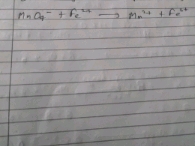CBSE Class 11-science Answered
Equivalent mass is defined as the number of parts by weight of a substance that combines with or displaces directly or indirectly 1.008 parts by weight of hydrogen or 8.0 parts by weight of oxygen or 35.5 parts by weight of chlorine.
Some methods of determining equivalent mass are given below:
1. Hydrogen displacement method:
Eq. M of an element = Wt. of element x 1.008
Wt. of hydrogen displaced
2. Oxide method:
Eq. M of an element = Wt. of element x 8
Wt. of oxygen displaced or combined
3. Chlorine method:
Eq. M of an element = Wt. of element x 35.5
Wt. of oxygen displaced or combined
4. Metal displacement method:
Wt. of metal added = Eq. Mass of metal added
Wt. of metal displaced Eq. Mass of metal displaced
W1 = E1
W2 E2
5. Neutralisation method:
Eq. Mass of acid or base = W
V X N
W = Wt. of an acid or base in gm
V = Volume of an acid or base in litre required for neutralisation
N = Normality of acid or base
6. Volatile chloride method:
Valency of metal = 2 x V.D of chloride
Eq. Mass of metal chloride
So E = 2 X V.D of chloride - 35.5
Valency