ICSE Class 10 Answered
what is interphase.explain briefly?
Asked by mohameedraza8558 | 05 Sep, 2015, 06:31: PM
- Interphase involves a series of changes which take place in a newly formed cell and its nucleus before it gets ready for division again. It is also called intermitosis.
- Interphase generally accounts for 95% of the total duration of the cell cycle. It is the preparatory phase and a period of great metabolic activity.
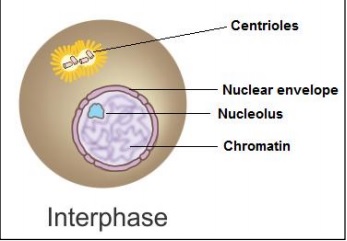
- In this stage, the nucleus and the cytoplasm remain metabolically and synthetically very active.
- During this phase, DNA replication, synthesis of nuclear histones, division of centrioles to form a new pair of centrioles, synthesis of energy-rich compounds and synthesis of RNA and proteins take place.
- The nuclear envelope remains intact.
- Chromosomes appear in the form of long, coiled, indistinctly visible chromatin fibres.
- The size of the nucleolus increases because of the accumulation of rRNA and ribosomal proteins.
- Interphase is further divided into three periods—first gap or G1 phase, synthetic or S phase and second gap or G2 phase. Duration of these phases is different in different organisms.
Answered by Sheetal Kolte | 06 Sep, 2015, 06:48: PM
Application Videos
Concept Videos
ICSE 10 - Biology
Asked by rajukurani51 | 14 Sep, 2021, 07:38: AM
ICSE 10 - Biology
Asked by rajukurani51 | 11 Sep, 2021, 07:40: AM
ICSE 10 - Biology
Asked by toraltrivedi51xb | 18 Sep, 2020, 07:52: PM
ICSE 10 - Biology
Asked by siddhirajput43.10spicertl | 19 May, 2020, 07:57: PM
ICSE 10 - Biology
Asked by Waliansari9965 | 02 Feb, 2020, 03:51: PM
ICSE 10 - Biology
Asked by sumitgour385 | 12 Apr, 2019, 07:48: PM