CBSE Class 10 Answered
What is meant by surface phenomenon?
Asked by sreenidhe05 | 22 Dec, 2020, 03:06: PM
A liquid stays together because of attraction between molecules. Consider a molecule well inside a liquid.
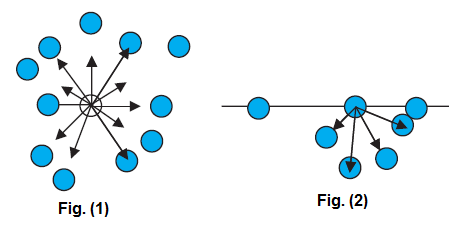
The intermolecular distances are such that it is attracted to all the surrounding molecules [Fig. 1].
This attraction results in a negative potential energy for the molecule, which depends on the number and
distribution of molecules around the chosen one. But the average potential energy of all the molecules is the same.
This is supported by the fact that to take a collection of such molecules (the liquid)and to disperse them far away
from each other in order to evaporate or vaporise, the heat of evaporation required is quite large.
For water it is of the order of 40 kJ/mol. Let us consider a molecule near the surface Fig. 2. Only lower half side
of it is surrounded by liquid molecules. There is some negative potential energy due to these, but obviously it is less than
that of a molecule in bulk, i.e., the one fully inside. Approximately itis half of the latter. Thus, molecules on a liquid surface
have some extra energy in comparison to molecules in the interior. A liquid thus tends to have the least surface area
which external conditions permit. Increasing surface area requires energy. Most surface phenomenon can be understood
in terms of this fact. The energy required for having a molecule at the surface, is roughly half the energy required to remove it
entirely from the liquid i.e., half the heat of evaporation.
Surface tension is equal to the surface energy per unit area of the liquid interface and is also equal to the
force per unit length exerted by the fluid .
(i) Surface tension is a force per unit length(or surface energy per unit area) acting in the plane of the interface between
the plane of the liquid and any other substance; it also is the extra energy that the molecules at the interface have as compared
to molecules in the interior.
(ii) At any point on the interface besides the boundary, we can draw a line and imagine equal and opposite
surface tension forces S per unit length of the line acting perpendicular to the line, in the plane of the interface.
The line is in equilibrium. Imagine a line of molecules at the surface. The molecules to the left pull the line towards them;
those to the right pull it towards them! This line of molecules is in equilibrium under tension.
Answered by Thiyagarajan K | 23 Dec, 2020, 08:02: PM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by agankitgupta938 | 18 Apr, 2024, 04:29: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by infinityupgraded | 13 Apr, 2024, 08:17: AM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by suryamr2019 | 08 Mar, 2024, 04:32: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by saurabhjd527 | 30 Jan, 2024, 07:55: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by subrasixty | 13 Jan, 2024, 05:05: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by nandanagnair | 17 Dec, 2023, 03:44: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by namish1088 | 16 Nov, 2023, 08:09: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by 0 0 | 19 Oct, 2023, 03:51: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by bubbynaik77 | 29 Sep, 2023, 09:34: PM
CBSE 10 - Physics
Asked by gurcharansingh37306 | 10 Sep, 2023, 12:53: PM