CBSE Class 12-science Answered
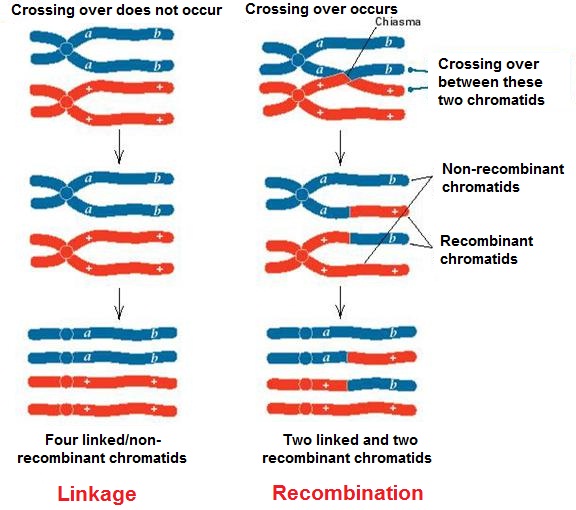
Linkage is a phenomenon of certain genes to stay together during inheritance through generations without any change or separation due to their being present on the same chromosome. Linkage was first suggested by Sutton and Boveri (1902-1903) when they propounded the chromosomal theory of inheritance. In 1911, Morgan and Castle proposed the chromosomal theory of linkage.
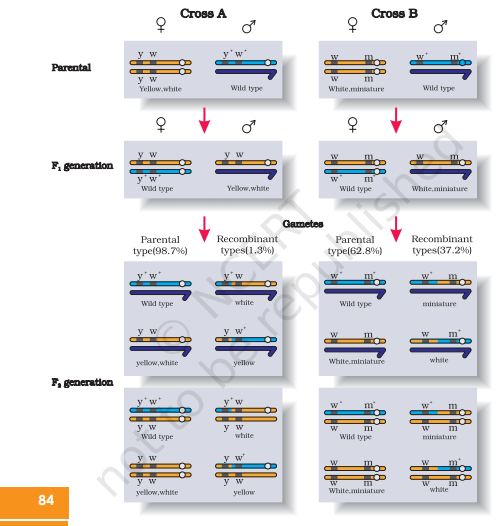
A new grouping of genes or a new combination of characters which is different from the parental types is called recombination. Crossing over involves mutual exchange of segments of genetic material between non-sister chromatids of two homologous chromosomes so as to produce recombinations or new combination of genes.