CBSE Class 11-science Answered
Under what conditions does full-filled orbital undergo hybridisation?(such as in NH3)
Asked by Benjamin | 10 Sep, 2015, 06:17: PM
Following are the features and conditions for hybridisation:
1. Only those orbitals which have approximately equal energies and belong to the same atom or ion can undergo hybridisation.
2. Number of hybrid orbitals produced is equal to the number of atomic orbitals mixed.
3. It is not mandatory that all the half-filled orbitals must participate in hybridisation, Also, it is not necessary that only half-filled orbitals should participate in hybridisation. Even completely filled orbitals with slightly different energies can also participate in hybridisation. This completely filled orbital with two electrons can act as lone pair of electrons as in case of ammonia.
4. Hybridisation never takes place in isolated atoms but it occurs only at the time of bond formation.
Answered by Prachi Sawant | 12 Sep, 2015, 05:26: PM
Concept Videos
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by Trisha Gupta | 30 Oct, 2022, 05:36: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by ABHILASHA | 22 Aug, 2020, 04:39: AM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by kpbhake | 12 Mar, 2018, 11:45: AM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by Topperlearning User | 08 Oct, 2014, 01:09: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 01:23: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by Topperlearning User | 13 Jun, 2016, 02:26: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 01:23: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
What is the hybrid state of B in BF3, Al in AlCl3, Be in BeCl2, C in CO2 and C2H4; S in SO2 and SO3.
Asked by Topperlearning User | 08 Oct, 2014, 01:33: PM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by Topperlearning User | 09 Oct, 2014, 09:30: AM
CBSE 11-science - Chemistry
Asked by Topperlearning User | 04 Jun, 2014, 01:23: PM


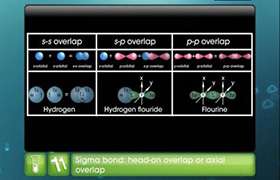
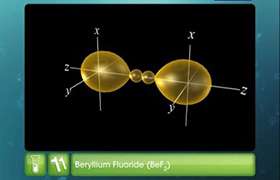
 on the basis of hybridisation
on the basis of hybridisation