different types of bond are formed between the orbitals of two or more atoms. |
|
This term is used in reference to one atom. |
Orbital overlapping is used in reference to two or more atoms. |
|
There is no bond formation and involves just redistribution of energy. |
There is bond formation. |
|
Hybrid orbitals are named by considering the type and number of atomic orbitals from which they arose. |
Single, double and triple bond are decided from the overlap of s and p orbitals. |
|
Hybridisation provides exact explanation for the structure of compounds like Methane (CH4). |
Concept of maximum orbital overlap fails to explain structure of compounds like Methane (CH4). |


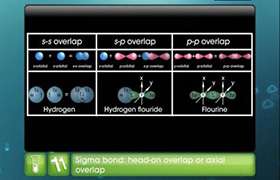
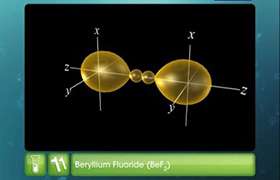
 on the basis of hybridisation
on the basis of hybridisation