ICSE Class 10 Answered
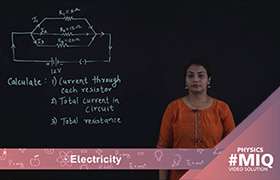
When a chemical reaction occurs in the solution, electrons gather on cathode, which becomes negatively charged. At the same time, electrons are drawn from the anode, giving it a positive charge. The difference in charge sets up a potential difference, or voltage, between the two electrodes. When they are connected by a conducting wire, electrons flow from the cathode to the anode, producing a current. When a chemical reaction occurs in the solution,electrons gather on cathode, which becomes negatively charged. At the same time, electrons are drawn from the anode, giving it a positive charge. The difference in charge sets up a potential difference, or voltage, between the two electrodes. When they are connected by a conducting wire, electrons flow from the cathode to the anode, producing current.