CBSE Class 12-science Answered
Asked by MANISHA MOHANTY | 15 May, 2014, 07:26: PM
Let us assume one electron as stationary, while the other electron moved towards the first at 2 x 106 m/s (twice the speed of the single electron).
let r represent the minimum distance between the particles. The work required to bring an electron from a distance of infinity to distance r
is = 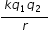
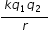
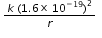 (Charge on one electron is 1.6 x 10-19 C)
(Charge on one electron is 1.6 x 10-19 C)The electron's original kinetic energy is converted into electrical potential energy.
At the minimum distance apart, the kinetic energy is zero, so all the kinetic energy has been converted into electrical potential energy.
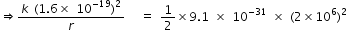
(value of k is 9 x 109)
on solving above equation
we get 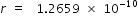 m
m
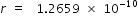 m
m
Answered by Ravindra Kapal | 16 May, 2014, 04:27: PM
Concept Videos
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by aishaisha091098 | 19 Apr, 2024, 04:54: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by dasrituparna1999 | 13 Apr, 2024, 06:56: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by khankaifi178 | 08 Jan, 2024, 10:12: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by sankaraganapathy007 | 09 Sep, 2023, 10:03: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by bmahalik21 | 05 Mar, 2023, 08:23: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by s3043632 | 22 Jan, 2023, 06:45: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by carnivalgirl8421 | 29 Jun, 2022, 11:18: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by priyr7687 | 28 Jun, 2022, 06:19: PM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by tahseenaamir07 | 25 Jun, 2022, 01:33: AM
CBSE 12-science - Physics
Asked by ekanathtanpure77 | 23 Jun, 2022, 07:56: PM








